Standard Normal Distribution Explained Youtube

Standard Normal Distribution Table Explained Youtube *** improved version of this video here: youtu.be tdlcbrlzbosi describe the standard normal distribution and its properties with respect to the perce. The normal, or gaussian, distribution is the most common distribution in all of statistics. here i explain the basics of how these distributions are created.

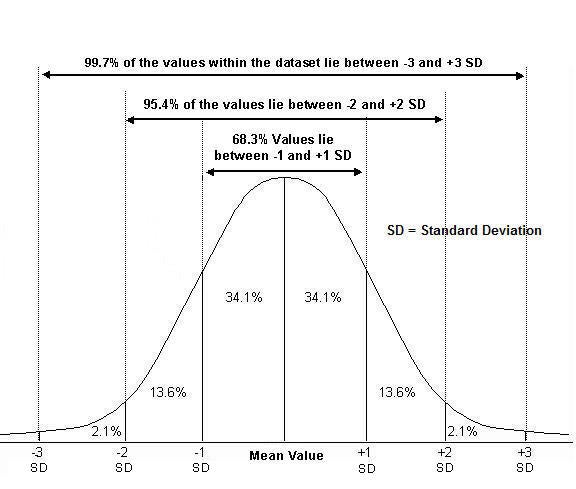
Standard Normal Distribution Explained Youtube Learn how to solve any normal probability distribution problem. this tutorial first explains the concept behind the normal distribution, then it discusses h. Step 1: calculate a z score. to compare sleep duration during and before the lockdown, you convert your lockdown sample mean into a z score using the pre lockdown population mean and standard deviation. a z score of 2.24 means that your sample mean is 2.24 standard deviations greater than the population mean. Height, birth weight, reading ability, job satisfaction, or sat scores are just a few examples of such variables. because normally distributed variables are so common, many statistical tests are designed for normally distributed populations. understanding the properties of normal distributions means you can use inferential statistics to compare. The values 50 – 6 = 44 and 50 6 = 56 are within one standard deviation from the mean 50. the z scores are –1 and 1 for 44 and 56, respectively. about 95% of the x values lie within two standard deviations of the mean. therefore, about 95% of the x values lie between –2σ = (–2) (6) = –12 and 2σ = (2) (6) = 12.

Normal Distribution And Use Of Standard Deviation Explained Youtube Height, birth weight, reading ability, job satisfaction, or sat scores are just a few examples of such variables. because normally distributed variables are so common, many statistical tests are designed for normally distributed populations. understanding the properties of normal distributions means you can use inferential statistics to compare. The values 50 – 6 = 44 and 50 6 = 56 are within one standard deviation from the mean 50. the z scores are –1 and 1 for 44 and 56, respectively. about 95% of the x values lie within two standard deviations of the mean. therefore, about 95% of the x values lie between –2σ = (–2) (6) = –12 and 2σ = (2) (6) = 12. The normal distribution is the most commonly used probability distribution in statistics. it has the following properties: symmetrical. bell shaped. mean and median are equal; both located at the center of the distribution. the mean of the normal distribution determines its location and the standard deviation determines its spread. A standard normal distribution is a specific type of normal distribution where: the mean is 0. the standard deviation is 1. this distribution is centered at zero, with most values falling within a few units of the mean. it is often used in scenarios where data needs to be standardized to make meaningful comparisons across different datasets.
Normal Distribution Explained Simply Part 2 Vrogue Co The normal distribution is the most commonly used probability distribution in statistics. it has the following properties: symmetrical. bell shaped. mean and median are equal; both located at the center of the distribution. the mean of the normal distribution determines its location and the standard deviation determines its spread. A standard normal distribution is a specific type of normal distribution where: the mean is 0. the standard deviation is 1. this distribution is centered at zero, with most values falling within a few units of the mean. it is often used in scenarios where data needs to be standardized to make meaningful comparisons across different datasets.

Comments are closed.