Respiratory Zone Structures A Diagrammatic View Of Re Vrogue Co
Respiratory Zone Structures A Diagrammatic View Of Re Vrogue Co The respiratory zone of the lungs is where gas exchange occurs. it comprises the smallest and most distal respiratory bronchioles, alveolar ducts, and alveoli. these structures are intimately associated with the pulmonary capillaries, facilitating the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide between the air and blood. Figure 22.2.1 22.2. 1: major respiratory structures the major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. the conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the organs and structures not directly involved in gas exchange.

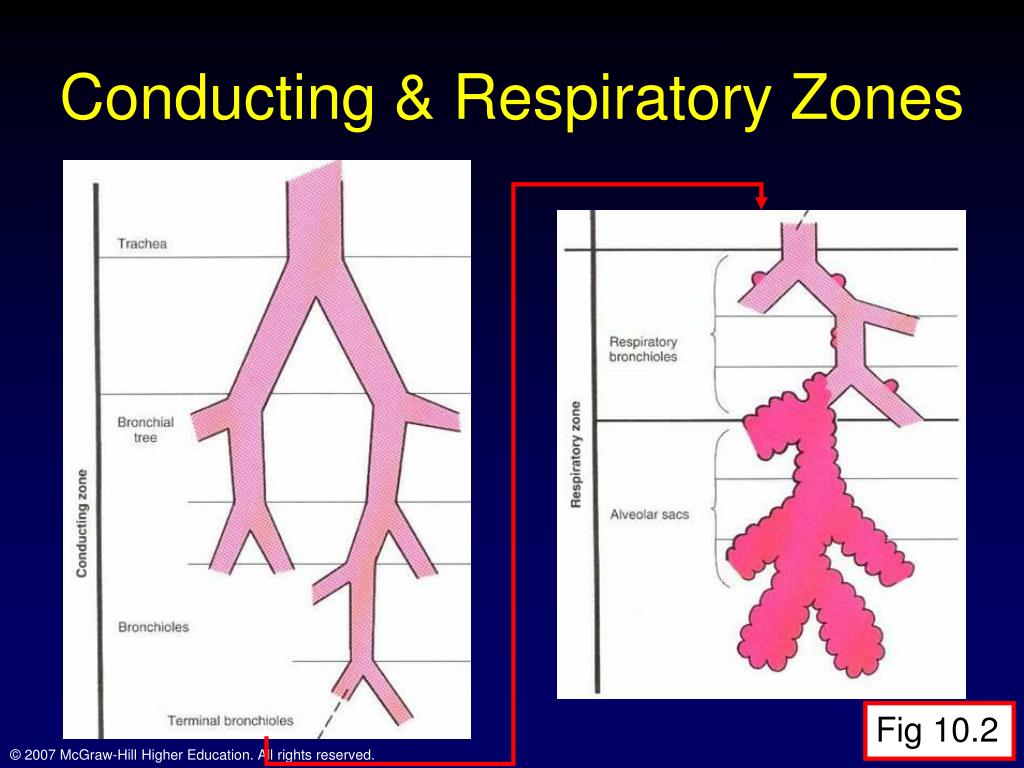
Respiratory Zone Structures A Diagrammatic View Of Re Vrogue Co Respiratory zone. in contrast to the conducting zone, the respiratory zone includes structures that are directly involved in gas exchange. the respiratory zone begins where the terminal bronchioles join a respiratory bronchiole, the smallest type of bronchiole (figure 22.10), which then leads to an alveolar duct, opening into a cluster of alveoli. Figure 1. the major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. the conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the organs and structures not directly involved in gas exchange. the gas exchange occurs in the respiratory zone. Figure \(\pageindex{1}\): major respiratory structures. the major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. (image credit: "major respiratory organs" by openstax is licensed under cc by 3.0) functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. The major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. the conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the organs and structures not directly involved in gas exchange. the gas exchange occurs in the respiratory zone.

Functional Anatomy Of The Respiratory System Anatomia Vrogue Co Figure \(\pageindex{1}\): major respiratory structures. the major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. (image credit: "major respiratory organs" by openstax is licensed under cc by 3.0) functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. The major respiratory structures span the nasal cavity to the diaphragm. functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into a conducting zone and a respiratory zone. the conducting zone of the respiratory system includes the organs and structures not directly involved in gas exchange. the gas exchange occurs in the respiratory zone. A bronchial tree (or respiratory tree) is the collective term used for these multiple branched bronchi. the main function of the bronchi, like other conducting zone structures, is to provide a passageway for air to move into and out of each lung. in addition, the mucous membrane traps debris and pathogens. Osmosis high yield notes. this osmosis high yield note provides an overview of anatomy and physiology of the respiratory system essentials. all osmosis notes are clearly laid out and contain striking images, tables, and diagrams to help visual learners understand complex topics quickly and efficiently. find more information about anatomy and.

Comments are closed.