Scalar And Vector Projections Kristakingmath

How To Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of One Vector Onto In this lesson we’ll look at the scalar projection of one vector onto another (also called the component of one vector along another), and then we’ll look at the vector projection of one vector onto another. we’ll follow a very specific set of steps in order to find the scalar and vector projections of one vector onto another. My vectors course: kristakingmath vectors courselearn how to find the scalar projections and vector projections of a onto b. the scalar pro.
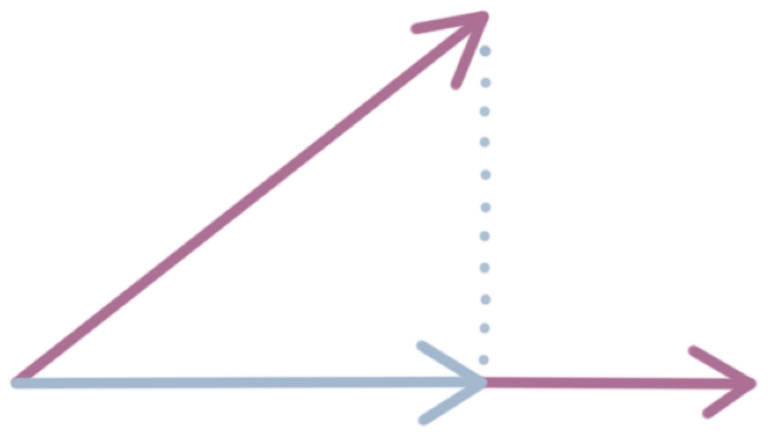
How To Find The Scalar And Vector Projections Of One Vector Onto Krista king’s math blog teaches you concepts from pre algebra through calculus 3. we’ll go over key topic ideas, and walk through each concept with example problems. Scalar triple product for coplanar vectors. vector functions and space curves. domain of the vector function. limit of the vector function. sketching the vector equation. projections of the curve. vector and parametric equations of a line segment. vector function for the curve of intersection of two surfaces. derivatives and integrals of vector. In this video i go over a quick review of the formulas for the scalar and vector projections of one vector onto another, as well as showing their visual repr. The scalar projection is tied to the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. as a result, the maximum scalar projection occurs when the vectors are aligned (cosine of 0° is 1), and the minimum when they are opposite (cosine of 180° is 1). vector projection non commutativity. unlike scalar projections, vector projections are not commutative.

Scalar And Vector Projections Kristakingmath Youtube In this video i go over a quick review of the formulas for the scalar and vector projections of one vector onto another, as well as showing their visual repr. The scalar projection is tied to the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. as a result, the maximum scalar projection occurs when the vectors are aligned (cosine of 0° is 1), and the minimum when they are opposite (cosine of 180° is 1). vector projection non commutativity. unlike scalar projections, vector projections are not commutative. The scalar projection is the magnitude of the vector projection. to calculate the scalar projection, square the components of the vector projection, add them and then square root. for example, if the vector projection is 3i 4j, then the scalar projection is √ (32 42) = 5. A scalar projection is given by the dot product of a vector with a unit vector for that direction. for example, the component notations for the vectors shown below are ab= 4,3 and d= 3,−1.25 . the scalar projection of vector ab onto \ (\ \hat {x}\) is given by. \ (\ \overrightarrow {a b} \times \hat {x}= (4 \cdot 1) (3 \cdot 0) (0 \cdot 0.

Comments are closed.