Paulings Rules Radius Ratio Polyhedron Coordination Numbers

Ppt Lecture 4 Chapter 13 In Perkins Crystal Chemistry Part 3 His studies found that crystal structures obey the following rules, now known as pauling's rules. rule 1. around every cation, a coordination polyhedron of anions forms, in which the cation anion distance is determined by the radius sums and the coordination number is determined by the radius ratio. The radius ratio rules are a first approximation which have some success in predicting coordination numbers, but many exceptions do exist. [3] in a set of over 5000 oxides, only 66% of coordination environments agree with pauling's first rule. oxides formed with alkali or alkali earth metal cations that contain multiple cation coordinations are.
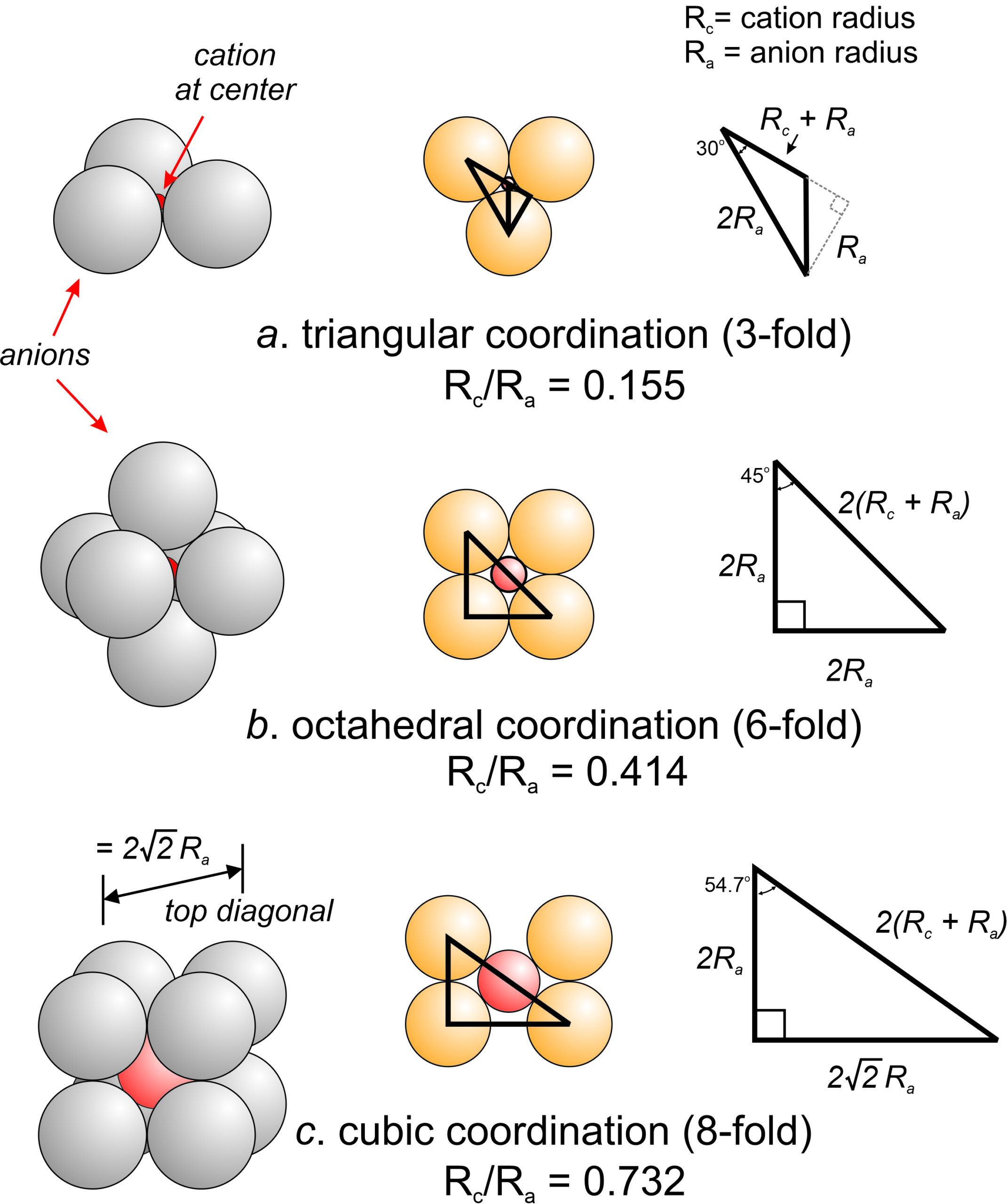
13 Crystal Structures Mineralogy Pauling noticed that size determines cn (rule #1). in the coordination polyhedron of anions about each cation, the cation anion distance is constrained by the radius sum and the coordination number of the cation is controlled by the radius ratio. ex: mg:o .72 1.36 = .53 therefore 6 c.n. Or may be absent altogether. coordination polyhedra are constrained by coordination numbers, but only uniquely determined by radius ratios and the type of bonding in a mineral. radius ratio coordination number ionic polyhedra covalent polyhedra 0 ∞ 2 line 0.155 ∞ 3 triangle 0.225 ∞ 4 tetrahedron 0.414 ∞ 4 square. Rule #1 a coordinated polyhedron of anions is formed about each cation, the cation anion distance equaling the sum of their characteristic packing radii and the coordination polyhedron being determined by the radius ratio. • pauling’s model treats the anions and cations of a crystal as if they were hard spheres packed so tightly together. Definition: pauling’s rules. rule 1.radius ratio principle: cation anion distances are equal to the sum of their effective ionic radii, and cation coordination numbers are determined by the ratio of cation to anion radii. rule 2.electrostatic valency principle: the strength of an ionic bond is equal to ionic charge divided by coordination number.

Paulings Rule Flashcards Quizlet Rule #1 a coordinated polyhedron of anions is formed about each cation, the cation anion distance equaling the sum of their characteristic packing radii and the coordination polyhedron being determined by the radius ratio. • pauling’s model treats the anions and cations of a crystal as if they were hard spheres packed so tightly together. Definition: pauling’s rules. rule 1.radius ratio principle: cation anion distances are equal to the sum of their effective ionic radii, and cation coordination numbers are determined by the ratio of cation to anion radii. rule 2.electrostatic valency principle: the strength of an ionic bond is equal to ionic charge divided by coordination number. Now, let's look at pauling's rules. pauling's rules. 1. a coordination polyhedron of anions is formed about each cation, the cation anion distance equaling the sum of their characteristic packing radii and their radius ratio determining both the nature of the coordination polyhedron and therefore the coordination number of the cation. 2. Pauling’s rules of mineral structure. rule 1: a coordination polyhedron of anions is formed around each cation, wherein: the cation anion distance is determined by the sum of the ionic radii, and. the coordination number of the polyhedron is determined by the cation anion radius ratio (ra:rx).

Comments are closed.