Respiratory Anatomy In The Lab
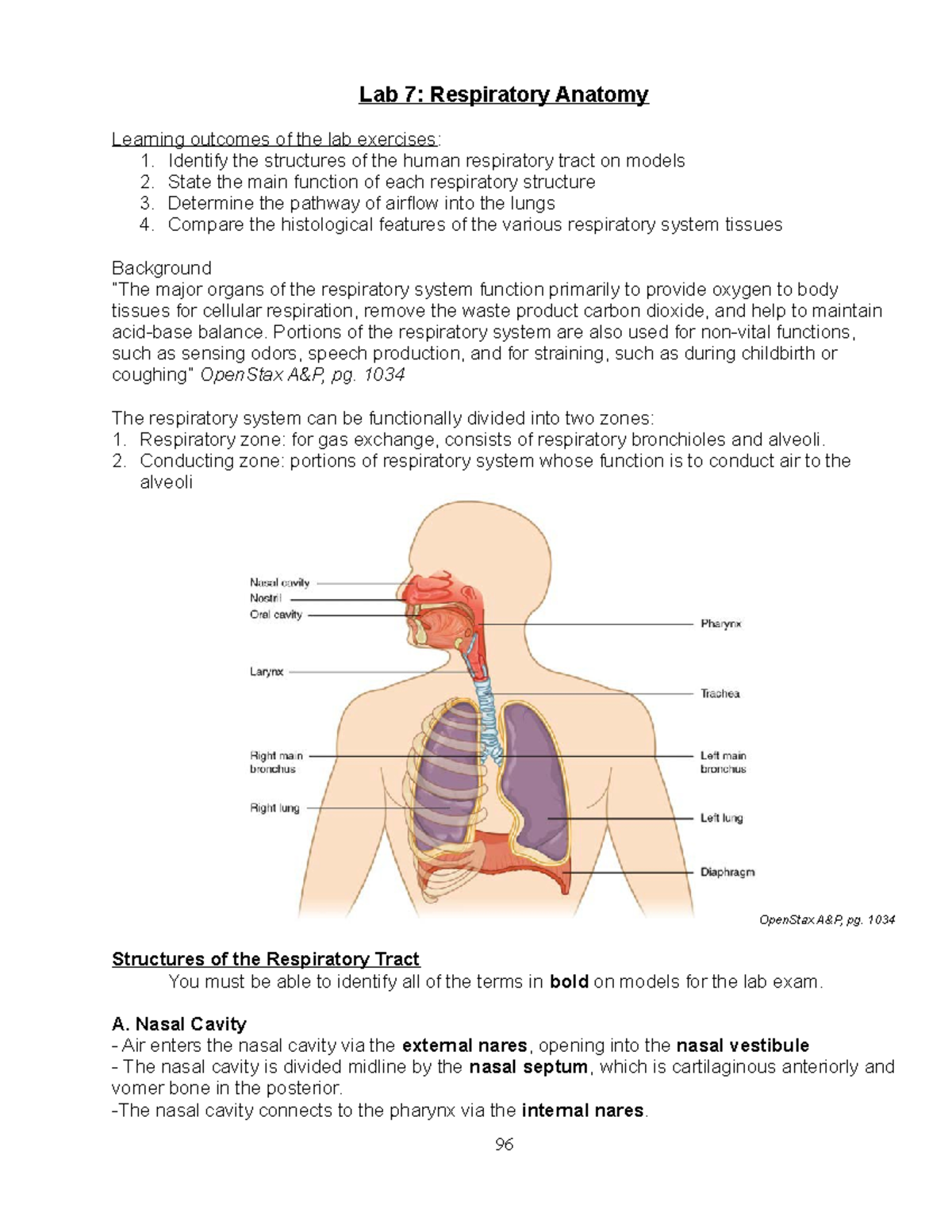
Ap2 Lab7 Anatomy Of The Respiratory System Lab Sp21 Lab 7 Normal quiet breathing moves approximately 500 ml of air into and out of the lungs with each breath. inspiratory reserve volume. the amount of air that can be taken in forcibly over the tidal volume is the inspiratory reserve volume, which is normally between 2100 ml to 3200 ml. expiratory reserve volume. Human respiratory anatomy shown using mostly models. structures include: nostrils (nares), nasal cavity, conchae (each concha described and shown), paranas.
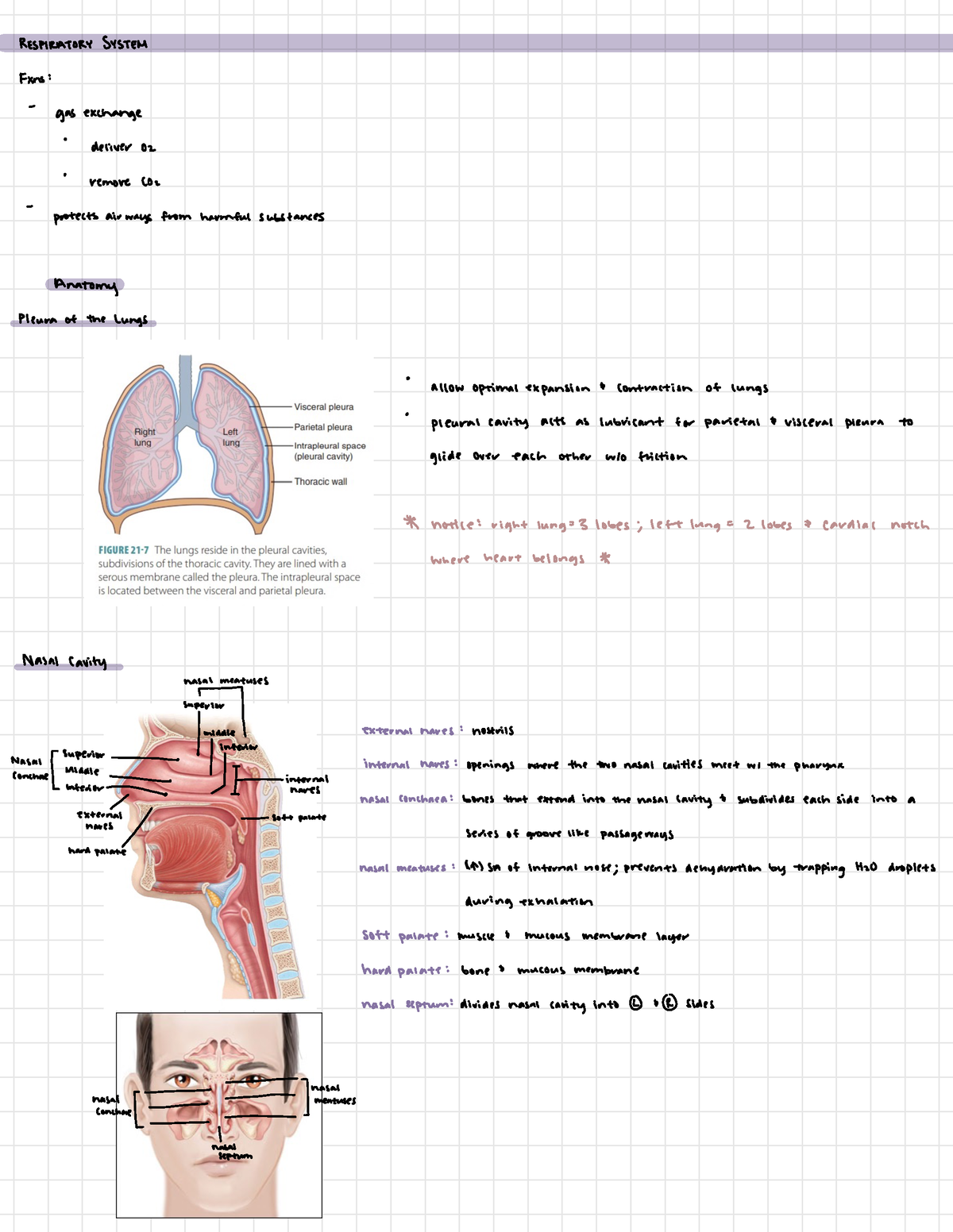
Lab 5 Respiratory Anatomy Physiology Respiratorysystem Fxns Gas The respiratory system, also called the pulmonary system, consists of several organs that function as a whole to oxygenate the body through the process of respiration (breathing). this process involves inhaling air and conducting it to the lungs where gas exchange occurs, in which oxygen is extracted from the air, and carbon dioxide expelled. Functionally, the respiratory system can be divided into the conducting zone, terminating at the terminal bronchioles; then air flows into the respiratory zone, where the actual gas exchange occurs. though we view each system individually in this lab, it is important to keep in mind that all organ systems overlap and work together in such a way. Introduction: breathing is an involuntary event. humans, when they are not exerting themselves, breathe approximately 15 times per minute on average. the primary function of the respiratory system is to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body’s tissues and remove carbon dioxide, a cell waste product. The cells of the human body require a constant stream of oxygen to stay alive. the respiratory system provides oxygen to the body's cells while removing carbon dioxide, a waste product that can be lethal if allowed to accumulate. there are 3 major parts of the respiratory system: the airway, the lungs, and the muscles of respiration.

Anatomy Lab Respiratory System 5 Diagram Quizlet Introduction: breathing is an involuntary event. humans, when they are not exerting themselves, breathe approximately 15 times per minute on average. the primary function of the respiratory system is to deliver oxygen to the cells of the body’s tissues and remove carbon dioxide, a cell waste product. The cells of the human body require a constant stream of oxygen to stay alive. the respiratory system provides oxygen to the body's cells while removing carbon dioxide, a waste product that can be lethal if allowed to accumulate. there are 3 major parts of the respiratory system: the airway, the lungs, and the muscles of respiration. The organs of the respiratory system form a continuous system of passages called the respiratory tract, through which air flows into and out of the body. the respiratory tract has two major divisions: the upper respiratory tract and the lower respiratory tract. the organs in each division are shown in figure 16.2.2 16.2. The structures of the upper respiratory system, or respiratory tract, allow us to breathe and speak. the nose and nasal cavities provide airways for respiration. the paranasal sinuses surround the nasal cavities. the pharynx connects the nasal and oral cavities to the larynx and esophagus. the larynx and vocal cords allow us to breathe and talk.

Comments are closed.