What Is A Food Web Energy Flow In An Ecosystem
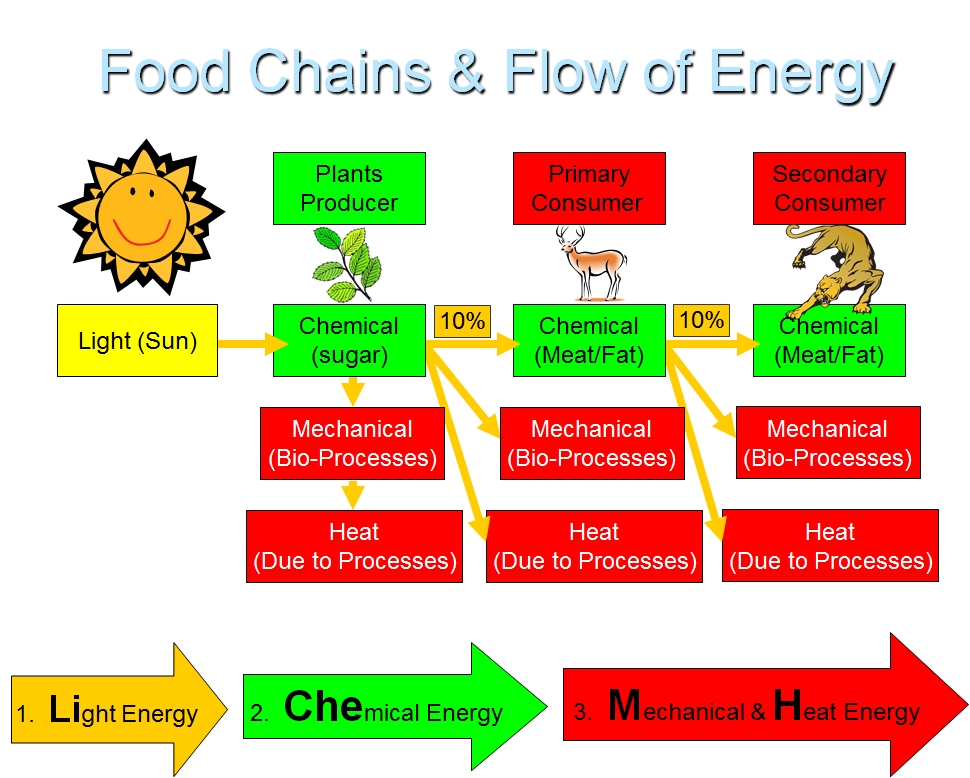
Food Webs Vista Heights 8th Grade Science The energy flow takes place via the food chain and food web. during the process of energy flow in the ecosystem, plants being the producers absorb sunlight with the help of the chloroplasts and a part of it is transformed into chemical energy in the process of photosynthesis. this energy is stored in various organic products in the plants and. Patterns of energy flow through different ecosystems may differ markedly in terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems (shurin et al. 2006). food webs (i.e., energy flow webs) can be used to reveal these.
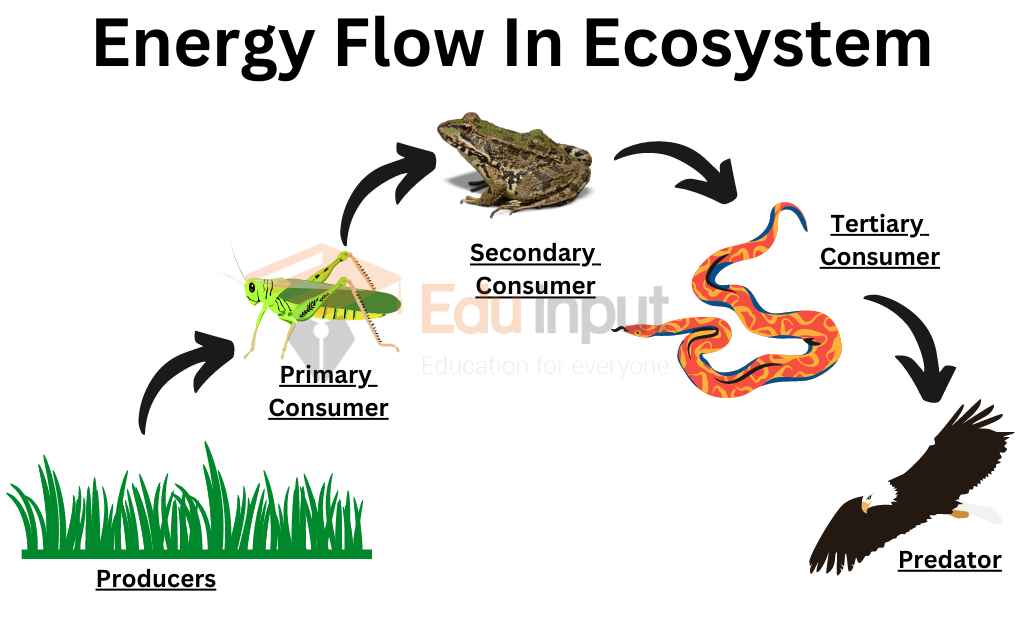
Energy Flow In Ecosystem Food web, a complex network of interconnecting and overlapping food chains showing feeding relationships within a community. a food chain shows how matter and energy from food are transferred from one organism to another, whereas a food web illustrates how food chains intertwine in an ecosystem. food webs also demonstrate that most organisms. A food webconsists of all the food chains in a single ecosystem. each living thing in an ecosystem is part of multiple food chains. each food chain is one possible path that energy and nutrients may take as they move through the ecosystem. all of the interconnected and overlapping food chains in an ecosystem make up a food web. Energy flow (ecology) a food pyramid and a corresponding food web, demonstrating some of the simpler patterns in a food web. a graphic representation of energy transfer between trophic layers in an ecosystem. energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] all living organisms can be organized into producers and. As ecosystems require a method to recycle material from dead organisms, grazing food webs have an associated detrital food web. for example, in a meadow ecosystem, plants may support a grazing food web of different organisms, primary and other levels of consumers, while at the same time supporting a detrital food web of bacteria and fungi.

Energy Flow Biology Britannica Energy flow (ecology) a food pyramid and a corresponding food web, demonstrating some of the simpler patterns in a food web. a graphic representation of energy transfer between trophic layers in an ecosystem. energy flow is the flow of energy through living things within an ecosystem. [1] all living organisms can be organized into producers and. As ecosystems require a method to recycle material from dead organisms, grazing food webs have an associated detrital food web. for example, in a meadow ecosystem, plants may support a grazing food web of different organisms, primary and other levels of consumers, while at the same time supporting a detrital food web of bacteria and fungi. As ecosystems require a method to recycle material from dead organisms, grazing food webs have an associated detrital food web. for example, in a meadow ecosystem, plants may support a grazing food web of different organisms, primary and other levels of consumers, while at the same time supporting a detrital food web of bacteria and fungi. Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each.
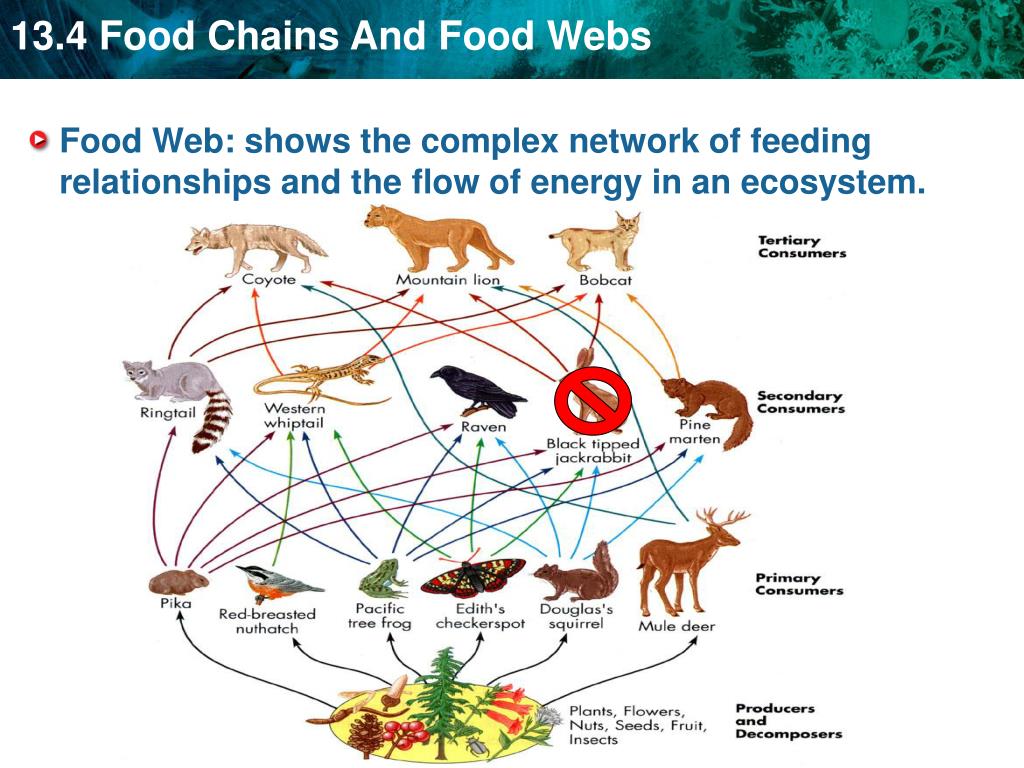
Ppt Key Concept Food Chains And Food Webs Model The Flow Of Energy In As ecosystems require a method to recycle material from dead organisms, grazing food webs have an associated detrital food web. for example, in a meadow ecosystem, plants may support a grazing food web of different organisms, primary and other levels of consumers, while at the same time supporting a detrital food web of bacteria and fungi. Trophic levels provide a structure for understanding food chains and how energy flows through an ecosystem. at the base of the pyramid are the producers, who use photosynthesis or chemosynthesis to make their own food. herbivores or primary consumers, make up the second level. secondary and tertiary consumers, omnivores and carnivores, follow in the subsequent sections of the pyramid. at each.
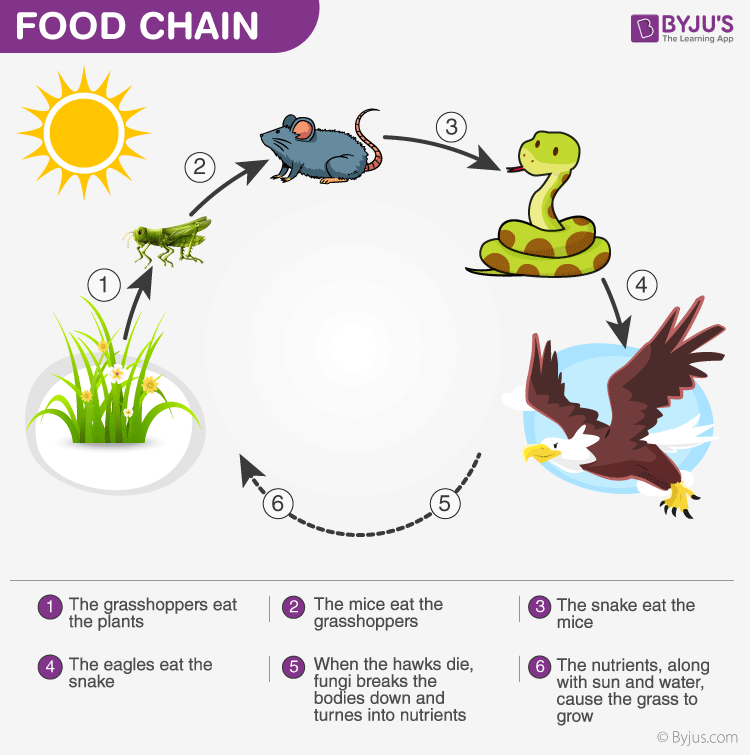
Energy Flow In Ecosystem Food Chain Food Web And Energy Py

Comments are closed.