Statistical Bell Curve
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/The-Normal-Distribution1-51cb75a3e0a34eb6bbff7e966557757e.jpg)
Bell Curve Definition Normal Distribution Meaning Example In Finance Learn about the properties, importance, and applications of the normal distribution, a symmetrical probability curve that represents many continuous data in nature and psychology. find out how to check, convert, and calculate data using the empirical rule and z scores. Probability theory. in probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real valued random variable. the general form of its probability density function is the parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while.
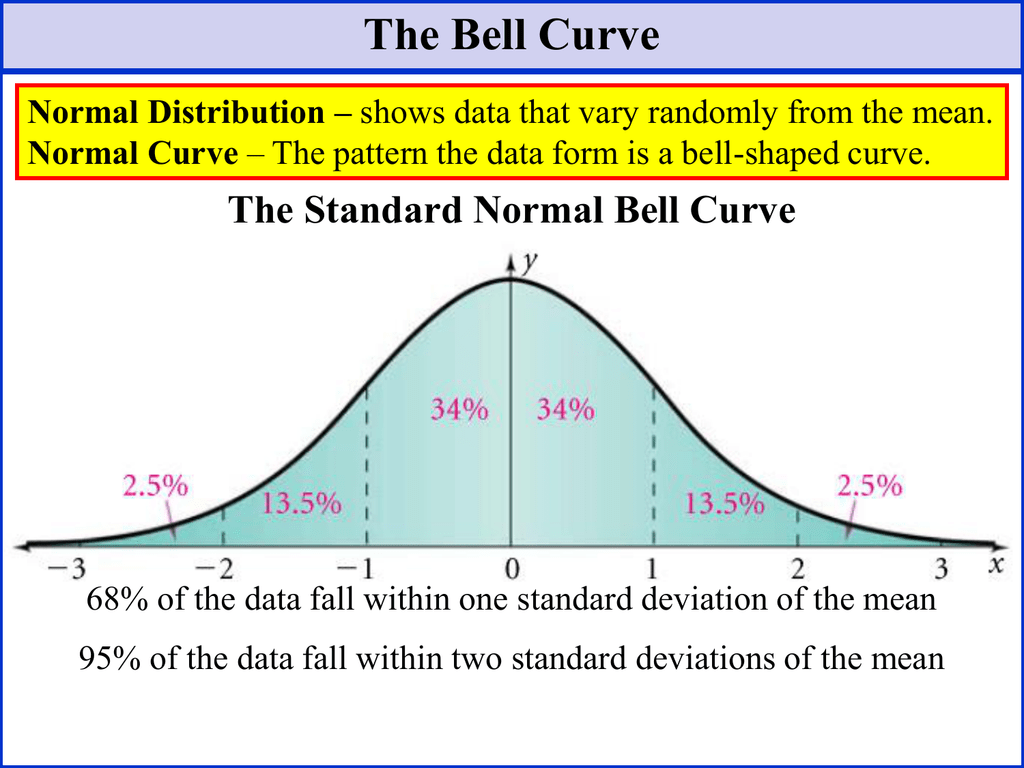
The Bell Curve The Standard Normal Bell Curve Learn what a normal distribution is, how it looks like, and why it matters in statistics. find out the empirical rule, the central limit theorem, and the formula of the normal curve. A bell curve is a symmetric curve centered around the mean, or average, of all the data points being measured. the width of a bell curve is determined by the standard deviation—68% of the data. The total area under a standard normal distribution curve is 100% (that’s “1” as a decimal). for example, the left half of the curve is 50%, or .5. so the probability of a random variable appearing in the left half of the curve is .5. of course, not all problems are quite that simple, which is why there’s a z table. all a z table does. Its familiar bell shaped curve is ubiquitous in statistical reports, from survey analysis and quality control to resource allocation. the graph of the normal distribution is characterized by two parameters: the mean , or average, which is the maximum of the graph and about which the graph is always symmetric; and the standard deviation , which.

The Bell Curve Theory Definition Examples Lesson Study The total area under a standard normal distribution curve is 100% (that’s “1” as a decimal). for example, the left half of the curve is 50%, or .5. so the probability of a random variable appearing in the left half of the curve is .5. of course, not all problems are quite that simple, which is why there’s a z table. all a z table does. Its familiar bell shaped curve is ubiquitous in statistical reports, from survey analysis and quality control to resource allocation. the graph of the normal distribution is characterized by two parameters: the mean , or average, which is the maximum of the graph and about which the graph is always symmetric; and the standard deviation , which. Below is a probability distribution plot produced by statistical software that shows the same percentile along with a graphical representation of the corresponding area under the bell curve. the value is slightly different because we used a z score of 0.65 from the table while the software uses the more precise value of 0.667. Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean. the mean, median, and mode of a normal distribution are equal. the area under the normal curve is equal to 1.0 1.0. normal distributions are denser in the center and less dense in the tails. normal distributions are defined by two parameters, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ).
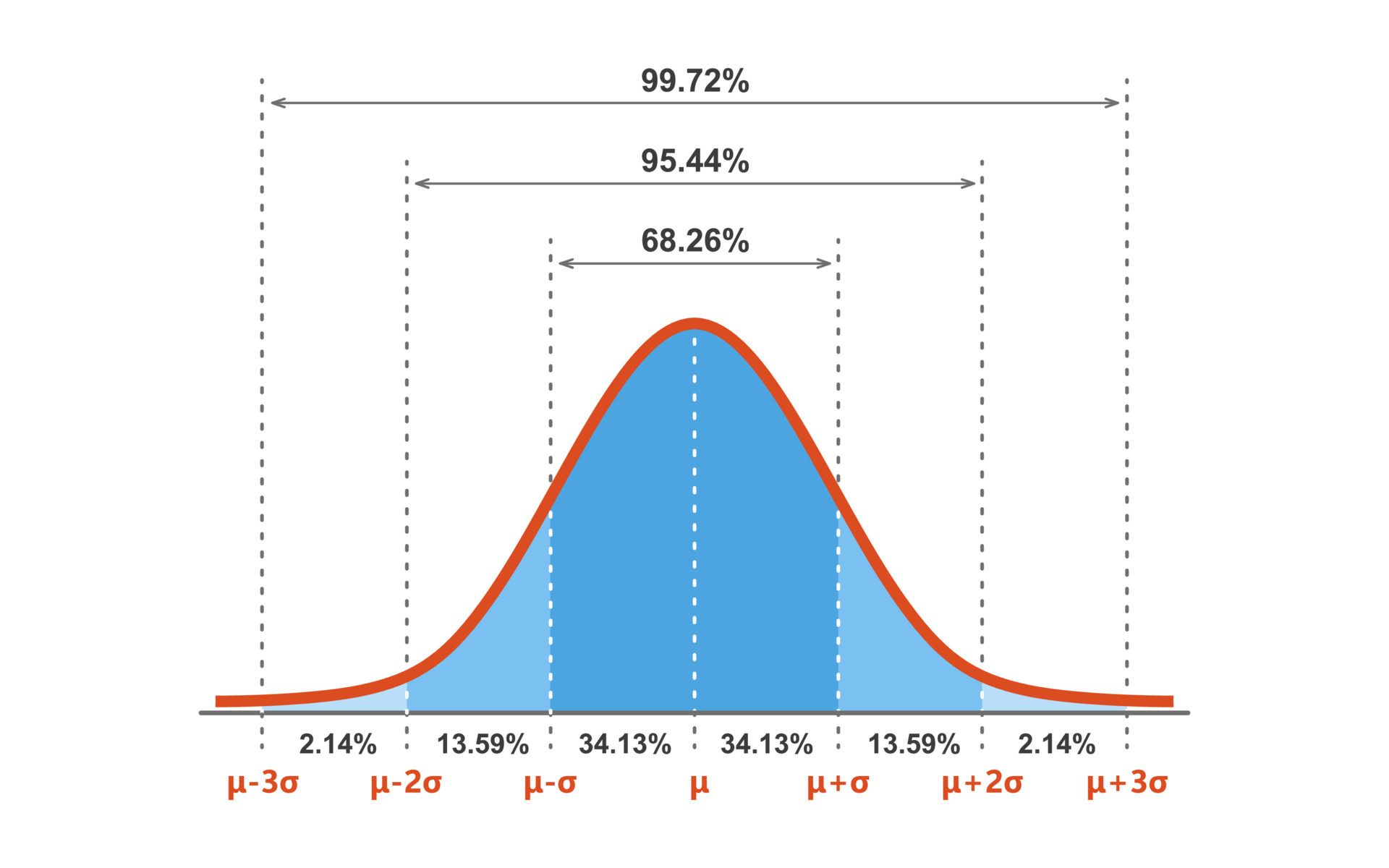
Gauss Distribution Standard Normal Distribution Gaussian Bell Graph Below is a probability distribution plot produced by statistical software that shows the same percentile along with a graphical representation of the corresponding area under the bell curve. the value is slightly different because we used a z score of 0.65 from the table while the software uses the more precise value of 0.667. Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean. the mean, median, and mode of a normal distribution are equal. the area under the normal curve is equal to 1.0 1.0. normal distributions are denser in the center and less dense in the tails. normal distributions are defined by two parameters, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ).

Statistical Bell Curve

Comments are closed.