Protein Folding Mechanism
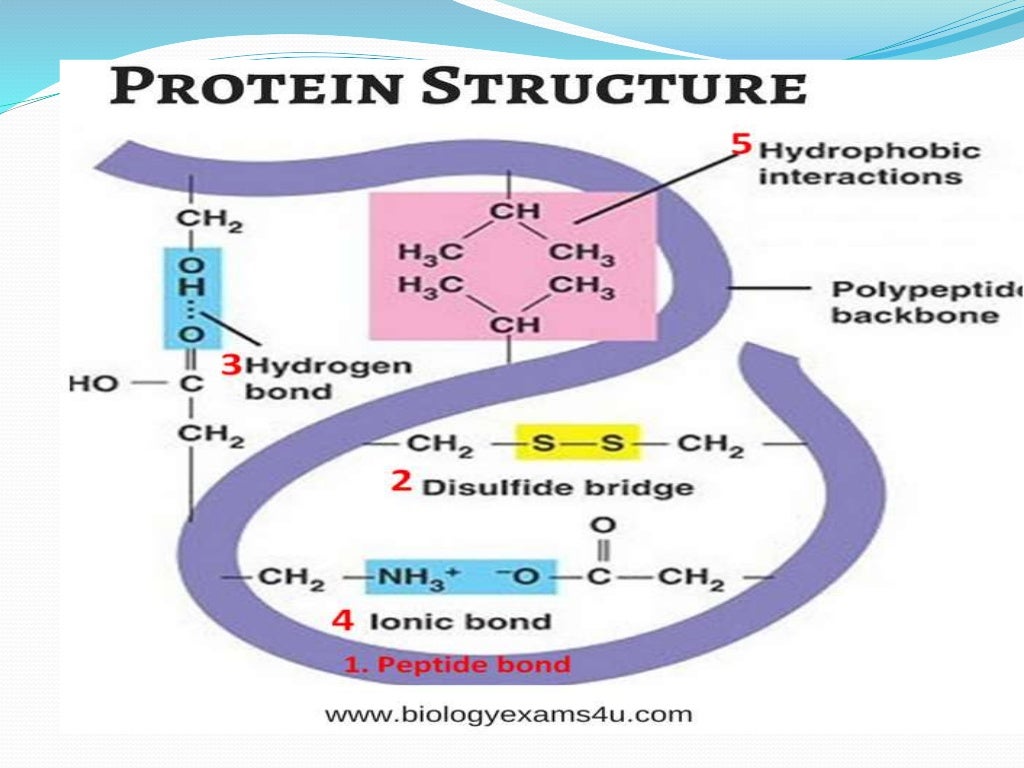
Protein Folding Mechanism Taking into account that er must manage folding and modification of proteins in concentrations surpassing 100 mg ml , recognition of unfolded proteins must be a highly precise mechanism to initiate the correct cellular response. additionally, other mechanisms constitute a stress adaptation pathway that could reestablish homeostasis of proteins. Protein folding. protein folding is the physical process by which a protein, after synthesis by a ribosome as a linear chain of amino acids, changes from an unstable random coil into a more ordered three dimensional structure. this structure permits the protein to become biologically functional.

Molecular Mechanism Of Protein Folding In The Cell Cell Predicting how proteins fold into specific native structures remains challenging. here, the authors develop a simple physical model that accurately predicts protein folding mechanisms, paving the. Examples of proteins with sh2 domains include protein tyrosine kinases (ptks), phosphatases (ptpases), a subunit of phospholipase c (plc‐γ1), the p85 subunit of phosphatidylinositol‐3oh kinase, the cytoplasmic tail of cell surface receptor proteins, and adaptor proteins like grb2; however, as of this writing, the total number of sh2‐containing proteins is well over 1100 according to the. Modern experimental kinetics of protein folding began in the early 1990s with the introduction of nanosecond laser pulses to trigger the folding reaction, providing an almost 106 fold improvement in time resolution over the stopped flow method being employed at the time. these experiments marked the beginning of the “fast folding” subfield that enabled investigation of the kinetics of. Folding mechanisms in lattices can also be distinctly tuned through design of sequences with different local and nonlocal content. 13 these simulations suggest that even if we have the computational power to sample all possible conformations for a real protein, the problem of protein structure stability prediction boils down to the precise estimation of noncovalent energetics that hold the.

Protein Folding Mechanism Modern experimental kinetics of protein folding began in the early 1990s with the introduction of nanosecond laser pulses to trigger the folding reaction, providing an almost 106 fold improvement in time resolution over the stopped flow method being employed at the time. these experiments marked the beginning of the “fast folding” subfield that enabled investigation of the kinetics of. Folding mechanisms in lattices can also be distinctly tuned through design of sequences with different local and nonlocal content. 13 these simulations suggest that even if we have the computational power to sample all possible conformations for a real protein, the problem of protein structure stability prediction boils down to the precise estimation of noncovalent energetics that hold the. While this may largely be true for most cellular proteins, o’brien et al. demonstrate that protein segments that are prone to be misfolded tend to fold correctly if they have higher rates of codon translation , suggesting that a much more sophisticated orchestration of mechanisms underlie co translational folding of proteins. the co translational protein folding occurs in eukaryotes due to a. The protein folding pathway depends on the same foldon units and foldon–foldon interactions that construct the native structure. keywords: protein folding, hydrogen exchange, protein structure. proteins must fold to their active native state when they emerge from the ribosome and when they repeatedly unfold and refold during their lifetime (1.

Folding Proteins Feel The Heat And Cold While this may largely be true for most cellular proteins, o’brien et al. demonstrate that protein segments that are prone to be misfolded tend to fold correctly if they have higher rates of codon translation , suggesting that a much more sophisticated orchestration of mechanisms underlie co translational folding of proteins. the co translational protein folding occurs in eukaryotes due to a. The protein folding pathway depends on the same foldon units and foldon–foldon interactions that construct the native structure. keywords: protein folding, hydrogen exchange, protein structure. proteins must fold to their active native state when they emerge from the ribosome and when they repeatedly unfold and refold during their lifetime (1.

Ijms Free Full Text Protein Folding And Mechanisms Of Proteostasis

Comments are closed.