Theory Of Consumer S Surplus Assignment Point
Theory Of Consumer S Surplus Assignment Point The concept of consumer’s surplus is based on the law of diminishing marginal utility. as we purchase more units of a commodity, its marginal utility goes on diminishing. the consumer is in equilibrium when marginal utility become equal to the given price. description: total social surplus is composed of consumer surplus and producer surplus. The economic theory of marginal utility, which is the additional gratification that an individual derives from purchasing one more unit of a product or service, is based on consumer surplus. to quantify the social benefits of public goods such as national highways, canals, and bridges, the idea of consumer surplus was established in 1844.
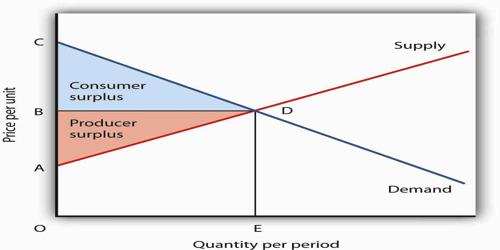
Theory Of Consumer S Surplus Assignment Point In these places, the consumers enjoy large surplus of satisfaction. consumer’s surplus thus indicates conjuncture advantages, i.e., the advantages of environment arid opportunities. distinction between value in use and value in exchange: consumer’s surplus draws a clear distinction between value in use and value in exchange. Definition of consumer surplus: 1. regarding this prof. marshall has said that “the excess of price which he (consumer) would be willing to pay rather than go without. the thing over that which he actually does pay, is the economic measure of this surplus satisfaction. it may be called “consumer’s surplus”. 2. The marshallian surplus: the consumers’ surplus is a concept introduced by marshall, who maintained that it can be measured in monetary units, and is equal to the difference between the amount of money that a consumer actually pays to buy a certain quantity of a commodity x, and the amount that he would be willing to pay for this quantity. Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above.
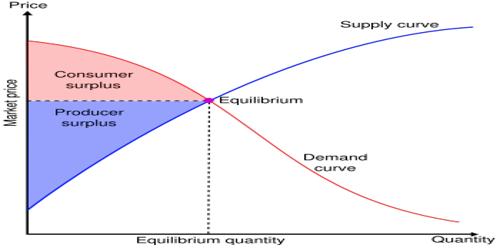
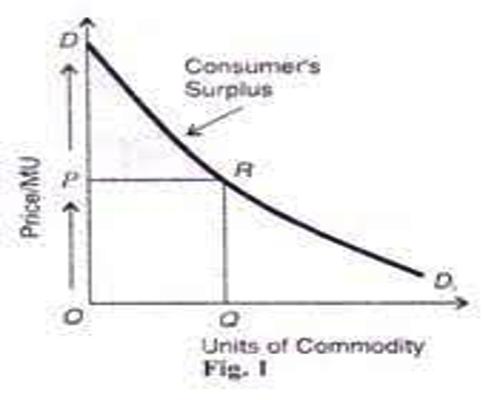
Importance Of Consumer S Surplus Assignment Point The marshallian surplus: the consumers’ surplus is a concept introduced by marshall, who maintained that it can be measured in monetary units, and is equal to the difference between the amount of money that a consumer actually pays to buy a certain quantity of a commodity x, and the amount that he would be willing to pay for this quantity. Consumer and producer surpluses are shown as the area where consumers would have been willing to pay a higher price for a good or the price where producers would have been willing to sell a good. in the sample market shown in the graph, equilibrium price is $10 and equilibrium quantity is 3 units. the consumer surplus area is highlighted above. Total net benefit or consumer surplus is the difference between the consumer’s willingness to pay and the amount (price) they actually pay for a given quantity. as noted from fig 4.2, the market price for a tablet computer is $200, therefore tim’s consumer surplus is $80 ($280 minus $200), josh’s consumer surplus is $60 ($260 − $200. The consumer surplus represents the consumer’s gains from trade, the value of consumption to the consumer net of the price paid. figure 2.2 consumer surplus. the consumer surplus can also be expressed using the demand curve, by integrating from the price up to where the demand curve intersects with the price axis.

Comments are closed.