Types Of Electromagnetic Waves Learn Definition Examples Facts Use
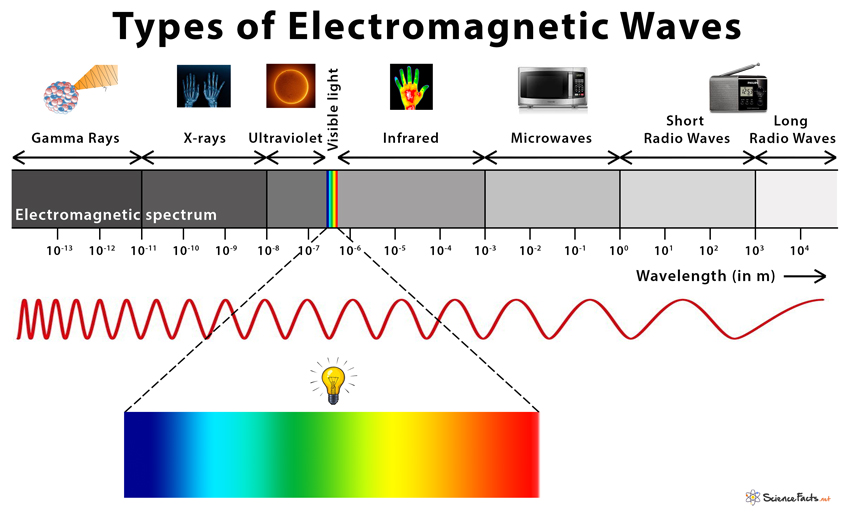
Types Of Electromagnetic Waves Learn Definition Examples Facts Use Types of electromagnetic waves. there are seven types of electromagnetic waves – radio wave, microwave, infrared, visible light, ultraviolet, x rays, and gamma rays. 1. radio waves. as the name suggests, radio waves are emitted by radio stations, tv stations, and cellphone towers. they have a wavelength range of 1 10 5 meters. 7 types of electromagnetic waves. the electromagnetic (em) spectrum encompasses all wave frequencies, including radio, visible light and x rays. all em waves are made up of photons that travel through space until they interact with matter; some waves are absorbed and others are reflected. though the sciences generally classify em waves into.
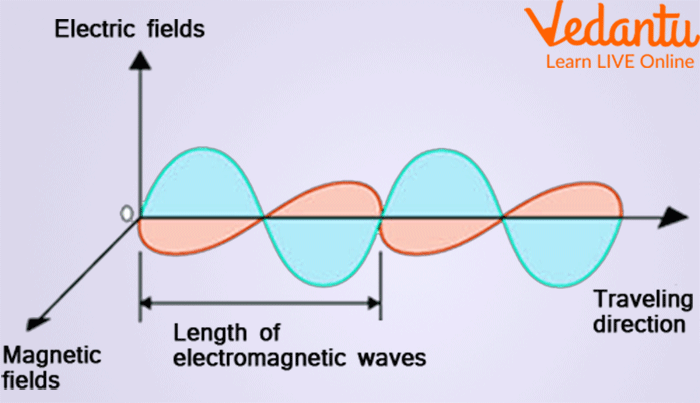
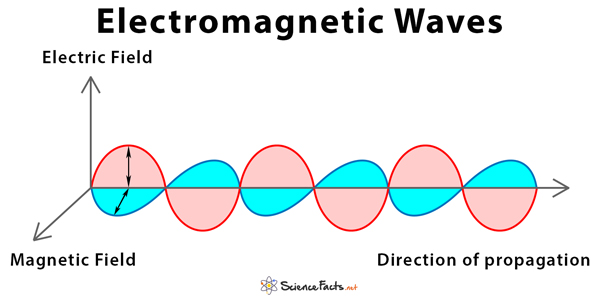
Electromagnetic Waves Definition Propagation And Types This is because electromagnetic waves can transmit energy through a vacuum, or without a medium. here are a few applications of electromagnetic waves in our lives. radio waves: for communication uses, such as television communication and radio. microwaves: used in a microwave oven to heat meals, and for satellite television. Radio waves have the longest wavelengths of all the electromagnetic waves. they range from around a foot long to several miles long. radio waves are often used to transmit data and have been used for all sorts of applications including radio, satellites, radar, and computer networks. microwaves. microwaves are shorter than radio waves with. Electromagnetic waves. electromagnetic radiation, is a form of energy emitted by moving charged particles. as it travels through space it behaves like a wave, and has an oscillating electric field component and an oscillating magnetic field. these waves oscillate perpendicularly to and in phase with one another. What is electromagnetic energy? electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. the human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. a radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x ray machine uses yet another portion.
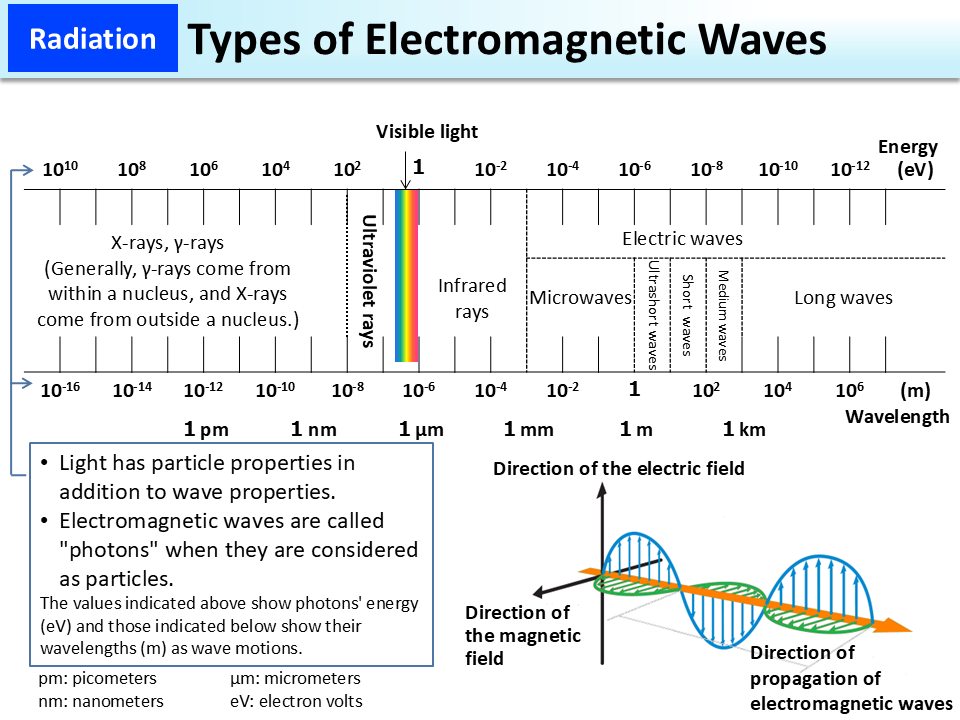
Types Of Electromagnetic Waves Moe Electromagnetic waves. electromagnetic radiation, is a form of energy emitted by moving charged particles. as it travels through space it behaves like a wave, and has an oscillating electric field component and an oscillating magnetic field. these waves oscillate perpendicularly to and in phase with one another. What is electromagnetic energy? electromagnetic energy travels in waves and spans a broad spectrum from very long radio waves to very short gamma rays. the human eye can only detect only a small portion of this spectrum called visible light. a radio detects a different portion of the spectrum, and an x ray machine uses yet another portion. The electromagnetic spectrum is the continuous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. it covers an enormous frequency range, from about 1 hertz (hz) at the extreme low end to over 10 25 hz at the high end, with no gaps in the frequency range. electromagnetic radiation refers to the waves of the electromagnetic field, propagating through space. Examples of electromagnetic waves traveling through space independent of matter are radio and television waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet light, x rays, and gamma rays. all of these waves travel at the same speed—namely, the velocity of light (roughly 300,000 kilometres, or 186,000 miles, per second).
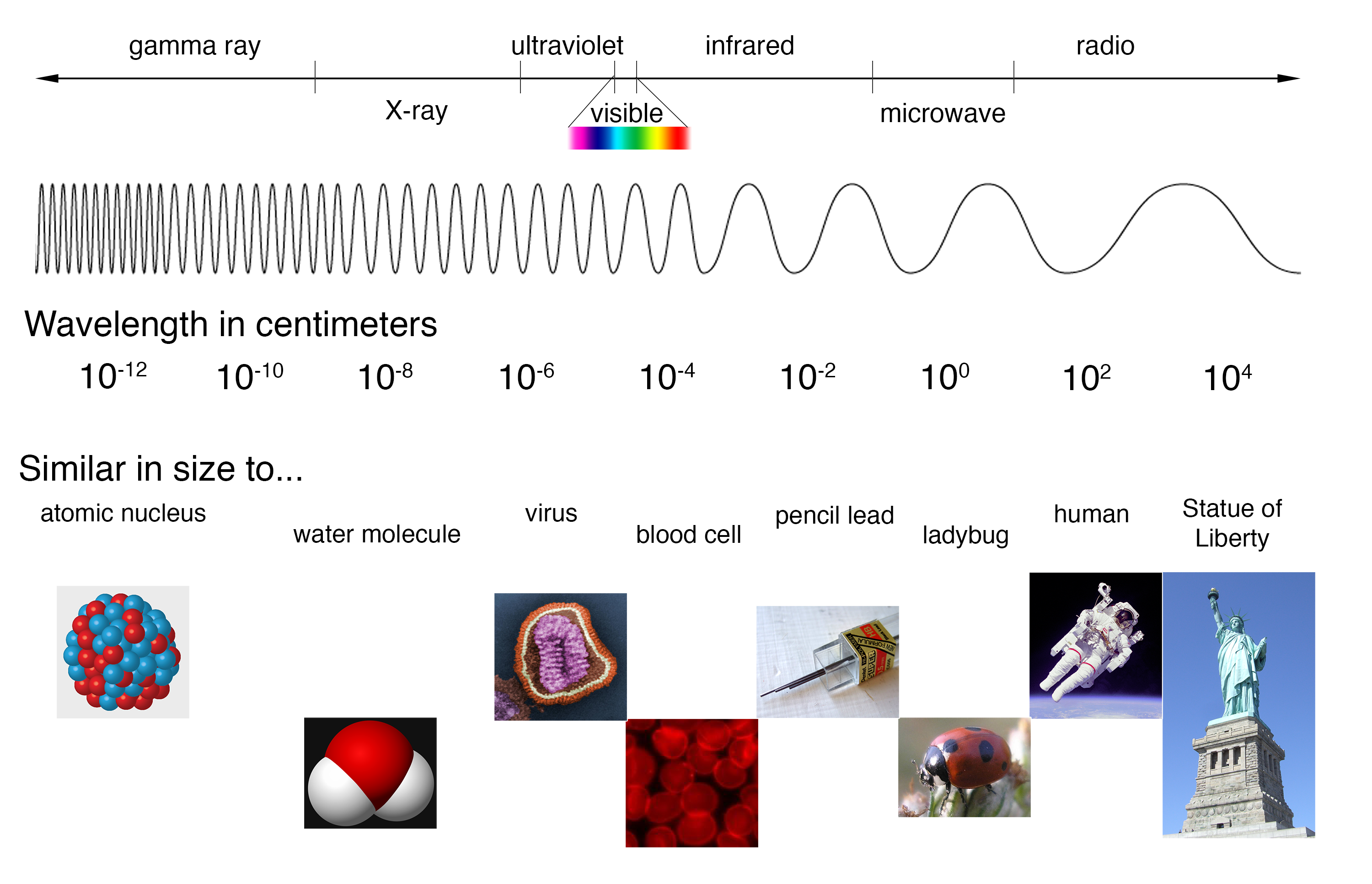
Spectra Introduction The electromagnetic spectrum is the continuous spectrum of electromagnetic radiation. it covers an enormous frequency range, from about 1 hertz (hz) at the extreme low end to over 10 25 hz at the high end, with no gaps in the frequency range. electromagnetic radiation refers to the waves of the electromagnetic field, propagating through space. Examples of electromagnetic waves traveling through space independent of matter are radio and television waves, microwaves, infrared rays, visible light, ultraviolet light, x rays, and gamma rays. all of these waves travel at the same speed—namely, the velocity of light (roughly 300,000 kilometres, or 186,000 miles, per second).
Electromagnetic Waves Definition Propagation And Types

Comments are closed.