The Ecological Footprint Explained

What Is An Ecological Footprint вђ Tommiemedia Ecological footprint is a method of gauging humans’ dependence on natural resources by calculating how much of the environment is needed to sustain a particular lifestyle. in other words, it. Anders hayden. an ecological footprint is a measure of the demands made by a person or group of people on global natural resources. it has become one of the most widely used measures of humanity’s effect upon the environment and has been used to highlight both the apparent unsustainability of current practices and global inequalities.
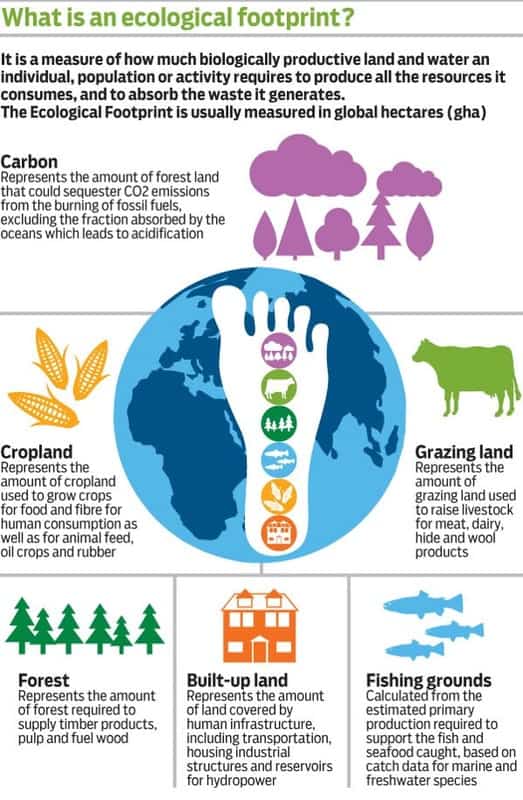
How To Measure And Reduce Your Ecological Footprint The ecological footprint tracks the use of productive surface areas. typically these areas are: cropland, grazing land, fishing grounds, built up land, forest area, and carbon demand on land. on the supply side, a city, state or nation’s biocapacity represents the productivity of its ecological assets (including cropland, grazing land, forest. The ecological footprint can be calculated for a single individual, city, region, country and the entire planet. it is also relevant for companies. the gap between ecological footprint and biocapacity is determined by several factors. our personal footprint is the product of how much we use and how efficiently this is being produced. The environmental footprint is calculated in terms of the number of planets or land area (better referred to in ecological footprint accounting as global hectares). this works to determine how much space we need to support our current lifestyle. this calculation can be done on an individual, national or planetary scale. The ecological footprint measures human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people and their economies. [1][2][3] it tracks human demand on nature through an ecological accounting system. the accounts contrast the biologically productive area people use to satisfy their consumption to the biologically.
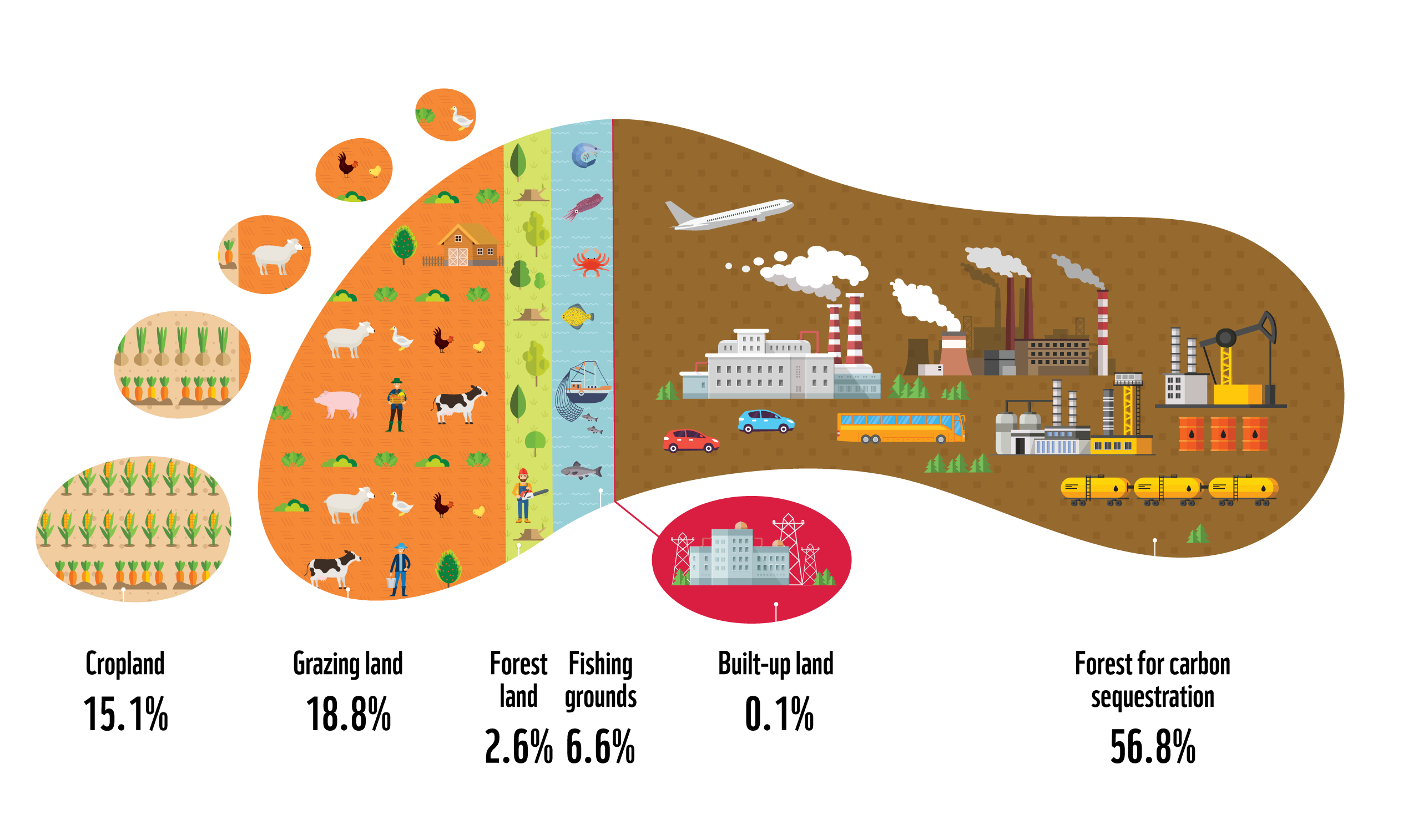
Ecological Footprint Wwf Hong Kong The environmental footprint is calculated in terms of the number of planets or land area (better referred to in ecological footprint accounting as global hectares). this works to determine how much space we need to support our current lifestyle. this calculation can be done on an individual, national or planetary scale. The ecological footprint measures human demand on natural capital, i.e. the quantity of nature it takes to support people and their economies. [1][2][3] it tracks human demand on nature through an ecological accounting system. the accounts contrast the biologically productive area people use to satisfy their consumption to the biologically. The ecological footprint measures the quantity of natural resources used to produce the goods and services consumed, as well as the amount of waste and gas emissions generated. the measurement unit is the hectare, which represents the land area required to sustain economic activities over a year. thus, the ecological footprint allows for. What the ecological footprint measures. the ecological footprint is a metric of human demand on ecosystems, or more precisely on the planet’s biocapacity. it tracks how much mutually exclusive, biologically productive area is necessary to renew people’s demand for nature’s products and services. the principles and the measurement methods.

Comments are closed.