Scalar Projections Notes Teacher Notes
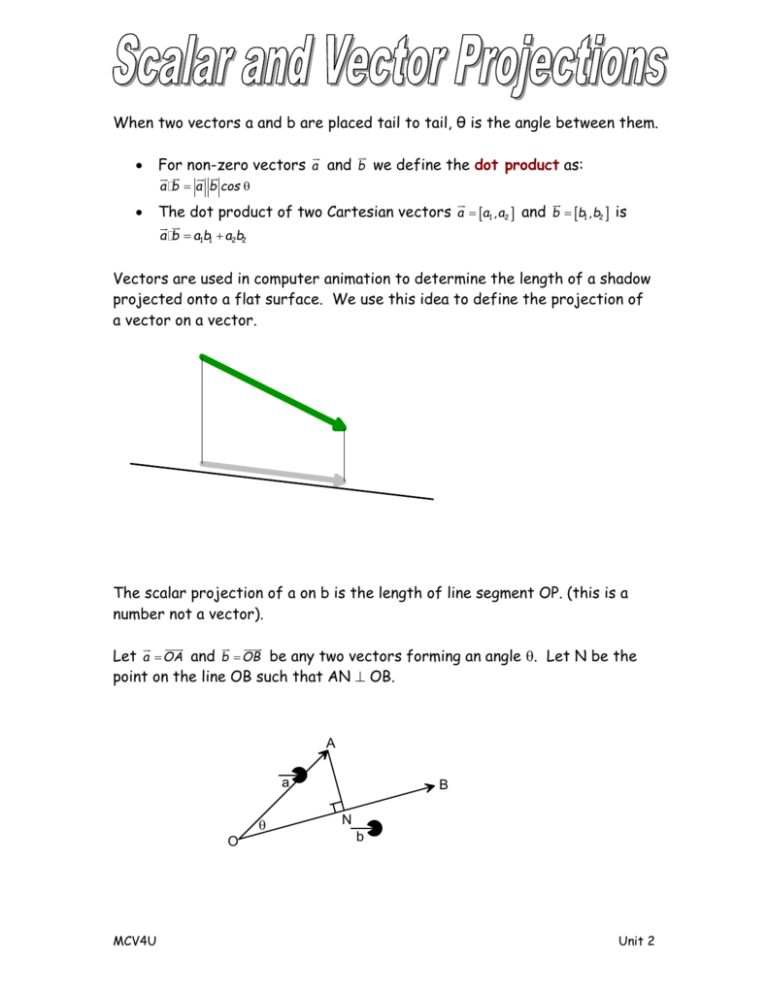
Scalar Projections Notes Teacher Notes Determine the scalar projection of the vector \(\ \vec{r}=\langle 27,39,52\rangle\) onto the direction of \(\ \vec{t}=\langle 44,26,17\rangle\). solution. the scalar projection of one vector onto the direction of the other is the dot product of the first vector with the unit vector representing the direction of the second vector. A scalar projection is given by the dot product of a vector with a unit vector for that direction. for example, the component notations for the vectors shown below are ab = 4, 3 and d = 3, − 1.25 . the scalar projection of vector ab onto ˆx is given by. → ab × ˆx = (4 ⋅ 1) (3 ⋅ 0) (0 ⋅ 0) = 4. the scalar projection of vector ab.
Scalar And Vector Projections Definition And Examples Scalar projections notes teacher notes. advertisement. when two vectors a and b are placed tail to tail, θ is the angle between them. . for non zero vectors a and b we define the dot product as: a b a b cos . . the dot product of two cartesian vectors a a1 ,a2 and b b1 ,b2 is. a b a1b1 a2b2. The scalar projection tells us the component of a vector ⃑ 𝐴 that points in the direction of another vector, ⃑ 𝐵. we may have already seen this in action, since the component form of a vector can be viewed as an application of scalar projection. we can see this by recalling that the unit vector in the direction of ⃑ 𝐵 is defined. Andymath is a free math website with the mission of helping students, teachers and tutors find helpful notes, useful sample problems with answers including step by step solutions, and other related materials to supplement classroom learning. if you have any requests for additional content, please contact andy at tutoring@andymath . he. In this lesson we’ll look at the scalar projection of one vector onto another (also called the component of one vector along another), and then we’ll look at the vector projection of one vector onto another. we’ll follow a very specific set of steps in order to find the scalar and vector projections of one vector onto another.

Analyzing Scalar And Vector Quantities Notes And Worksheets Tpt Andymath is a free math website with the mission of helping students, teachers and tutors find helpful notes, useful sample problems with answers including step by step solutions, and other related materials to supplement classroom learning. if you have any requests for additional content, please contact andy at tutoring@andymath . he. In this lesson we’ll look at the scalar projection of one vector onto another (also called the component of one vector along another), and then we’ll look at the vector projection of one vector onto another. we’ll follow a very specific set of steps in order to find the scalar and vector projections of one vector onto another. The definition of scalar projection is simply the length of the vector projection. when the scalar projection is positive it means that the angle between the two vectors is less than 90 ∘. when the scalar projection is negative it means that the two vectors are heading in opposite directions. the vector projection formula can be written two. A scalar projection is given by the dot product of a vector with a unit vector for that direction. when the scalar projection is positive, it means that the angle between the two vectors is less than 90 ∘. when the scalar projection is negative, it means that the two vectors are heading in opposite directions. for example, the component forms.
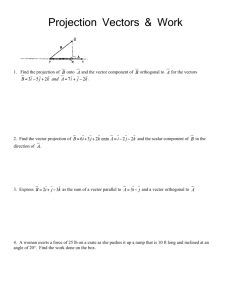
Vector Projections The definition of scalar projection is simply the length of the vector projection. when the scalar projection is positive it means that the angle between the two vectors is less than 90 ∘. when the scalar projection is negative it means that the two vectors are heading in opposite directions. the vector projection formula can be written two. A scalar projection is given by the dot product of a vector with a unit vector for that direction. when the scalar projection is positive, it means that the angle between the two vectors is less than 90 ∘. when the scalar projection is negative, it means that the two vectors are heading in opposite directions. for example, the component forms.

Mcq The Scalar Projection Of Vector 3i J 2k On Vector I 2j 3k Is

Comments are closed.