X Ray Diffraction Definition Diagram Equation Facts Britannica

X Ray Diffraction Definition Diagram Equation Facts Britannica The atomic planes of the crystal act on the x rays in exactly the same manner as does a uniformly ruled diffraction grating on a beam of light. a beam of x rays contacts a crystal with an angle of incidence θ. it is reflected off the atoms of the crystal with the same angle θ. the x rays reflect off atomic planes in the crystal that are a. Diffraction, the spreading of waves around obstacles. diffraction takes place with sound; with electromagnetic radiation, such as light, x rays, and gamma rays; and with very small moving particles such as atoms, neutrons, and electrons, which show wavelike properties. one consequence of diffraction is that sharp shadows are not produced.
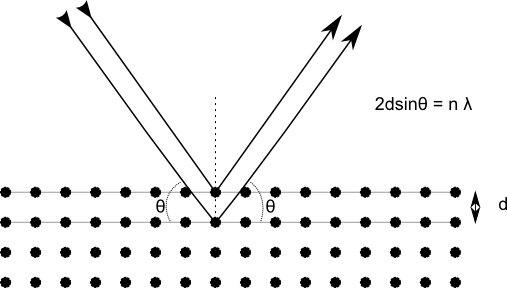
X Ray Diffraction Definition Diagram Equation Facts 54 Off Bragg law, in physics, the relation between the spacing of atomic planes in crystals and the angles of incidence at which these planes produce the most intense reflections of electromagnetic radiations, such as x rays and gamma rays, and particle waves, such as those associated with electrons and neutrons. for maximum intensity of reflected. X ray diffraction is a generic term for phenomena associated with changes in the direction of x ray beams due to interactions with the electrons around atoms. it occurs due to elastic scattering, when there is no change in the energy of the waves. the resulting map of the directions of the x rays far from the sample is called a diffraction pattern. If we use cu αradiation as x ray source, and the first order bragg diffraction peak is found at the semi angle 35 。 ,calculate the d spacing of the crystal. x rays with wavelength 1.54 a are reflected from the (2,1,1) planes of a cubic crystal. the d spacing is found to be 5.12a. calculate the crystal parameter. X ray diffraction is a common technique that determine a sample's composition or crystalline structure. for larger crystals such as macromolecules and inorganic compounds, it can be used to determine the structure of atoms within the sample. if the crystal size is too small, it can determine sample composition, crystallinity, and phase purity.

X Ray Diffraction Definition Diagram Equation Facts Britannica If we use cu αradiation as x ray source, and the first order bragg diffraction peak is found at the semi angle 35 。 ,calculate the d spacing of the crystal. x rays with wavelength 1.54 a are reflected from the (2,1,1) planes of a cubic crystal. the d spacing is found to be 5.12a. calculate the crystal parameter. X ray diffraction is a common technique that determine a sample's composition or crystalline structure. for larger crystals such as macromolecules and inorganic compounds, it can be used to determine the structure of atoms within the sample. if the crystal size is too small, it can determine sample composition, crystallinity, and phase purity. X ray diffraction. last time we discussed how to generate x rays; now, let’s talk about one application that plays a big role in materials characterization. x ray diffraction is a tool that allows us to probe the crystal structure of a sample. let’s walk through the process: first, we need to generate x rays: this process is shown on the. The principles of x ray diffraction. 6.1. x ray reflection according to w. l. bragg. consider a set of n 1 equidistant atomic planes of spacing d, and a monochromatic plane x wave falling on it at a glancing angle θ (fig. 6 1 (1)). it is assumed that each atomic plane reflects a very small fraction of the incident amplitude, small enough so.

Comments are closed.