Transposons
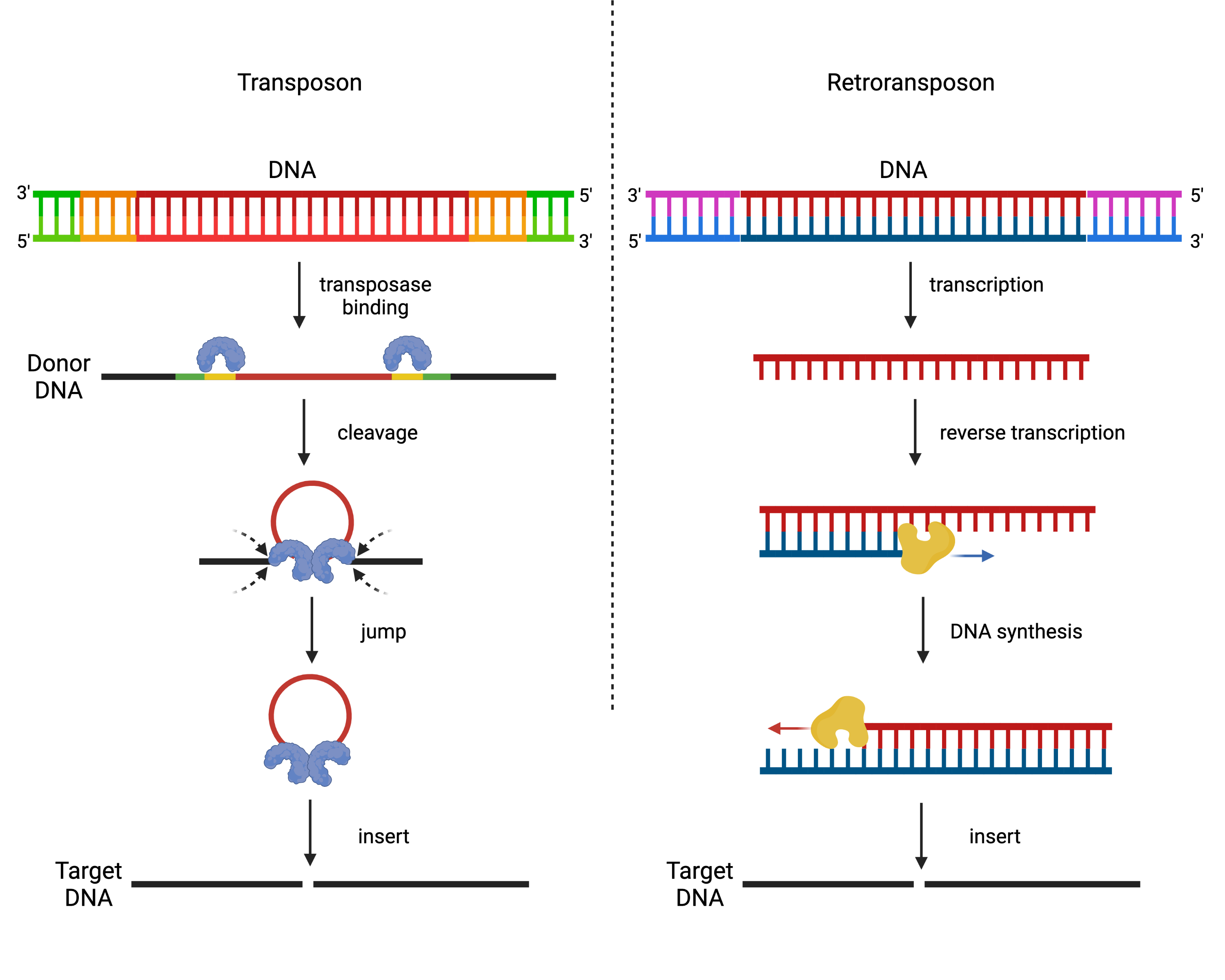
Transposable Elements Epigenetics And Evolution This Is Epigenetics Dna transposon. dna transposons are dna sequences, sometimes referred to "jumping genes", that can move and integrate to different locations within the genome. [1] they are class ii transposable elements (tes) that move through a dna intermediate, as opposed to class i tes, retrotransposons, that move through an rna intermediate. [2]. Transposon, class of genetic elements that can “jump” to different locations within a genome. although these elements are frequently called “jumping genes,” they are always maintained in an integrated site in the genome. in addition, most transposons eventually become inactive and no longer move. transposons were first discovered in.

Transposon Tools Domus Biotechnologies Learn about transposable elements, or "jumping genes", that move from one location to another in the genome. find out the types, functions, and evolutionary impacts of dna transposons and retrotransposons in eukaryotes. Dna transposons move from one genomic location to another by a cut and paste mechanism. they are powerful forces of genetic change and have played a significant role in the evolution of many genomes. as genetic tools, dna transposons can be used to introduce a piece of foreign dna into a genome. Transposons are segments of dna that can move around to different positions in the genome of a single cell. in the process, they may cause mutations and increase (or decrease) the amount of dna in the genome of the cell, and if the cell is the precursor of a gamete, in the genomes of any descendants. these mobile segments of dna are sometimes. Learn about transposons, segments of dna that can move throughout the genome, and their types, functions, and examples. find out how transposons are involved in gene mutations, antibiotic resistance, and genetic engineering.

Transposons вђ Evolution Naturally Inspiring Transposons are segments of dna that can move around to different positions in the genome of a single cell. in the process, they may cause mutations and increase (or decrease) the amount of dna in the genome of the cell, and if the cell is the precursor of a gamete, in the genomes of any descendants. these mobile segments of dna are sometimes. Learn about transposons, segments of dna that can move throughout the genome, and their types, functions, and examples. find out how transposons are involved in gene mutations, antibiotic resistance, and genetic engineering. Development. there are transposons in a wide variety of organisms, from bacteria and yeasts to humans. transposition can take place from one site to another of the same chromosome, or from one chromosome to another (in eukaryotic organisms whose genome is organized into several chromosomes), or even from a chromosome site to a plasmid site (in organisms containing plasmids, genetic elements. A transposable element (te) is a nucleic acid sequence that can change its position within a genome, sometimes creating or reversing mutations. learn about the discovery, classification, and functions of tes, such as retrotransposons and dna transposons.

Comments are closed.