Stomach Mucosa Histology

File Normal Gastric Mucosa Low Mag Jpg Stomach wall. the stomach wall consists of 4 layers of tissue. from deep (external) to superficial (internal) these are the serosa, muscularis externa, submucosa and mucosa. this layered arrangement follows the same general structure in all regions of the stomach, and throughout the entire gastrointestinal tract. Lightly eosinophilic to clear bubbly vacuolated cytoplasm. lack an apical mucin cap. all mucous cells have round, basally oriented nuclei. parietal cells. produce hydrochloric acid via h k atpase pump (varela: histology, parietal cells, 2019) hydrochloric acid maintains gastric acidity (ph 1.5 to 3.5), which:.
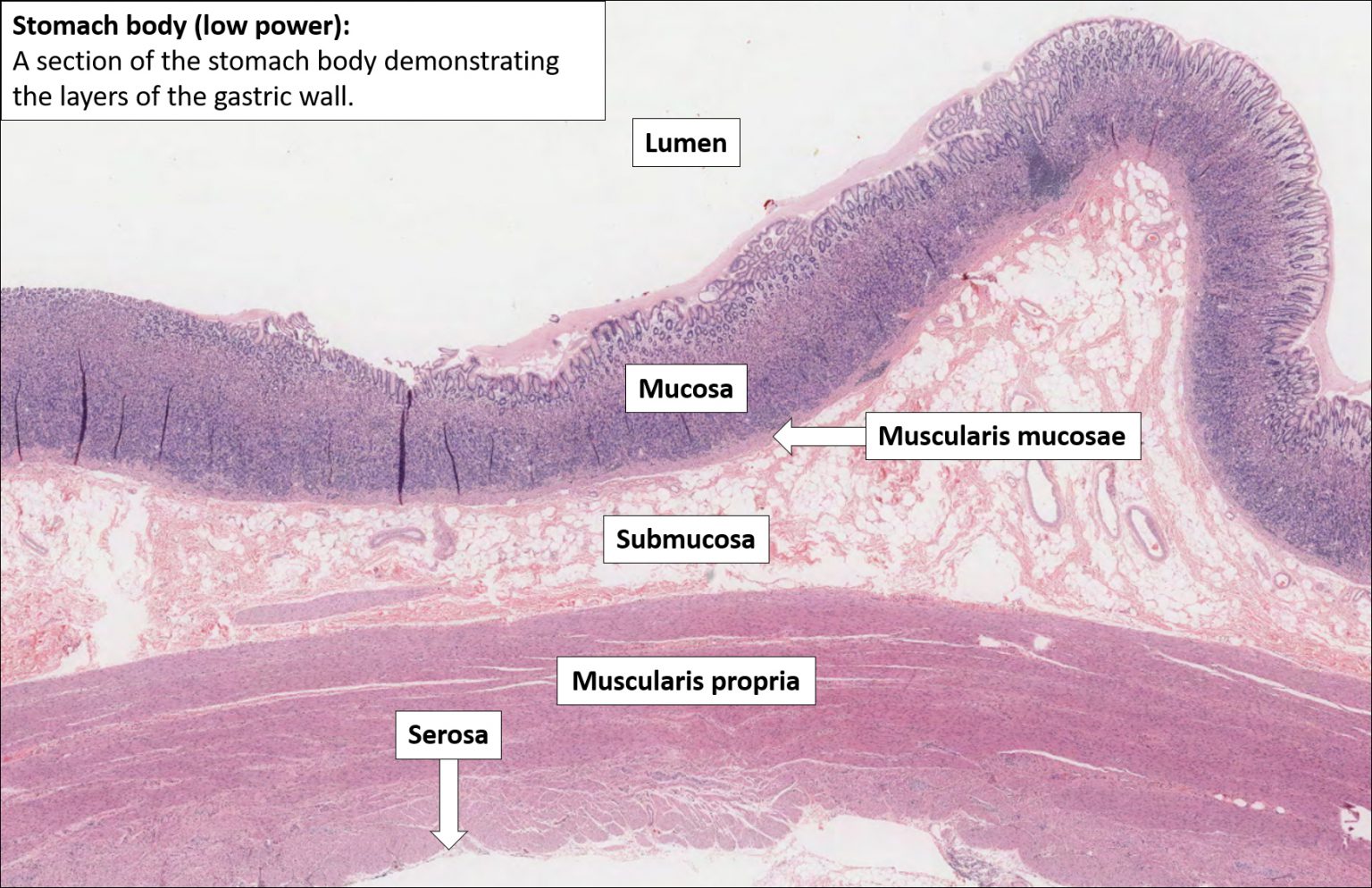
Stomach вђ Normal Histology вђ Nus Pathweb Nus Pathweb 1) the gastroesophageal junction, 2) the cardia, 3) the fundus and body, 4) the antrum and 5) the pylorus. histologically, the entire stomach is made up of simple tubular glands and foveolae (gastric pits) and there are essentially only 2 types of mucosa: oxyntic (fundus and body). cross section of stomach mucosa showing the foveolae and glands. Structure of the stomach. food starts to be digested and absorbed in the stomach, although absorption is mostly limited to water, alcohol and some drugs. the stomach is an expandable, muscular bag, and it keeps swallowed food inside it by contracting the muscular pyloric sphincter. food can stay in the stomach for 2 hours or more. The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the gastric pits, to which the gastric glands empty. in humans, it is about one mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. it consists of simple secretory columnar epithelium, an underlying supportive layer of loose connective tissue called the lamina. The gastric wall comprises four layers: the mucosa, delineated below by the muscularis mucosae; the submucosa; the muscularis propria, and the subserosa, covered by the serosa. the submucosa is rich in elastic fibres and contains fibroblasts, adipocytes, smooth muscle cells and mast cells.
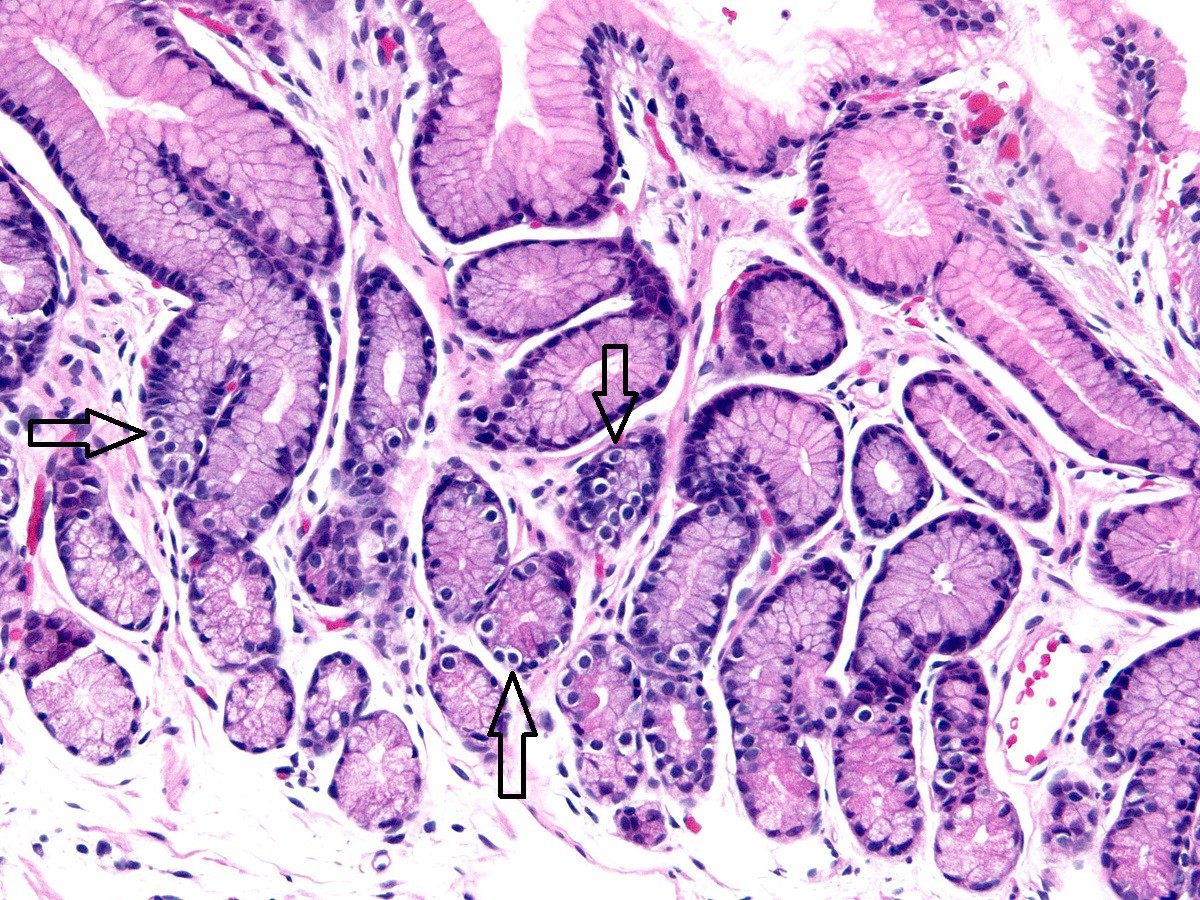
Normal Gastric Mucosa Histology The gastric mucosa is the mucous membrane layer of the stomach, which contains the gastric pits, to which the gastric glands empty. in humans, it is about one mm thick, and its surface is smooth, soft, and velvety. it consists of simple secretory columnar epithelium, an underlying supportive layer of loose connective tissue called the lamina. The gastric wall comprises four layers: the mucosa, delineated below by the muscularis mucosae; the submucosa; the muscularis propria, and the subserosa, covered by the serosa. the submucosa is rich in elastic fibres and contains fibroblasts, adipocytes, smooth muscle cells and mast cells. The stomach is an expanded portion of the gastrointestinal tract or gi tract that partially digests food by breaking it down mechanically and chemically to form a pulpy acidic fluid called chyme. the stomach has four main regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. the wall of the stomach is composed of four layers: the mucosa, submucosa. The gastric wall comprises four layers: the mucosa underlined by the muscularis mucosae, submucosa, muscularis propria and subserosa covered by the serosal lining. the mucosa is composed of two epithelial components: gastric pits (the foveolae) and deeper glands (cardiac, fundic and pyloric glands) that contain endocrine cells.
:background_color(FFFFFF):format(jpeg)/images/library/12176/stomach-mucosa-and-muscular-layers_english.jpg)
Stomach Histology Mucosa Glands And Layers Kenhub The stomach is an expanded portion of the gastrointestinal tract or gi tract that partially digests food by breaking it down mechanically and chemically to form a pulpy acidic fluid called chyme. the stomach has four main regions: the cardia, fundus, body, and pylorus. the wall of the stomach is composed of four layers: the mucosa, submucosa. The gastric wall comprises four layers: the mucosa underlined by the muscularis mucosae, submucosa, muscularis propria and subserosa covered by the serosal lining. the mucosa is composed of two epithelial components: gastric pits (the foveolae) and deeper glands (cardiac, fundic and pyloric glands) that contain endocrine cells.
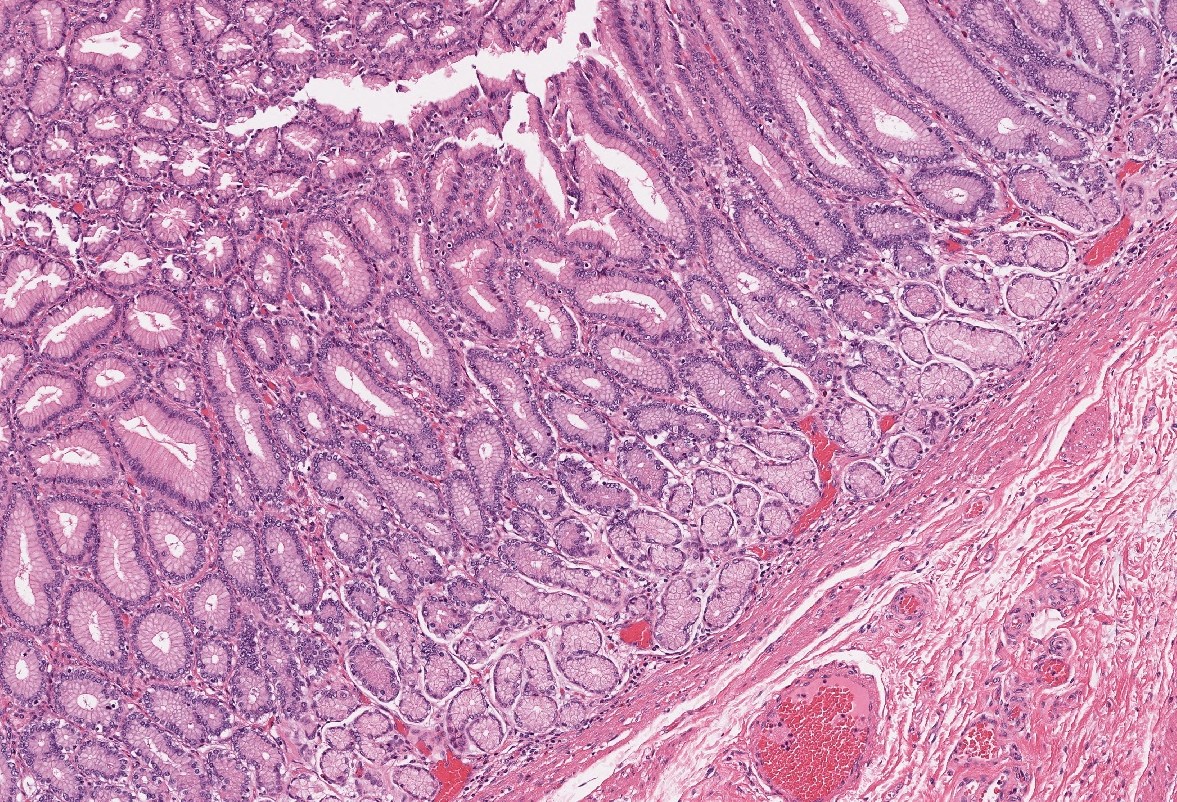
Pathology Outlines Histology

Comments are closed.