Strategy For Calculating Projection Vector Youtube

Calculus 3 Vector Projections Orthogonal Components Youtube This calculus 3 video tutorial explains how to find the vector projection of u onto v using the dot product and how to find the vector component of u orthogo. In an euclidean vectorspace you can calculate the orthogonal projection of an vector onto a linear subspace. that orthogonal projection satisfies a best appr.

Strategy For Calculating Projection Vector Youtube Determining the projection of a vector on s linewatch the next lesson: khanacademy.org math linear algebra matrix transformations lin trans examp. The scalar projection is the magnitude of the vector projection. to calculate the scalar projection, square the components of the vector projection, add them and then square root. for example, if the vector projection is 3i 4j, then the scalar projection is √ (32 42) = 5. We can use technology to determine the projection of one vector onto another. go to wolframalpha . to find the projection of \(\overrightarrow{u}=\left\langle 4,\left.3\right\rangle \right.\) onto \(\vec{v}=\langle 2,8\rangle\), use the “projection” command. The formula for calculating the projection of a vector onto another vector is this. the left side of the equation is read, "the projection of vector b onto vector a." the steps for using this formula are demonstrated within the video found in the next section.

Math21a Vector Projection Equations Youtube We can use technology to determine the projection of one vector onto another. go to wolframalpha . to find the projection of \(\overrightarrow{u}=\left\langle 4,\left.3\right\rangle \right.\) onto \(\vec{v}=\langle 2,8\rangle\), use the “projection” command. The formula for calculating the projection of a vector onto another vector is this. the left side of the equation is read, "the projection of vector b onto vector a." the steps for using this formula are demonstrated within the video found in the next section. In matrix form, − axˆ) = had one column and so this equation looked like: at(b − xa) = 0. note that e = b − axˆ is in the nullspace of at and so is in the left nullspace of a. we know that everything in the left nullspace of. at(b 0. when we were projecting onto a line, a only. a is perpendicular to the column space of a, so this is. At aˆx = at b. if at a is invertible we can solve for ˆx to get: ˆx = (at a)−1at b. now, the projection vector p is the vector aˆx, so. p = a(at a)−1at b. in general, to calculate the projection of any vector onto the space w we multiply the vector by the projection matrix p = a(at a)−1at . wow, that was a lot of work!.
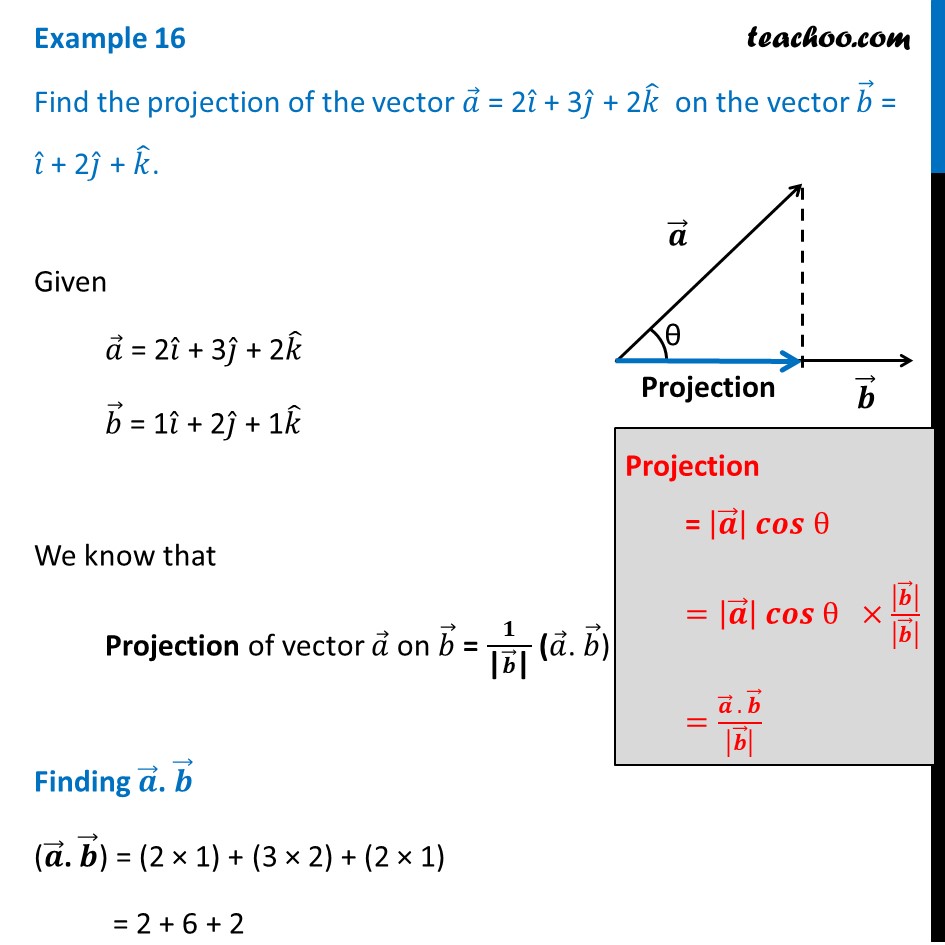
Find The Projection Of The Vector A 2i 3j 2k On Vector B I 2j K In matrix form, − axˆ) = had one column and so this equation looked like: at(b − xa) = 0. note that e = b − axˆ is in the nullspace of at and so is in the left nullspace of a. we know that everything in the left nullspace of. at(b 0. when we were projecting onto a line, a only. a is perpendicular to the column space of a, so this is. At aˆx = at b. if at a is invertible we can solve for ˆx to get: ˆx = (at a)−1at b. now, the projection vector p is the vector aˆx, so. p = a(at a)−1at b. in general, to calculate the projection of any vector onto the space w we multiply the vector by the projection matrix p = a(at a)−1at . wow, that was a lot of work!.

Comments are closed.