Understanding Your Electric Bill Whats A Demand Charge
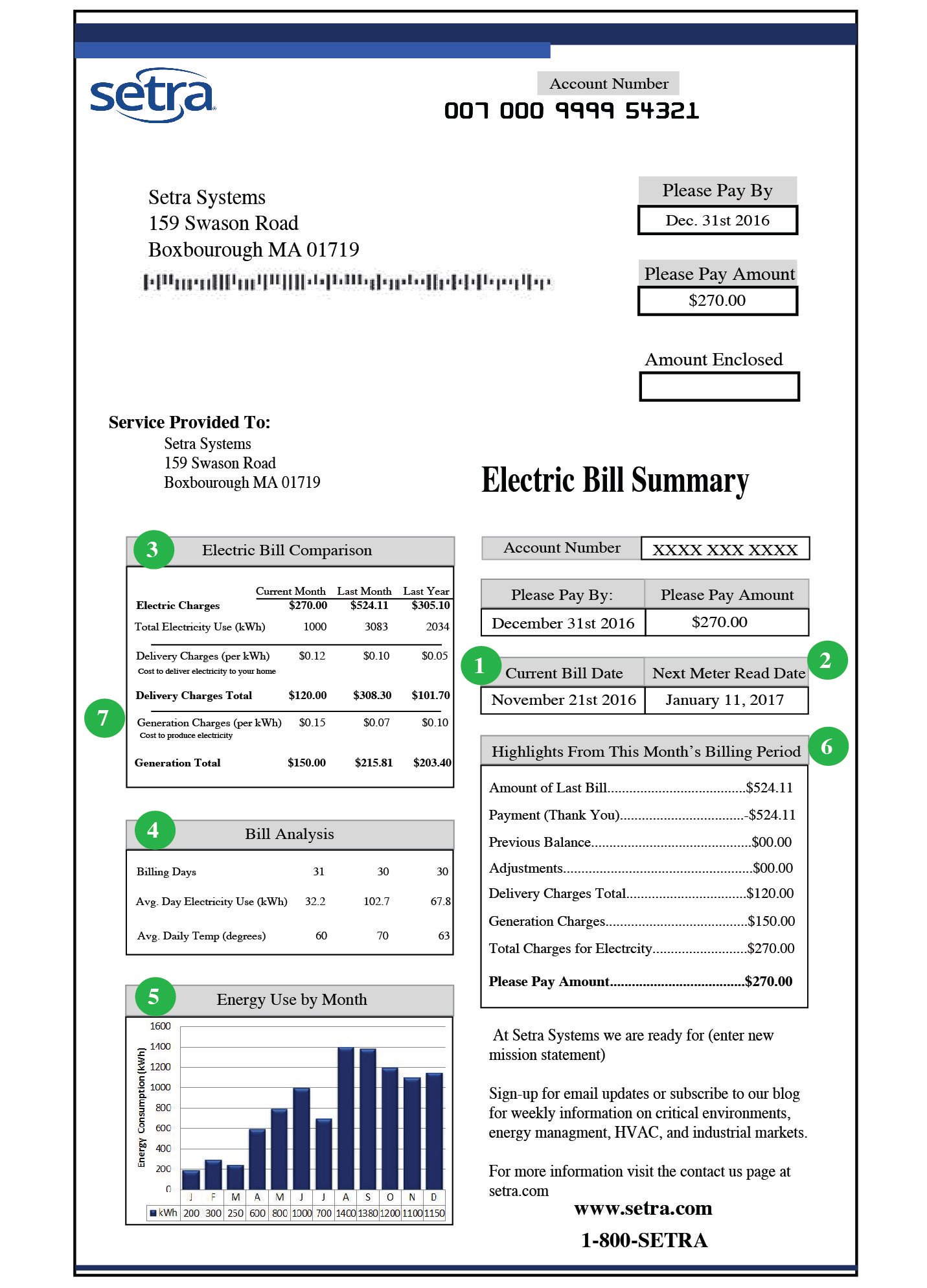
How To Read Your Electric Bill To understand how demand charges work and impact your electricity bill, it is important to understand how utilities charge for electricity. providing reliable electricity requires utilities to plan for and provide enough electric generating capacity to meet peak demand (expressed in kilowatts: kw), generate enough electricity to meet annual consumption on the grid (expressed in kilowatt hours. When a building is charged for both energy and peak demand, there is a different rate for each measurement. for example, your electricity provider may charge $0.10 per kwh, and $6 per kw of peak demand. if you consumed 50,000 kwh and had a peak demand of 160 kwh, you get an energy charge of $5,000 and a demand charge of $960, adding up to $5,960.
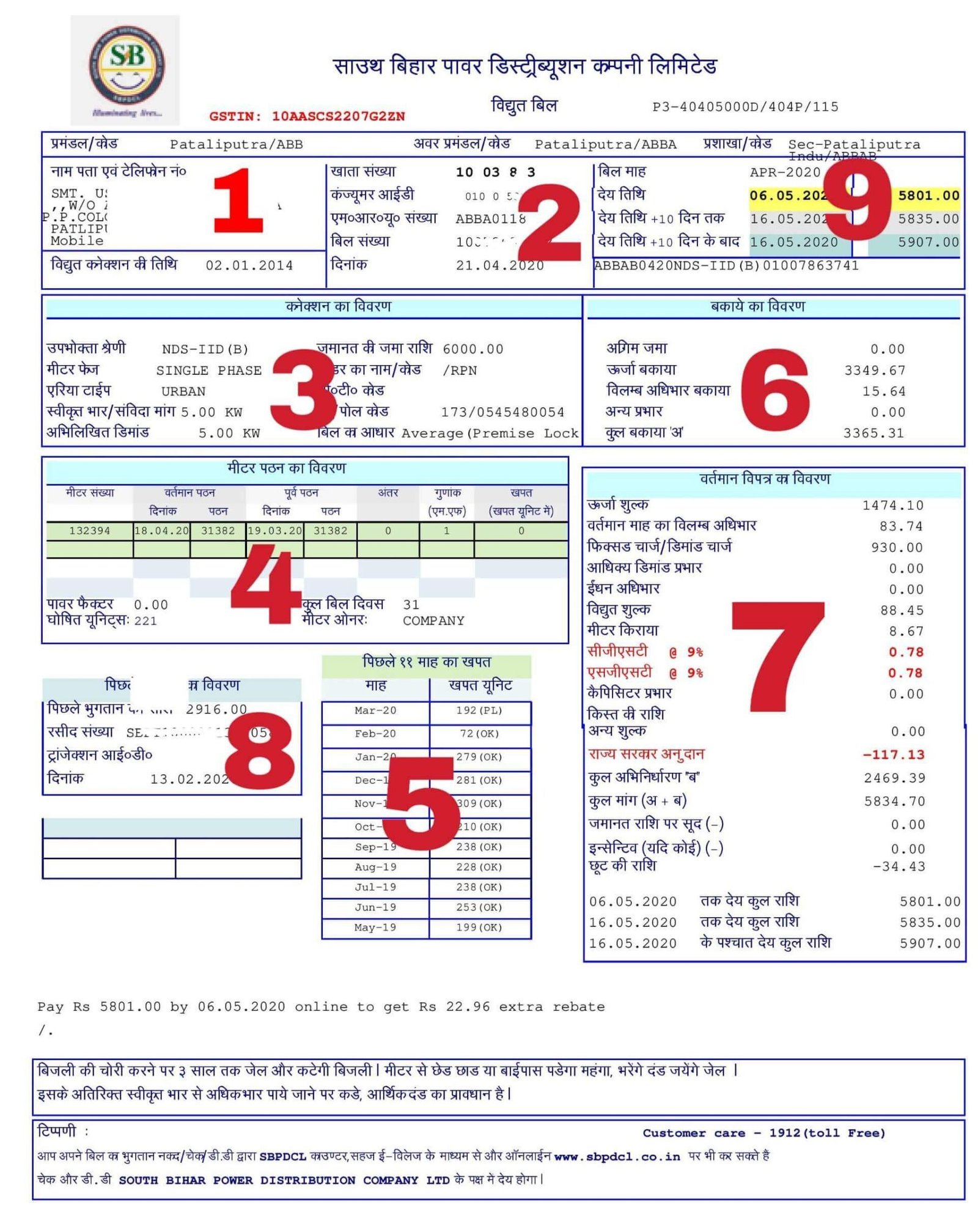
Know Your Electricity Bill Understanding Complete Detail Zaroori Baatein Less than 10 kw of monthly demand. service charge: $15.25 customer first 600 kwh: $0.03225 kwh all other kwh: $0.02076 kwh. medium general service. greater than 10 kw of monthly demand. service charge: $43.00 customer demand charge: $2.20 kw first 10,000 kwh: $0.03438 kwh all other kwh: $0.02927 kwh. If the utility charges a flat rate of $15 kw for demand, let’s calculate: no solar or battery: 91.51 x $15 = $1,372 (default bill) this is what the business owes for demand charges. pv only system: 77.12 x $15 = $1,168. demand charges after installing solar. solar pv battery. 49.97 x $15 = $749. If you're wondering about the "demand charge" line item on your electric bill, you're not alone. in this video geared toward commercial and industrial custom. 10,000 kwh * $0.10 kwh 100 kw * $10 kw = $2,000. demand charges just doubled this monthly bill. your demand charge can also be influenced by a characteristic called the power factor. power factor is a measure of how efficiently your site uses electrical energy. if your equipment uses energy inefficiently, it will exhibit a low power factor.

How To Read Your Electricity Bill If you're wondering about the "demand charge" line item on your electric bill, you're not alone. in this video geared toward commercial and industrial custom. 10,000 kwh * $0.10 kwh 100 kw * $10 kw = $2,000. demand charges just doubled this monthly bill. your demand charge can also be influenced by a characteristic called the power factor. power factor is a measure of how efficiently your site uses electrical energy. if your equipment uses energy inefficiently, it will exhibit a low power factor. The total amount of energy demand is 300 kw (3 machines x 100 kw of demand). the plant operator decides to run these machines continuously for a 10 hour shift. over the course of 10 hours, the three machines use 3,000 kilowatt hours (kwh) of electricity (300 kw of demand x 10 hours of usage). this example illustrates the key difference between. Some common things to look out for on your bills are the meter number, consumption reading, demand reading, pf, charges based on consumption, charges based on demand, penalties, riders and fees, and fixed charges (. figure 4. the following sections will provide an overview of these key aspects of electricity bills.

Making Sense Of Your Electricity Bill Renewable Energy Help Centre The total amount of energy demand is 300 kw (3 machines x 100 kw of demand). the plant operator decides to run these machines continuously for a 10 hour shift. over the course of 10 hours, the three machines use 3,000 kilowatt hours (kwh) of electricity (300 kw of demand x 10 hours of usage). this example illustrates the key difference between. Some common things to look out for on your bills are the meter number, consumption reading, demand reading, pf, charges based on consumption, charges based on demand, penalties, riders and fees, and fixed charges (. figure 4. the following sections will provide an overview of these key aspects of electricity bills.

Comments are closed.