What Is A Secondary Consumer In A Food Web
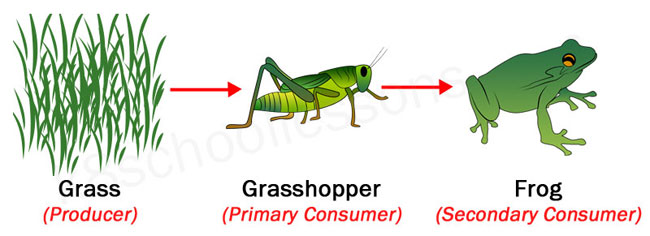
Food Chains And Food Webs Examples Of Food Chains And Food Webs A secondary consumer is an organism that eats primary consumers for energy. primary consumers are herbivores that only eat plants. secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores, and they regulate the population of primary consumers and provide energy to tertiary consumers. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.

Food Chain And Food Webs Explained A food chain is a network of links in a food web. here, the producers are consumed by the predators primary and secondary consumers and then the detritivores and finally by decomposers. when many such individual food chains occur in an ecosystem, it is known as food web. a food chain shows a direct transfer of energy between organisms. Secondary consumers occupy the third trophic level in a typical food chain. they are organisms that feed on primary consumers for nutrients and energy. while primary consumers are always herbivores; organisms that only feed on autotrophic plants, secondary consumers can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat only animals, but omnivores eat. Secondary consumers. secondary consumers are the organisms that reside on the third trophic level and depend on primary consumers for food. they can be carnivores or omnivores. carnivores eat other animals, whereas omnivores eat both plants and animals. in a desert, a snake is a secondary consumer, eating mice. A food web is a graphic representation of a holistic, nonlinear web of primary producers, primary consumers, and higher level consumers used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics (figure 1). figure 1. example of simplified food chains (a) and food webs (b) of terrestrial and marine ecosystems.

Comments are closed.