Secondary Consumers Definition Types And Examples

Secondary Consumers Definition Examples Video Lesson Transcript Spiders, snakes, and seals are all examples of carnivorous secondary consumers. omnivores are the other type of secondary consumer. they eat both plant and animal materials for energy. bears and skunks are examples of omnivorous secondary consumers that both hunt prey and eat plants. however, some omnivores are simply scavengers. Secondary consumers can be defined as a group of living organisms that mainly feed on primary consumers or herbivores to get energy. they are placed on the third trophic level in a food chain. some secondary consumers also feed on both producers and primary consumers. so, secondary consumers range from carnivores that consume meat to omnivores.
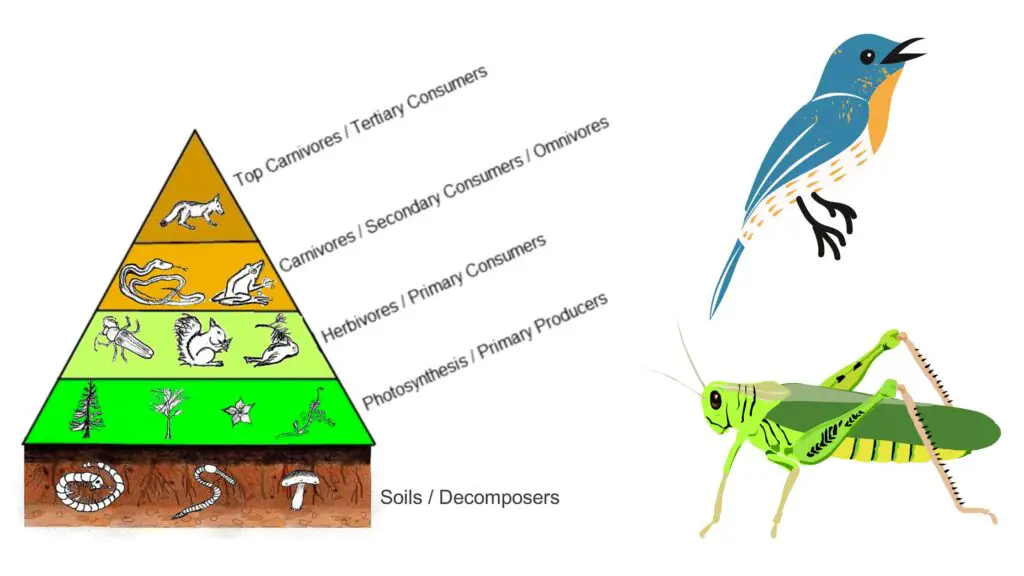
Secondary Consumers Definition Types Functions Examples Biology Definition of secondary consumers. secondary consumers are organisms that primarily feed on primary consumers, which are herbivores, in a food chain. they occupy the third trophic level and can be either carnivores, who eat only other animals, or omnivores, who consume both animal and plant matter. their role is vital in transferring energy. 1. examples of aquatic secondary consumers. aquatic environments are endowed with massive amounts of food sources. as such, they support numerous types of secondary consumers. piranha is a good example of aquatic omnivores. piranhas eat fish, birds, snails, and aquatic plants. smaller, less predatory sharks also qualify to be secondary consumers. Examples of secondary consumers include snakes, hawks, and lions. tertiary consumers. tertiary consumers are at the third trophic level. they are carnivores or predators that eat secondary consumers. these animals are even more significant than their prey. examples of tertiary consumers include bears and sharks. quaternary consumers. Secondary consumers are organisms that receive their energy from primary consumers. most secondary consumers are carnivores, meaning they survive by eating animal tissues. carnivores can be.

Comments are closed.