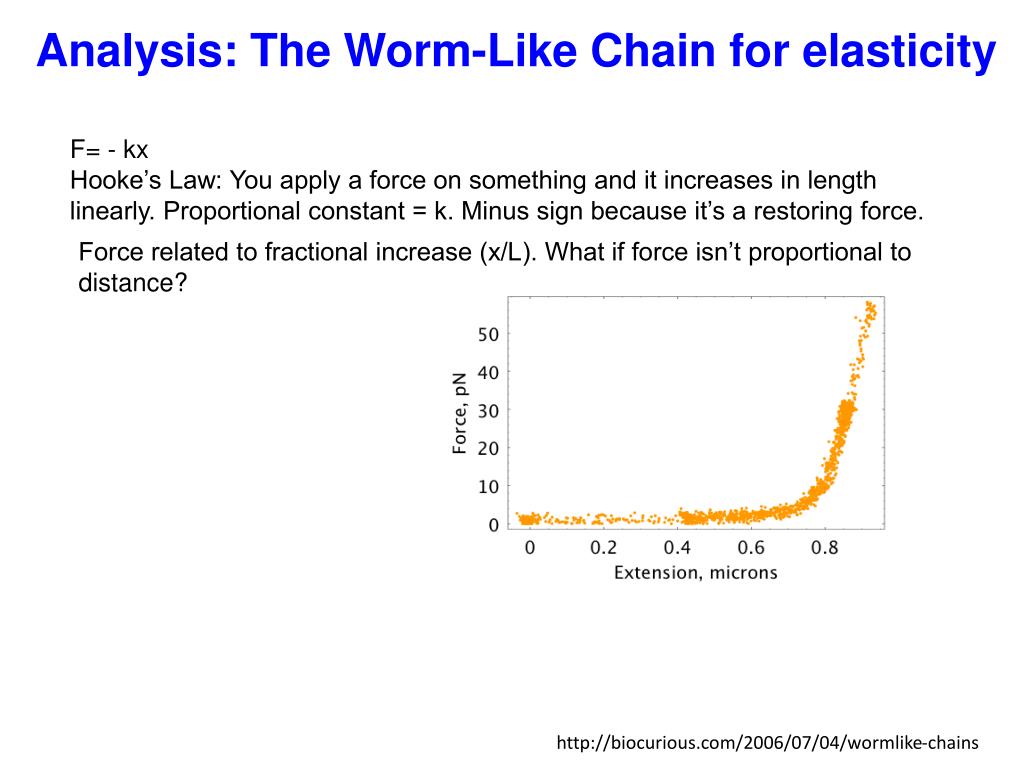
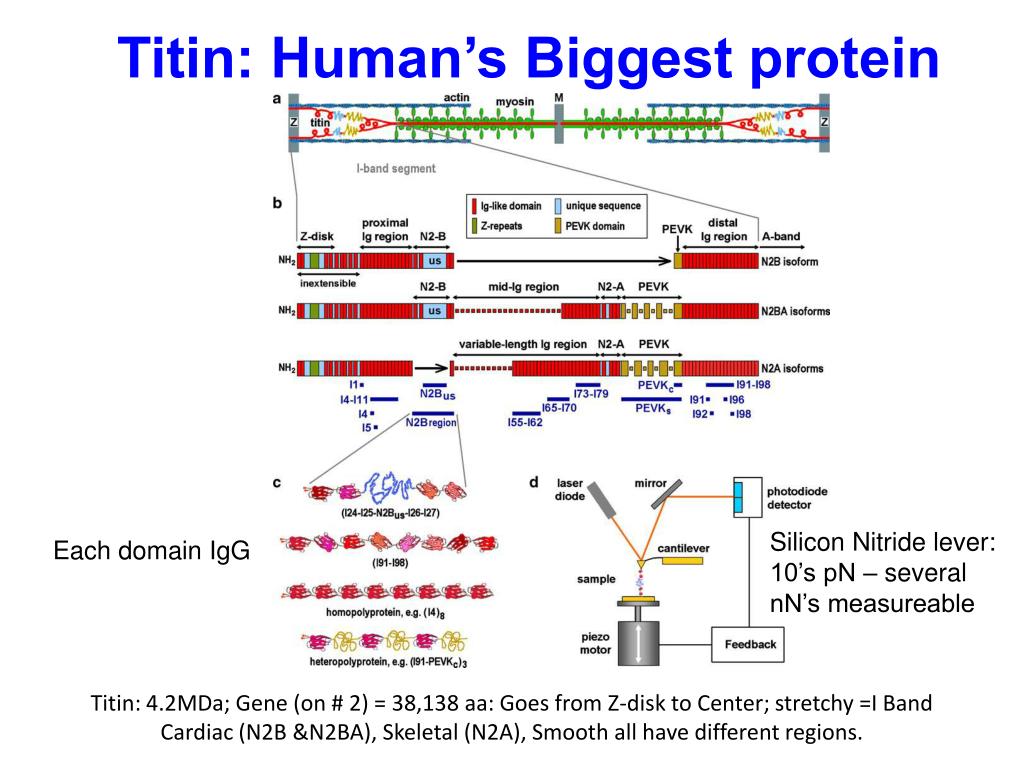
Ppt Experimental Protein Folding Atomic Force Microscopy Powerpoint

Ppt Experimental Protein Folding Atomic Force Microscopy Powerpoint Experimental protein folding atomic force microscopy. muller, biochemistry, 2008. extracellular surface of cx26 gap junction hemichannels. in the presence of ca 2 , the hemichannel surface structures moved radially to close the channel entrance. slideshow 2621312 by nedra. Sonu bishnoi. follow. atomic force microscopy (afm) works by scanning a probe over a sample surface to build up a topographic map with single atom level resolution without the need for sample preparation. it was invented in 1986 by binning and first used a cantilever with a diamond tip. the main components are a microscope stage to move the tip.
Ppt Experimental Protein Folding Atomic Force Microscopy Powerpoint Experimental protein folding atomic force microscopy. experimental protein folding atomic force microscopy. muller, biochemistry, 2008. extracellular surface of cx26 gap junction hemichannels. in the presence of ca 2 , the hemichannel surface structures moved radially to close the channel entrance. 290 views • 5 slides. Force spectroscopy with afm has been applied to a number of proteins to study their mechanical properties, in particular to proteins that support forces such as extracellular, cytoskeletal and blood proteins, like filamin, talin and the von willebrand factor, but also to membrane proteins [ 20 23 ]. C. chemist sohaib. atomic force microscopy (afm) was developed in 1986 as an extension of scanning tunneling microscopy to image non conductive surfaces. afm uses a sharp probe at the end of a flexible cantilever to measure the tiny forces between the probe and sample surface. as the probe scans the surface, these interatomic forces cause the. The document summarizes atomic force microscopy (afm). afm was invented in 1985 and works by scanning a probe tip across a sample surface while monitoring interatomic forces. afm can be used to create high resolution topographic images of samples without extensive preparation. it has advantages over other techniques as it can image samples in.
Ppt Experimental Protein Folding Atomic Force Microscopy Powerpoint C. chemist sohaib. atomic force microscopy (afm) was developed in 1986 as an extension of scanning tunneling microscopy to image non conductive surfaces. afm uses a sharp probe at the end of a flexible cantilever to measure the tiny forces between the probe and sample surface. as the probe scans the surface, these interatomic forces cause the. The document summarizes atomic force microscopy (afm). afm was invented in 1985 and works by scanning a probe tip across a sample surface while monitoring interatomic forces. afm can be used to create high resolution topographic images of samples without extensive preparation. it has advantages over other techniques as it can image samples in. Abstract. since its invention in 1986, the atomic force microscope (afm) has emerged as a flexible and powerful tool for exploring a variety of biological processes, including cell adhesion, protein folding, and protein–protein interactions. this review focuses on the application of the afm to studies of protein–protein interactions. Abstract. this review is focused on the atomic force microscopy (afm) capabilities to study the properties of protein biomolecules and to detect the proteins in solution. the possibilities of application of a wide range of measuring techniques and modes for visualization of proteins, determination of their stoichiometric characteristics and.

Comments are closed.