Solved Problems On Braggs Law
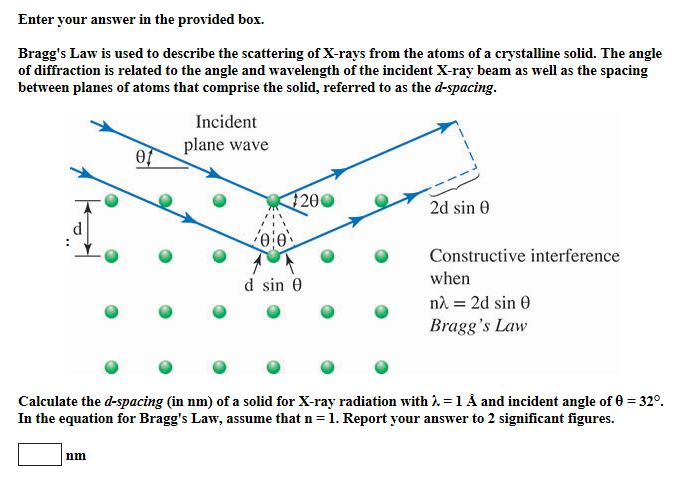
Solved Enter Your Answer In The Provided Box Bragg S Law Is Chegg Chapter 3 x ray diffraction. consider a crystal as made out of parallel planes of ions, spaced a distance d apart. the conditions for a sharp peak in the intensity of the scattered radiation are. bragg’s condition. bragg angle θ is just the half of the total angle 2 θ which the incident beam is deflected. Get engineering physics now with the o’reilly learning platform. o’reilly members experience books, live events, courses curated by job role, and more from o’reilly and nearly 200 top publishers. solved problems 1. a beam of x rays of wavelength 0.071 nm is diffracted by (110) plane of rock salt with lattice constant of 0.28 nm.
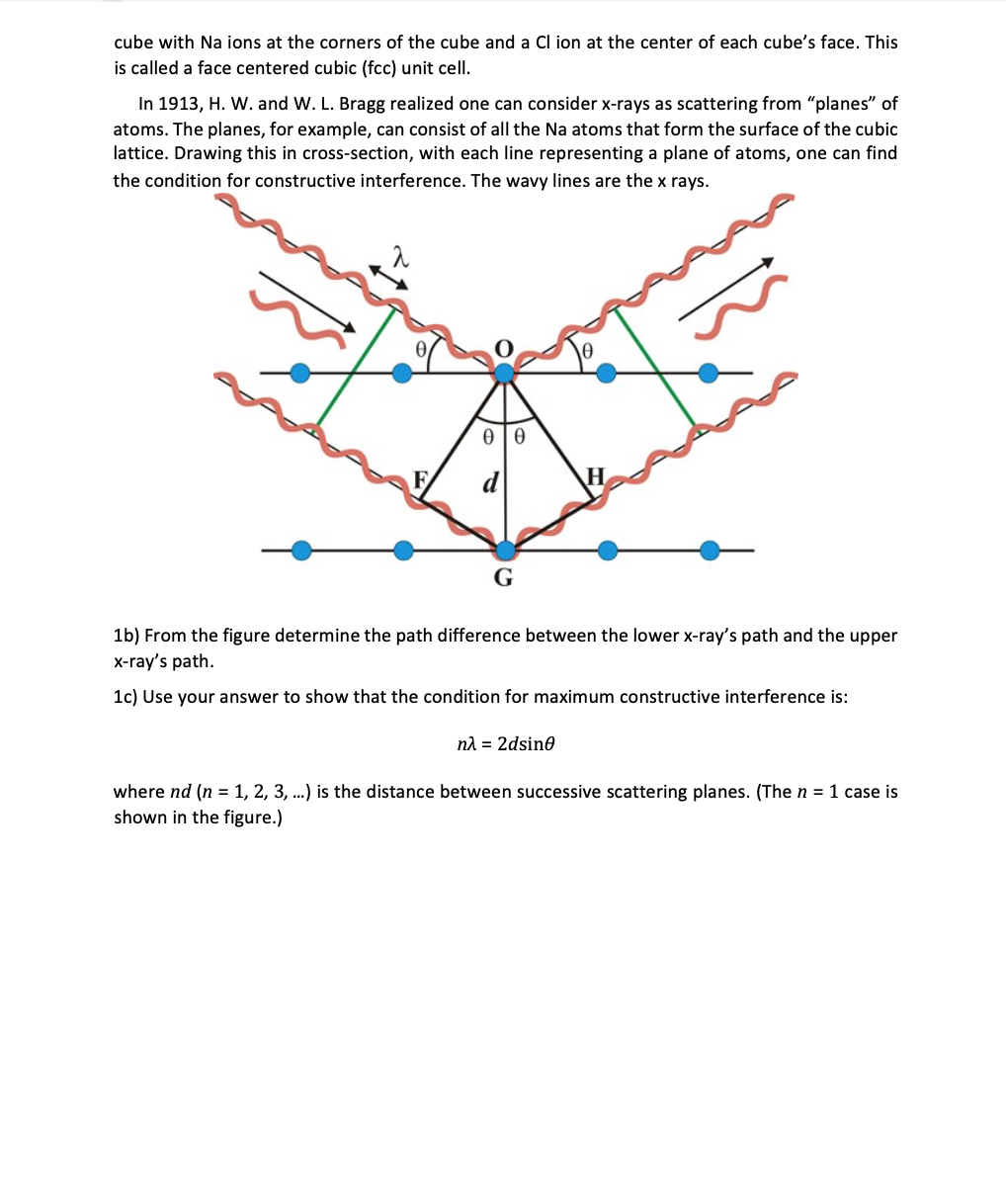
Solved X Ray Diffraction Bragg Scattering Bragg S Law Chegg Bragg equation. according to bragg equation: nλ = 2d sinΘ. therefore, according to the equation of bragg’s law: the equation explains why the faces of crystals reflect x ray beams at particular angles of incidence (Θ, λ). the variable d indicates the distance between the atomic layers, and the variable the variable d indicates the. Bragg's law. bragg's law is the result of experiments derived by physicist sir william lawrence bragg in 1912 and first presented on the same year to the cambridge philosophical society.\(^{[1]}\) william lawrence bragg and his father, sir william henry bragg, were awarded the nobel prize in physics in 1915 for their work in determining crystal structures beginning with nacl, zns, and diamond. The result is bragg’s law of diffraction: mλ = 2d sin θ, m = 1, 2, 3 …. (bragg's law) (7.1.1) if only two rows are involved, the transition from constructive to destructive interference as θ changes is gradual. however, if interference from many rows occurs, then the constructive interference peaks become very sharp with mostly. Sketch the reflection of incident radiation off atomic planes, and derive braggs’ law for this geometry. identify which planes produce x ray diffraction peaks in fcc and bcc crystals. given a graph of x ray intensity vs. angle, or the 2θ values of the diffraction peaks, determine the crystal structure and lattice constant of the sample.

Solved Bragg S Law For X Ray Diffraction Is 2d Sin9 Ma Chegg The result is bragg’s law of diffraction: mλ = 2d sin θ, m = 1, 2, 3 …. (bragg's law) (7.1.1) if only two rows are involved, the transition from constructive to destructive interference as θ changes is gradual. however, if interference from many rows occurs, then the constructive interference peaks become very sharp with mostly. Sketch the reflection of incident radiation off atomic planes, and derive braggs’ law for this geometry. identify which planes produce x ray diffraction peaks in fcc and bcc crystals. given a graph of x ray intensity vs. angle, or the 2θ values of the diffraction peaks, determine the crystal structure and lattice constant of the sample. The bragg law is 2dsinθ = nλ λ = 2dsinθ = 2×(0.282 nm)×sin7o = 0.069 nm (1) to find the minimum voltage v0, use duane hunt law that says that the kinetic energy of the electrons ev0 must be at least equal to the energy of the x ray photon hf: ev0 ≥hf = hc λ = 1240 ev −nm 0.069 nm = 18,000 ev (2) or v0 ≥18,000 volts (3) compton effect. Bragg's law is satisfied and diffraction is occurring. the meter indicates how well the phases of the two rays match. the small light on the meter is green when bragg's equation is satisfied and red when it is not satisfied. the meter can be observed while the three variables in bragg's are changed by clicking on the scroll bar arrows and by.

Solved Braggs Law Is Used To Describe The Scattering Of X Rays From The bragg law is 2dsinθ = nλ λ = 2dsinθ = 2×(0.282 nm)×sin7o = 0.069 nm (1) to find the minimum voltage v0, use duane hunt law that says that the kinetic energy of the electrons ev0 must be at least equal to the energy of the x ray photon hf: ev0 ≥hf = hc λ = 1240 ev −nm 0.069 nm = 18,000 ev (2) or v0 ≥18,000 volts (3) compton effect. Bragg's law is satisfied and diffraction is occurring. the meter indicates how well the phases of the two rays match. the small light on the meter is green when bragg's equation is satisfied and red when it is not satisfied. the meter can be observed while the three variables in bragg's are changed by clicking on the scroll bar arrows and by.

Comments are closed.