What Type Of Consumer Eats Both Plants Animals At Sheree Bowen Blog
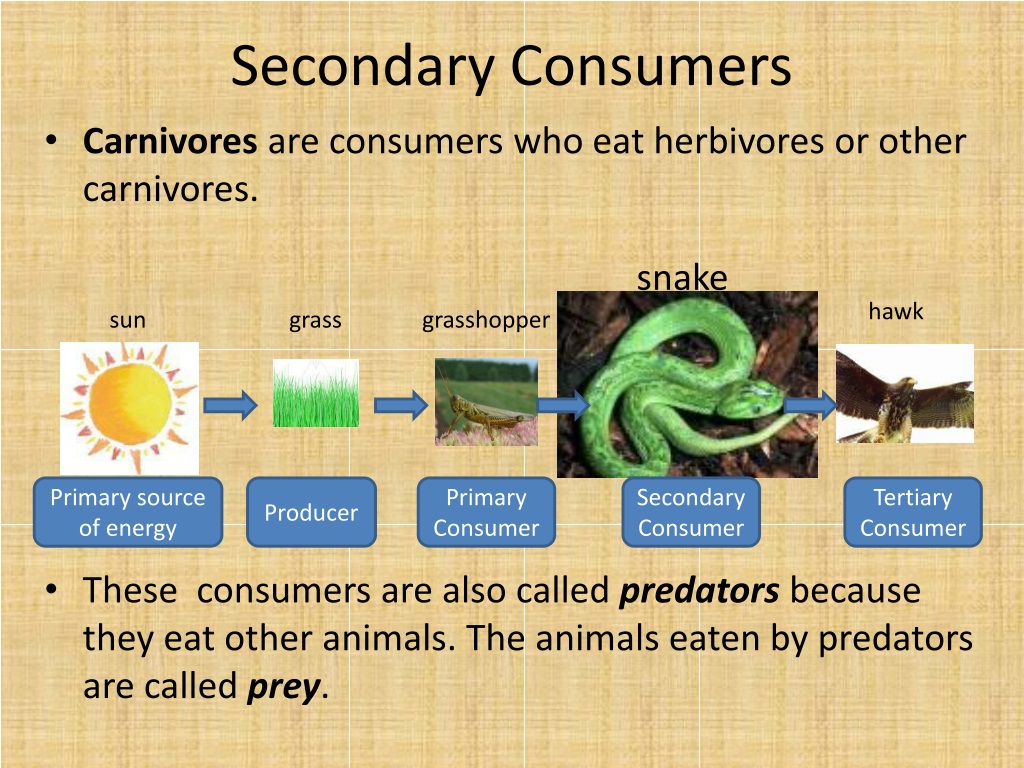
What Type Of Consumer Eats Both Plants Animals At Sheree Bowen Blog Eats both plants and animals. eats plants producers. secondary consumer. eats other consumers (could be carnivore, omnivore, or detritivore) detritivore. Spiders, snakes, and seals are all examples of carnivorous secondary consumers. omnivores are the other type of secondary consumer. they eat both plant and animal materials for energy. bears and skunks are examples of omnivorous secondary consumers that both hunt prey and eat plants. however, some omnivores are simply scavengers.

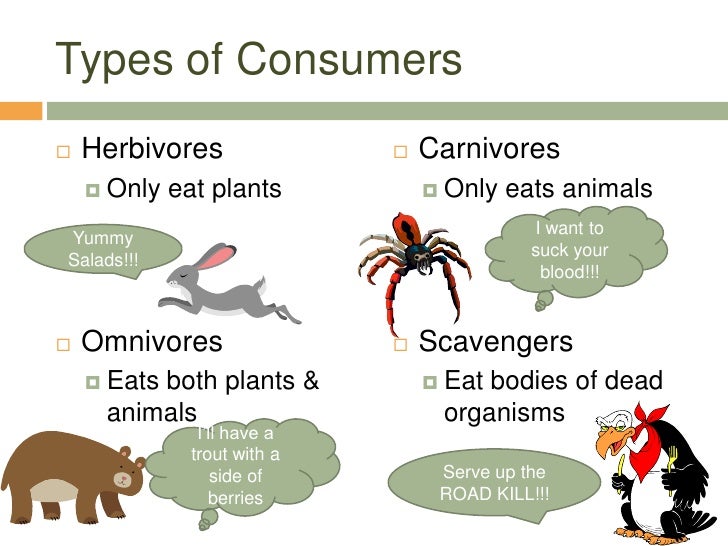
What Type Of Consumer Eats Both Plants Animals At Sheree Bowen Blog A rabbit eats the grass. a fox eats the rabbit. when the fox dies, bacteria break down its body, returning it to the soil where it provides nutrients for plants like grass. of course, many different animals eat grass, and rabbits can eat other plants besides grass. foxes, in turn, can eat many types of animals and plants. The consumers that eat both plants and animals are called omnivores. here is a list of some common examples of omnivorous animals: humans. bears. raccoons. pigs. crows. consumers are organisms within an ecosystem that obtain energy and nutrients by consuming other organisms. they are a vital part of the food chain or food web, as they rely on. The animal kingdom is diverse, with species adapted to a wide range of diets. these diets fall into three broad categories: herbivorous, carnivorous, and omnivorous. herbivores are animals that primarily consume plant material. carnivores are those that eat other animals. omnivores have a diet that includes both plant and animal matter. Which type of consumer is a pitcher plant? omnivores. omnivores are organisms that eat both plants and animals as primary food sources. humans are an example of an omnivorous species. although some humans eat foods derived only from plants or only from animals, the majority of humans eat foods from both sources.
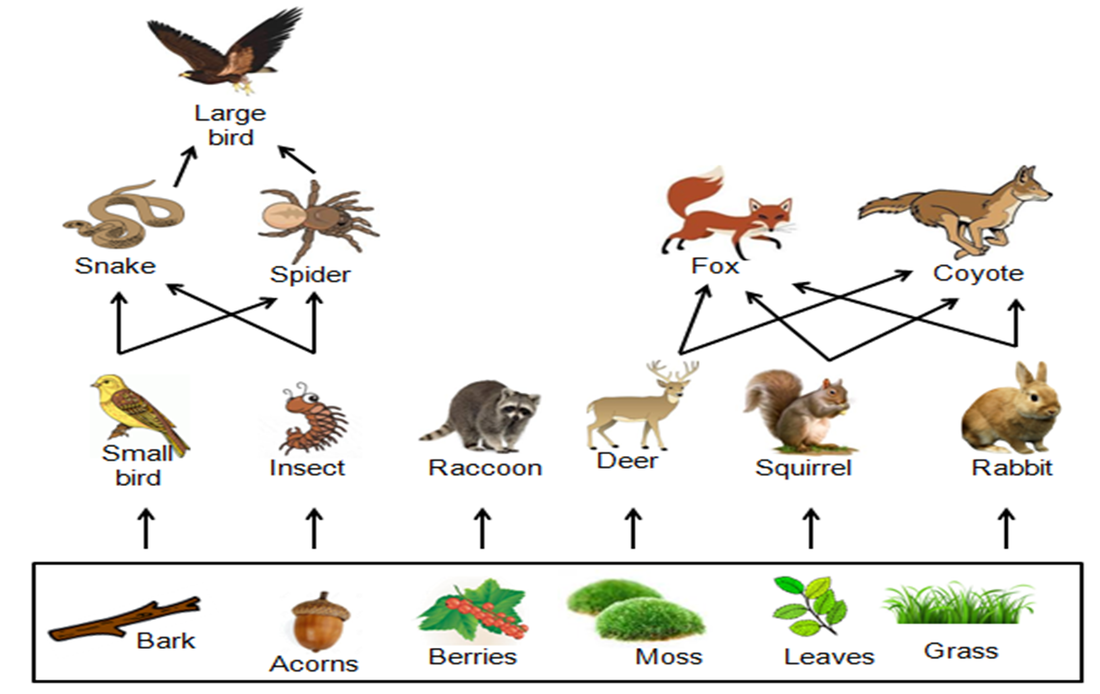
What Type Of Consumer Eats Both Plants Animals At Sheree Bowen Blog The animal kingdom is diverse, with species adapted to a wide range of diets. these diets fall into three broad categories: herbivorous, carnivorous, and omnivorous. herbivores are animals that primarily consume plant material. carnivores are those that eat other animals. omnivores have a diet that includes both plant and animal matter. Which type of consumer is a pitcher plant? omnivores. omnivores are organisms that eat both plants and animals as primary food sources. humans are an example of an omnivorous species. although some humans eat foods derived only from plants or only from animals, the majority of humans eat foods from both sources. Vast swampy region flowing south of lake okeechobee in florida. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.
Ecosystem Unit Vast swampy region flowing south of lake okeechobee in florida. food chain. noun. group of organisms linked in order of the food they eat, from producers to consumers, and from prey, predators, scavengers, and decomposers. food web. noun. all related food chains in an ecosystem. also called a food cycle. herbivore. Food chains. a food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher level consumers, and finally decomposers. these levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics.

Comments are closed.