What The Meaning Of Metabolic Heat At Brenda Olivo Blog
What The Meaning Of Metabolic Heat At Brenda Olivo Blog The body tightly regulates the. what the meaning of metabolic heat. from guides.hostos.cuny.edu. chapter 11 metabolic pathways and energy production che 120 what the meaning of metabolic heat web thermoregulation is the maintenance of physiologic core body temperature by balancing heat generation with heat loss. the body tightly regulates the body. Metabolic health is a complicated subject, that can’t be boiled to weight or even blood sugar levels alone. monitoring markers of metabolic health like your blood sugar, cholesterol, and blood pressure regularly (aka at least yearly) allows you to keep tabs on your current lifestyle choices, and make the appropriate adjustments if one of those markers starts to (or has) strayed from ideal.

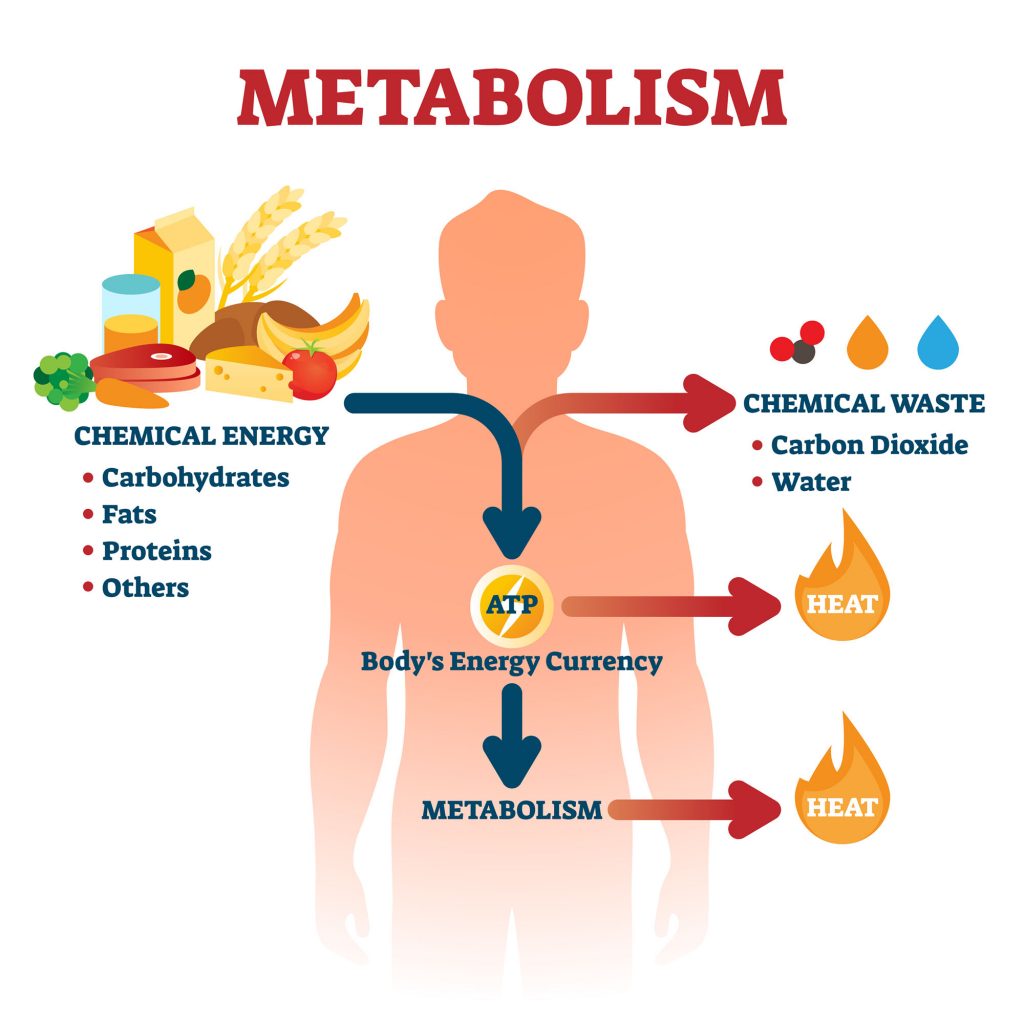
What The Meaning Of Metabolic Heat At Brenda Olivo Blog Metabolic heat production can increase by >10 fold during high intensity physical exertion, which can overwhelm the heat dissipation mechanisms and promote heat storage in the body [6,7]. global warming would have wide ranging impact on human health, functions and activities, which in turn, would have downstream effects on the operation and. Humans are endotherms, animals that keep their body temperature within a stable range using heat production and heat dissipation. the ability to produce heat from calories is an essential mechanism required for life sustaining cellular reactions that need a sufficient intake of calories. the molecules in food contain energy, or calories, stored in chemical bonds. metabolic reactions can. Metabolism. your metabolism constantly provides your body with energy for essential body functions like breathing and digestion. your body needs a minimum number of calories (the basal metabolic rate or bmr) to sustain these functions. factors like age, sex, muscle mass and physical activity affect metabolism or bmr. Thermogenesis is a metabolic process in which the body produces heat. it plays a crucial role in maintaining body temperature and regulating energy expenditure. the term “thermogenesis” comes from the greek words “thermo,” meaning heat, and “genesis,” meaning creation. this natural process occurs in various tissues and can be.

Ppt Energy Metabolism And Body Temperature Powerpoint Presentation Metabolism. your metabolism constantly provides your body with energy for essential body functions like breathing and digestion. your body needs a minimum number of calories (the basal metabolic rate or bmr) to sustain these functions. factors like age, sex, muscle mass and physical activity affect metabolism or bmr. Thermogenesis is a metabolic process in which the body produces heat. it plays a crucial role in maintaining body temperature and regulating energy expenditure. the term “thermogenesis” comes from the greek words “thermo,” meaning heat, and “genesis,” meaning creation. this natural process occurs in various tissues and can be. The opposite state is known as metabolic syndrome, where people have three or more of the following traits: a waistline of 35 inches for women and 40 inches for men. fasting glucose above 100 mg dl. hdl cholesterol less than 40 mg dl. triglycerides above 150 mg dl. high blood pressure (130 85 or higher). Metabolic heat production is the heat released from muscle metabolism in animals. muscle function requires a steady supply of atp. atp is generated from the oxidation of metabolites in the mitochondria, a process which requires oxygen. there are two ways of increasing body temperature through metabolic heat production: shivering and non.

Comments are closed.