Normal Skin Histology Explained By A Dermatopathologist Youtube

Normal Skin Histology Explained By A Dermatopathologist Youtube A complete organized library of all my videos, digital slides, pics, & sample pathology reports is available here: kikoxp posts 5084 (dermpath) &. Excerpt from my normal skin histology video: kikoxp posts 3660. a complete organized library of all my videos, digital slides, pics, & sample pat.

Histology Of The Skin Youtube Understanding the normal histology of the skin is crucial in diagnosing and understanding skin diseases and conditions. 🖐️ different cells and structures, such as melanocytes, langerhans cells, and hair follicles, play specific roles in the skin's function. Sample pathology report templates for basal cell carcinoma: kikoxp posts 5093a complete organized library of all my videos, digital slides, pics,. Normal skin. the illustrations of normal skin in the figure below show comparatively thin skin from the wrist (bottom) and thicker skin from the bottom of the foot (left, an acral site). note, only acral sites have a stratum lucidum (a clear layer of dead skin cells). fine, spiny intercellular desmosomes in the stratum spinosum are also visible. Here are some video highlights. skin anatomy. the body’s largest organ takes on a variety of appearances depending on the anatomic location. the two outermost layers—the epidermis and the dermis—work closely together. the epidermis, or outer layer, typically has four or five distinct layers of cells but lacks blood vessels or nerve endings.

Normal Skin Histology Explained By A Dermatopathologist Normal skin. the illustrations of normal skin in the figure below show comparatively thin skin from the wrist (bottom) and thicker skin from the bottom of the foot (left, an acral site). note, only acral sites have a stratum lucidum (a clear layer of dead skin cells). fine, spiny intercellular desmosomes in the stratum spinosum are also visible. Here are some video highlights. skin anatomy. the body’s largest organ takes on a variety of appearances depending on the anatomic location. the two outermost layers—the epidermis and the dermis—work closely together. the epidermis, or outer layer, typically has four or five distinct layers of cells but lacks blood vessels or nerve endings. Learning objectives. to understand how specimens for dermatopathology are surgically grossed, processed and embedded to retain proper orientation in the final microscope slide. to understand the histology of skin specimens. to understand how to recognize and successfully handle all types of dermatopathology specimens received in your laboratory. That means it consists of layers of flattened cells. skin, hair and nails are keratinised, meaning they have a dead and hardened impermeable surface made of a protein called keratin. mucous membranes are non keratinised and moist. the epidermis has three main types of cell: langerhans cells (immune cells).
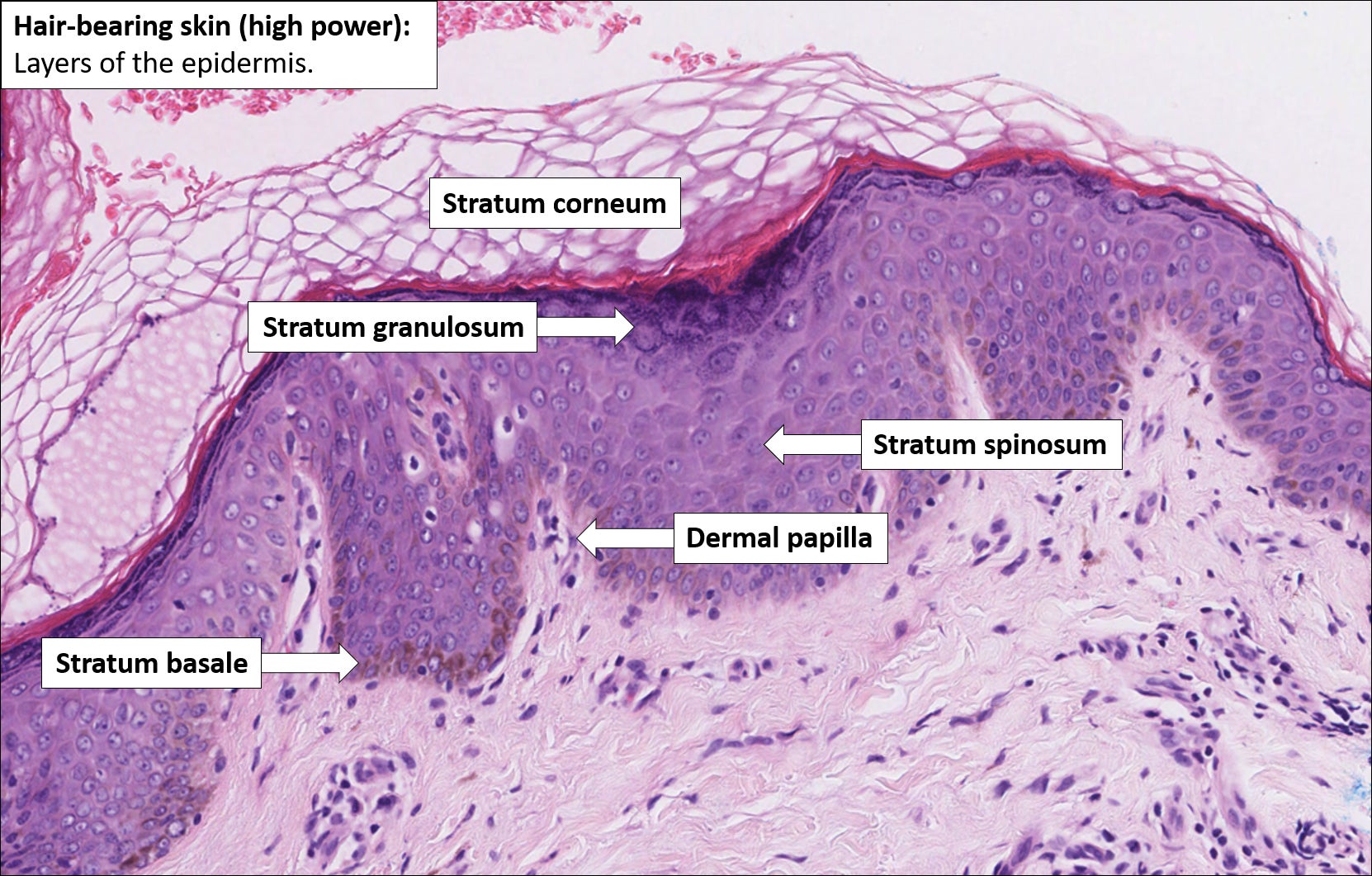
Skin вђ Normal Histology вђ Nus Pathweb Nus Pathweb Learning objectives. to understand how specimens for dermatopathology are surgically grossed, processed and embedded to retain proper orientation in the final microscope slide. to understand the histology of skin specimens. to understand how to recognize and successfully handle all types of dermatopathology specimens received in your laboratory. That means it consists of layers of flattened cells. skin, hair and nails are keratinised, meaning they have a dead and hardened impermeable surface made of a protein called keratin. mucous membranes are non keratinised and moist. the epidermis has three main types of cell: langerhans cells (immune cells).

Dermatopathology101 Normal Skin Histology Non Neoplastic Skin

Comments are closed.