Salivary Gland Cancer Macmillan Cancer Support

Salivary Gland Cancer Macmillan Cancer Support Call the macmillan support line on 0808 808 00 00. chat to our specialists online. visit our head and neck cancer forum to talk with people who have been affected by head and neck cancer, share your experience, and ask an expert your questions. further support and information is available through the swallows. The salivary glands make saliva (spit). the biggest pairs of salivary glands are the parotid glands at the sides of the mouth, just in front of the ears. this is the most common place for salivary gland cancer to develop. tumours that develop in the salivary glands can be non cancerous (benign) but some are cancer.

Salivary Gland Cancer Macmillan Cancer Support Pleomorphic adenomas are the most common salivary gland tumour. they are considered benign but some of them develop into cancer which is what’s happened. you have a cancer inside a benign adenoma. the fact that it’s aggressive is neither here nor there. it’s what the histopathologist sees under his microscope. Salivary gland cancer uk. salivary gland cancer uk supports people with rare salivary gland cancers, such as adenoid cystic carcinoma, acc, and unknown carcinoma. macmillan is also here to support you. if you would like to talk, you can: call the macmillan support line on 0808 808 00 00. chat to our specialists online. Most salivary gland cancers occur in the parotid glands. those account for about 80% of all salivary gland cancer diagnoses. the next most frequent location is in the submandibular glands. the remainder usually occur in the minor salivary glands inside the mouth. the most common type of parotid gland cancer is called mucoepidermoid, followed by. New here, say hello stage 3 salivary gland cancer. new; head and neck cancer forum requires membership for participation click to join.
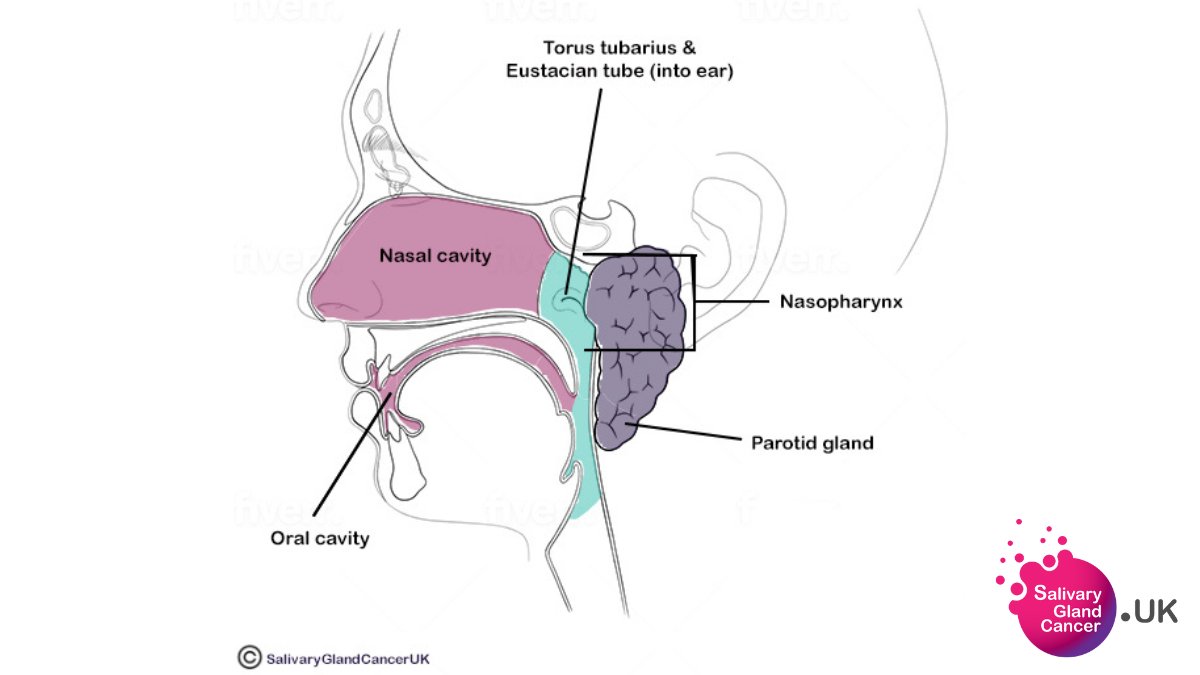
What Are Salivary Gland Cancers Salivary Gland Cancer Uk Most salivary gland cancers occur in the parotid glands. those account for about 80% of all salivary gland cancer diagnoses. the next most frequent location is in the submandibular glands. the remainder usually occur in the minor salivary glands inside the mouth. the most common type of parotid gland cancer is called mucoepidermoid, followed by. New here, say hello stage 3 salivary gland cancer. new; head and neck cancer forum requires membership for participation click to join. Cancer cells in a salivary gland can sometimes travel to the lung and grow there. when cancer cells do this, it’s called metastasis.to doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the salivary gland where it started. cancer is always named for the place where it starts. Salivary gland cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the salivary glands. being exposed to certain types of radiation may increase the risk of salivary gland cancer. signs and symptoms of salivary gland cancer include a lump or trouble swallowing. tests that examine the head, neck, and the inside of.
The Salivary Glands Canadian Cancer Society Vrogue Co Cancer cells in a salivary gland can sometimes travel to the lung and grow there. when cancer cells do this, it’s called metastasis.to doctors, the cancer cells in the new place look just like the ones from the salivary gland where it started. cancer is always named for the place where it starts. Salivary gland cancer is a rare disease in which malignant (cancer) cells form in the tissues of the salivary glands. being exposed to certain types of radiation may increase the risk of salivary gland cancer. signs and symptoms of salivary gland cancer include a lump or trouble swallowing. tests that examine the head, neck, and the inside of.

Comments are closed.