Projection Of A Vector On A Line Definition And Examples
Vector Projection At Vectorified Collection Of Vector Projection In this article, we are going to discuss the projection of a vector on a line with many solved examples. what is meant by projection of a vector on a line? assume that the vector ab makes an angle θ with the directed line, say “l” in the anti clock direction as shown in the figure. thus, the projection of vector ab on the directed line. The vector projection is a scalar value. the vector projection of one vector over another is obtained by multiplying the given vector with the cosecant of the angle between the two vectors. vector projection has numerous applications in physics and engineering, for representing a force vector with respect to another vector.

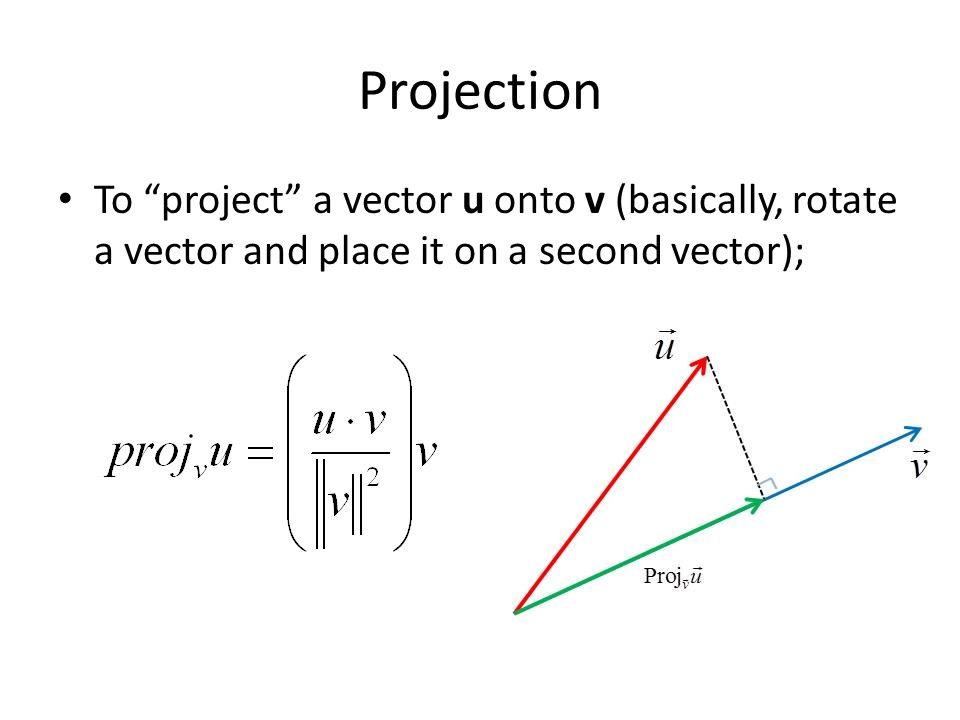
Projection Of A Vector On A Line Definition And Examples Vector projection. the vector projection (also known as the vector component or vector resolution) of a vector a on (or onto) a nonzero vector b is the orthogonal projection of a onto a straight line parallel to b. the projection of a onto b is often written as or a∥b. the vector component or vector resolute of a perpendicular to b, sometimes. The vector projection formula derivation is discussed below: let us assume, op = \vec a a and oq = \vec b b and the angle between op and oq is θ. drawn pn perpendicular to oq. in the right triangle opn, cos θ = on op. ⇒ on = op cos θ. ⇒ on = | \vec a a| cos θ. on is the projection vector of \vec a a on \vec b b. The vector projection is of two types: scalar projection that tells about the magnitude of vector projection and the other is the vector projection which says about itself and represents the unit vector. if the vector veca is projected on vecb then vector projection formula is given below: \ [\large proj {b}\,a=\frac {\vec {a}\cdot\vec {b. The projection of a given point on the line is a vector located on the line, that is closest to (in euclidean norm). this corresponds to a simple optimization problem: this particular problem is part of a general class of optimization problems known as least squares. it is also a special case of a euclidean projection on a general set. example.

Projection Vector Formula Definition Derivation Example The vector projection is of two types: scalar projection that tells about the magnitude of vector projection and the other is the vector projection which says about itself and represents the unit vector. if the vector veca is projected on vecb then vector projection formula is given below: \ [\large proj {b}\,a=\frac {\vec {a}\cdot\vec {b. The projection of a given point on the line is a vector located on the line, that is closest to (in euclidean norm). this corresponds to a simple optimization problem: this particular problem is part of a general class of optimization problems known as least squares. it is also a special case of a euclidean projection on a general set. example. A projection on a vector space is a linear operator such that . when has an inner product and is complete, i.e. when is a hilbert space, the concept of orthogonality can be used. a projection on a hilbert space is called an orthogonal projection if it satisfies for all . The vector projection of a vector a on a nonzero vector b is the orthogonal projection of a onto a straight line parallel to b. vector projection formula the vector projection of a on b is the unit vector of b by the scalar projection of a on b :.

Comments are closed.