What Is Bell Curve Explained Bell Curve With Standard Deviation

Bell Curve And Standard Deviation How to check data. a bell shaped curve, also known as a normal distribution or gaussian distribution, is a symmetrical probability distribution in statistics. it represents a graph where the data clusters around the mean, with the highest frequency in the center, and decreases gradually towards the tails. Word problems with normal distribution: “between”: steps. step 1: identify the parts of the word problem. the word problem will identify: the mean (average or μ). standard deviation (σ). number selected (i.e. “choose one at random” or “select ten at random”). x: the numbers associated with “between” (i.e. “between $5,000 and.
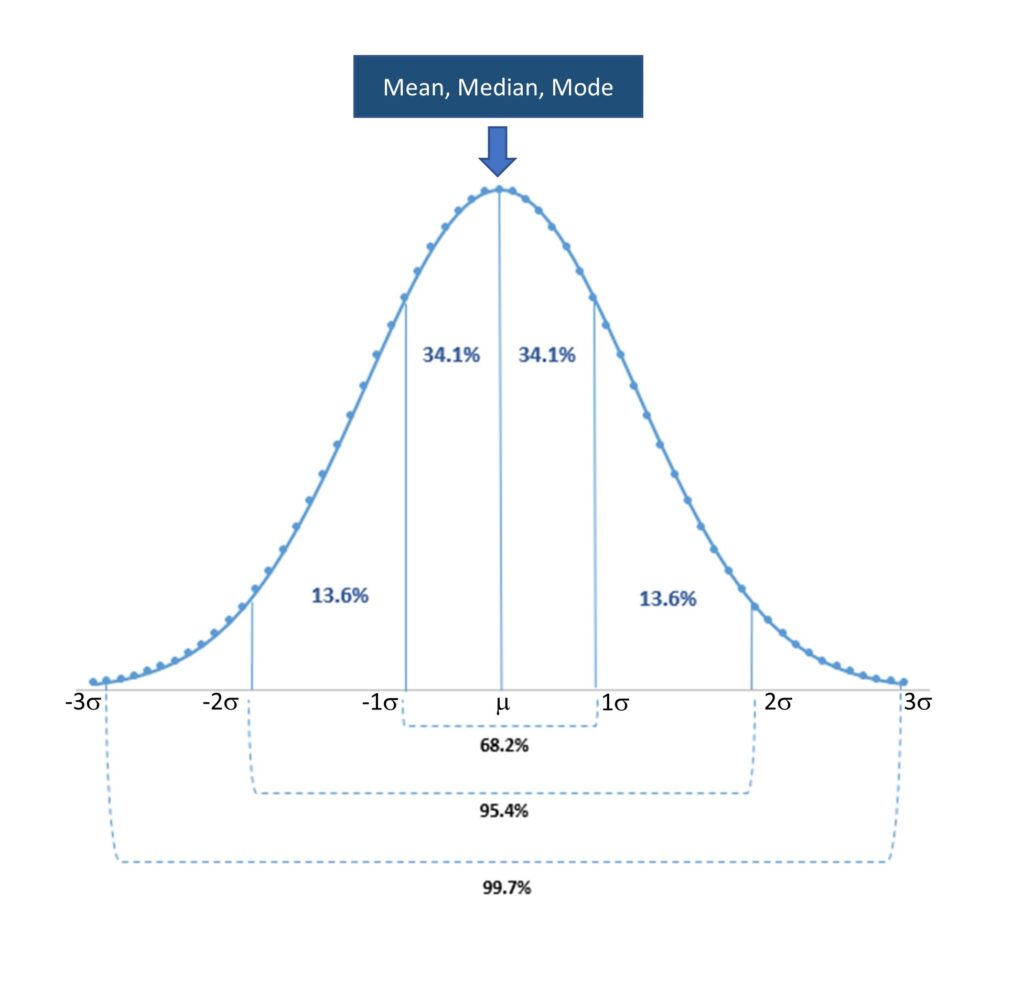
What Is Bell Curve Explained Bell Curve With Standard Deviation A bell curve is a symmetric curve centered around the mean, or average, of all the data points being measured. the width of a bell curve is determined by the standard deviation—68% of the data. The data follows a normal distribution with a mean score (m) of 1150 and a standard deviation (sd) of 150. following the empirical rule: around 68% of scores are between 1,000 and 1,300, 1 standard deviation above and below the mean. around 95% of scores are between 850 and 1,450, 2 standard deviations above and below the mean. Probability theory. in probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real valued random variable. the general form of its probability density function is the parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while. The standard deviation is a measure of how spread out numbers are (read that page for details on how to calculate it). when we calculate the standard deviation we find that generally: 68% of values are within. 1 standard deviation of the mean. 95% of values are within. 2 standard deviations of the mean.
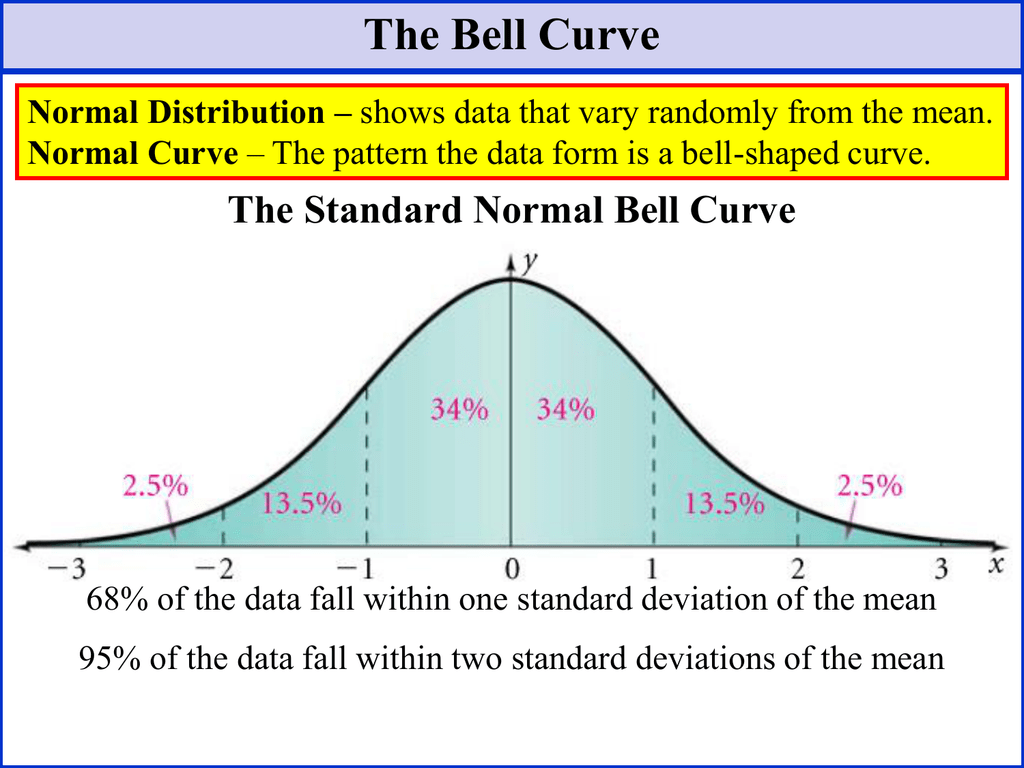
The Bell Curve The Standard Normal Bell Curve Probability theory. in probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real valued random variable. the general form of its probability density function is the parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while. The standard deviation is a measure of how spread out numbers are (read that page for details on how to calculate it). when we calculate the standard deviation we find that generally: 68% of values are within. 1 standard deviation of the mean. 95% of values are within. 2 standard deviations of the mean. Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean. the mean, median, and mode of a normal distribution are equal. the area under the normal curve is equal to 1.0 1.0. normal distributions are denser in the center and less dense in the tails. normal distributions are defined by two parameters, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ). Its familiar bell shaped curve is ubiquitous in statistical reports, from survey analysis and quality control to resource allocation. the graph of the normal distribution is characterized by two parameters: the mean , or average, which is the maximum of the graph and about which the graph is always symmetric; and the standard deviation , which.

Comments are closed.