Retaining Walls Explained Types Forces Failure And Reinforcement
Retaining Walls Explained Types Forces Failure And Reinforcement The wall has basically 3 parts. stem, toe slab and heel slab. toe and heel slab make up for the foundation of the wall. some walls have a key provided in footing to prevent it from sliding. retaining wall drainage. the stem may be provided with drain holes with slope for the water drainage. In this video we will be learning about retaining wall. this video is divided into 4 parts. first we will learn about general types of retaining walls and it.
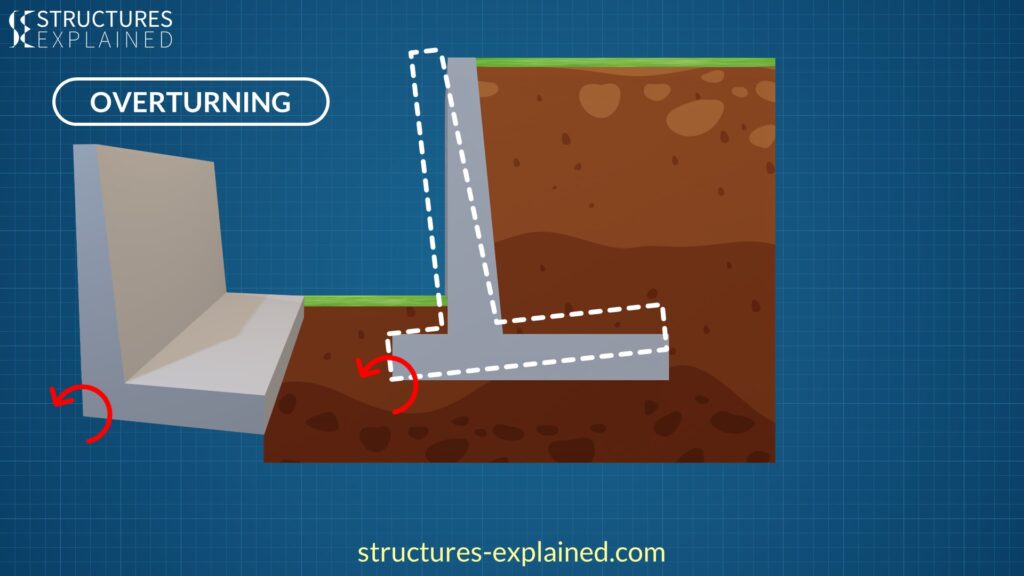
Retaining Walls Types And Failure Modes Revite Vrogue Co Types of retaining wall failures: to design retaining walls, it is necessary to define "failure" and to know how walls can fail. under static conditions, retaining walls are acted upon by body forces related to the mass of the wall, by soil pressures, and by external forces such as those transmitted by braces. Distressed cantilever wall in cincinnati, ohio is tilting about 10 degrees. it was buttressed by three steel h piles embedded in drilled piers and faced with masonry to “blend” in with the neighborhood’s many masonry walls (far right). note weepholes that aren’t weeping much. stacked crib walls placed too close to one another at a. A retaining wall is a structure that retains the sloped or vertical cut soil. the soil level is different on both sides of the walls. a retaining wall is subjected to horizontal load and hence designed for the same. the load acting on the wall depends upon the height of fill material, type of fill material, surcharge, water table and drainage. There are various types of loads and forces acting on retaining wall, which are: lateral earth pressure. surcharge loads. axial loads. wind on projecting stem. impact forces. seismic earth pressure. seismic wall self weight forces.

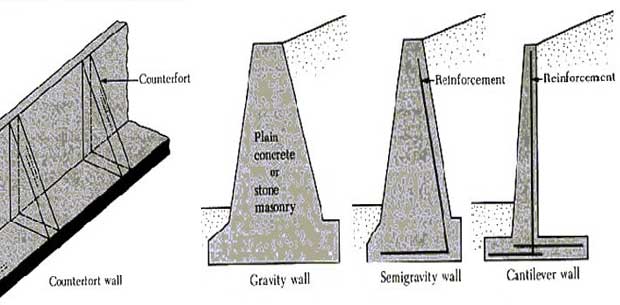
Retaining Walls Explained Types Forces Failure And Re Vrogue Co A retaining wall is a structure that retains the sloped or vertical cut soil. the soil level is different on both sides of the walls. a retaining wall is subjected to horizontal load and hence designed for the same. the load acting on the wall depends upon the height of fill material, type of fill material, surcharge, water table and drainage. There are various types of loads and forces acting on retaining wall, which are: lateral earth pressure. surcharge loads. axial loads. wind on projecting stem. impact forces. seismic earth pressure. seismic wall self weight forces. Each type is designed to suit the specific needs of a project according to the site conditions. the four main types of retaining walls are gravity retaining walls, cantilever retaining walls, embedded retaining walls, and reinforced soil retaining walls. the types of retaining walls you should choose for your project depend on a number of. Backfilling: as the blocks are stacked, the voids behind the wall are typically filled with granular material to provide drainage and stability. applications: retaining walls: srws are commonly used for creating retaining walls to stabilize slopes, prevent erosion, and support changes in elevation.

Comments are closed.