The Tear Film Lipid Layer Mov

Human Tear Film Model Showing The Lipid Layer With Nonpolar And Polar The vast majority of the tear film is an aqueous phase containing various mucin concentrations depending on the layer and a thin superficial lipid layer 50 100 nm in thickness. [1] the inner layer is formed by mucins secreted mostly by the goblet cells in the conjunctival epithelium, and to a lesser extent, by the acinar cells of the lacrimal. Tear film lipid is composed of a thin layer of polar lipids interfacing with the underlying secretory mucus layer and a thicker layer of non polar lipids at the air interface (figure 1). the lipid layer functions as a smooth optical surface, reduces surface tension of the tear film, prevents anterior migration of aqueous tears on to the lid.

Pdf The Role Of The Tear Film Lipid Layer In Tear Dynamics And In Dry The tear film lipid layer (tfll) is a complex lipid composition secreted by meibomian glands. the ≥200 lipids that form the core of this composition make up the outermost layer of the tear film, where they serve important roles such as maintaining an optimal surface tension thus preventing tears from spilling over, generating a smooth refractive surface required for clear vision, and. Schematics of (a) the tear film and (b) the constrained drop surfactometry (cds) for biophysical simulations of the tear film lipid layer (tfll). cds uses the air water surface of a sessile drop (∼4 mm in diameter, ∼0.3 cm 2 in surface area, and ∼20 μl in volume), constrained on a carefully machined pedestal with knife sharp edges, to. The tear film is a unique thin fluid layer of approximately 3μm thick and 3μl in volume that covers the outer mucosal surfaces of the eye. as such it is the interface of the ocular surface with the environment. this film is transparent and has an aqueous mucin phase, decreasing in mucin concentration towards a distinct superficial lipid layer. The outermost layer of the tear film is composed predominantly of lipids and is referred to as the tear film lipid layer (tfll). its main role is to reduce surface tension of the tear film. moreover, it helps with the tear film re spreading after blinks, provides a smooth optical surface, and prevents water evaporation; although this last point.

Structure Of The Tear Film And Simplified Pathogeny Of Ded A The tear film is a unique thin fluid layer of approximately 3μm thick and 3μl in volume that covers the outer mucosal surfaces of the eye. as such it is the interface of the ocular surface with the environment. this film is transparent and has an aqueous mucin phase, decreasing in mucin concentration towards a distinct superficial lipid layer. The outermost layer of the tear film is composed predominantly of lipids and is referred to as the tear film lipid layer (tfll). its main role is to reduce surface tension of the tear film. moreover, it helps with the tear film re spreading after blinks, provides a smooth optical surface, and prevents water evaporation; although this last point. The tear film is depicted as a three layered structure: lipid, aqueous, and mucous layers. within each layer possesses a different composition which dictates its function. Abstract. human cornea is covered by an aqueous tear film, and the outermost layer of the tear film is coated by lipids. this so called tear film lipid layer (tfll) reduces surface tension of the tear film and helps with the film re spreading after blinks. alterations of tear lipids composition and properties are related to dry eye syndrome.
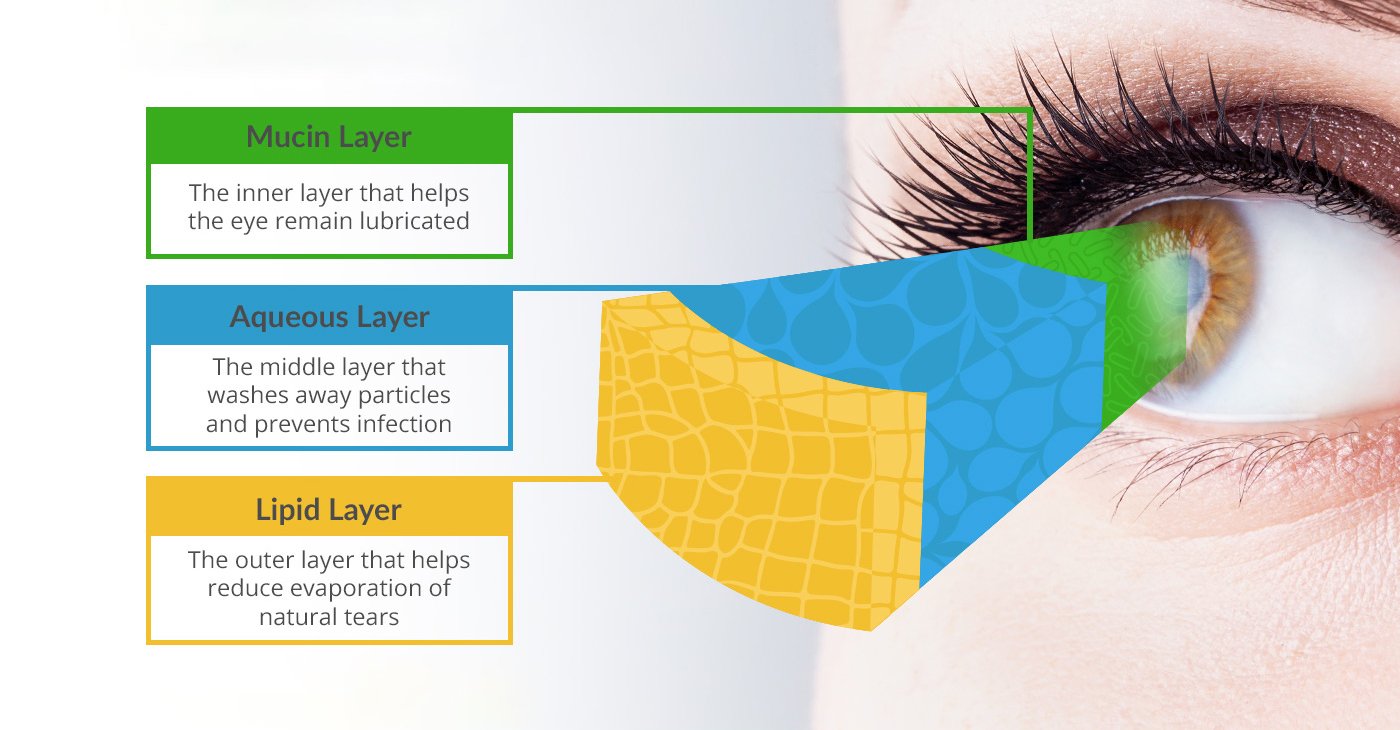
Unlocking The Science Behind Dry Eyes Understanding Tears And The Tear The tear film is depicted as a three layered structure: lipid, aqueous, and mucous layers. within each layer possesses a different composition which dictates its function. Abstract. human cornea is covered by an aqueous tear film, and the outermost layer of the tear film is coated by lipids. this so called tear film lipid layer (tfll) reduces surface tension of the tear film and helps with the film re spreading after blinks. alterations of tear lipids composition and properties are related to dry eye syndrome.

Comments are closed.