Resonant Rlc Circuits

Series Resonance In A Series Rlc Resonant Circuit Electrical Academia In complex form, the resonant frequency is the frequency at which the total impedance of a series rlc circuit becomes purely “real”, that is no imaginary impedance’s exist. this is because at resonance they are cancelled out. so the total impedance of the series circuit becomes just the value of the resistance and therefore: z = r. The resonance of a series rlc circuit occurs when the inductive and capacitive reactances are equal in magnitude but cancel each other because they are 180 degrees apart in phase. the sharp minimum in impedance which occurs is useful in tuning applications. the sharpness of the minimum depends on the value of r and is characterized by the "q.
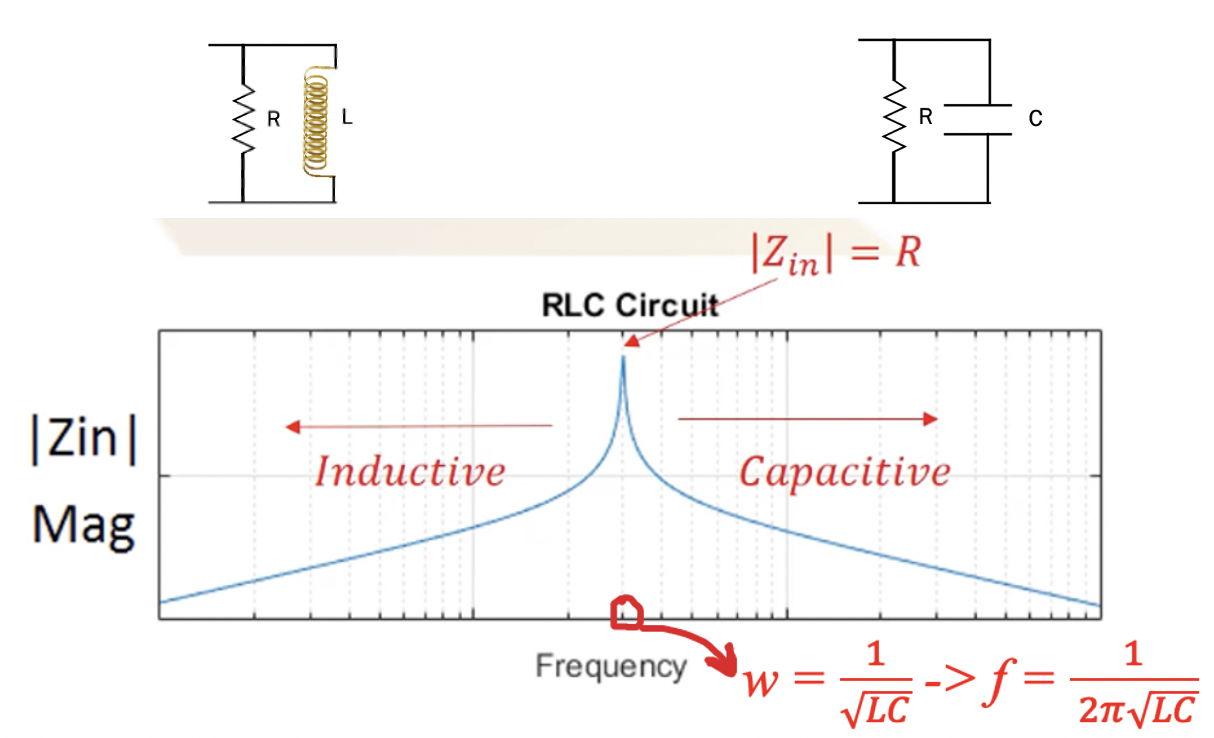
Understanding Rlc Resonance Circuit In Series And Parallel Rahsoft The resonant frequency for a rlc circuit is calculated from equation 15.6.5, which comes from a balance between the reactances of the capacitor and the inductor. since the circuit is at resonance, the impedance is equal to the resistor. then, the peak current is calculated by the voltage divided by the resistance. solution. The resonant frequency for a driven rlc circuit is the same as a circuit in which there is no damping, hence undamped resonant frequency. the resonant frequency peak amplitude, on the other hand, does depend on the value of the resistor and is described as the damped resonant frequency. The shock absorber damps the motion and dissipates energy, analogous to the resistance in an rlc circuit. the mass and spring determine the resonant frequency. a pure lc circuit with negligible resistance oscillates at \(f 0\), the same resonant frequency as an rlc circuit. it can serve as a frequency standard or clock circuit—for example, in. • therefore at the resonant frequency the impedance seen by the source is purely resistive. • this implies that at resonance the inductor capacitor combination acts as a short circuit. • the current flowing in the system is in phase with the source voltage. the power dissipated in the rlc circuit is equal to the power dissipated by the.

Comments are closed.