Normal Distribution What It Is Uses And Formula
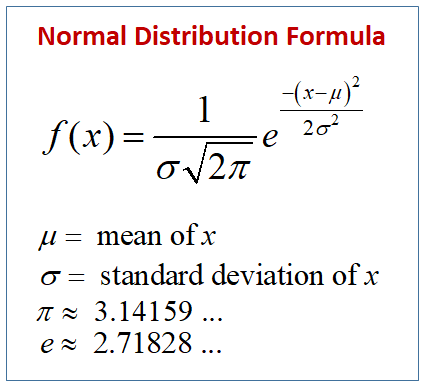
Normal Distribution Solutions Examples Formulas Videos Height, birth weight, reading ability, job satisfaction, or sat scores are just a few examples of such variables. because normally distributed variables are so common, many statistical tests are designed for normally distributed populations. understanding the properties of normal distributions means you can use inferential statistics to compare. Normal distribution problems and solutions. question 1: calculate the probability density function of normal distribution using the following data. x = 3, μ = 4 and σ = 2. solution: given, variable, x = 3. mean = 4 and. standard deviation = 2. by the formula of the probability density of normal distribution, we can write; hence, f(3,4,2) = 1.106.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Clipboard01-fdb217713438416cadafc48a1e4e5ee4.jpg)
Normal Distribution What It Is Uses And Formula Formula. the normal distribution follows the following formula. note that only the values of the mean (μ ) and standard deviation (σ) are necessary. normal distribution formula. where: x = value. For example, some tests such proportions tests (which use the binomial distribution) and the poisson rate tests (for count data and use the poisson distribution) have a form that uses a normal approximation tests. these normal approximation tests uses z scores for the normal distribution rather than values for the “native” distribution. A normal distribution is determined by two parameters the mean and the variance. a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 is called a standard normal distribution. figure 1. a standard normal distribution (snd). this is the distribution that is used to construct tables of the normal distribution. The simplest case of a normal distribution is known as the standard normal distribution or unit normal distribution. this is a special case when and , and it is described by this probability density function (or density): the variable has a mean of 0 and a variance and standard deviation of 1.
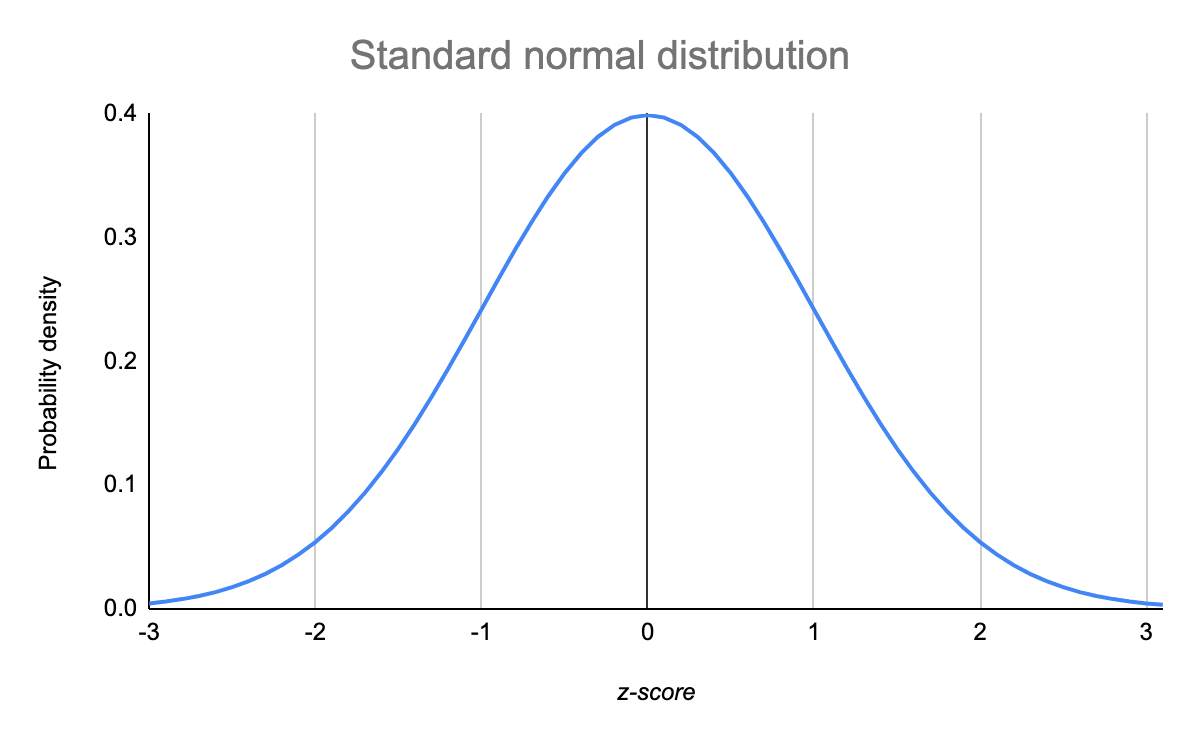
Normal Distribution Examples Formulas Uses A normal distribution is determined by two parameters the mean and the variance. a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 is called a standard normal distribution. figure 1. a standard normal distribution (snd). this is the distribution that is used to construct tables of the normal distribution. The simplest case of a normal distribution is known as the standard normal distribution or unit normal distribution. this is a special case when and , and it is described by this probability density function (or density): the variable has a mean of 0 and a variance and standard deviation of 1. Step 1: calculate a z score. to compare sleep duration during and before the lockdown, you convert your lockdown sample mean into a z score using the pre lockdown population mean and standard deviation. a z score of 2.24 means that your sample mean is 2.24 standard deviations greater than the population mean. The normal distribution, also called the gaussian distribution, is a probability distribution commonly used to model phenomena such as physical characteristics (e.g. height, weight, etc.) and test scores. due to its shape, it is often referred to as the bell curve: the graph of a normal distribution with mean of 0 0 and standard deviation of 1 1.
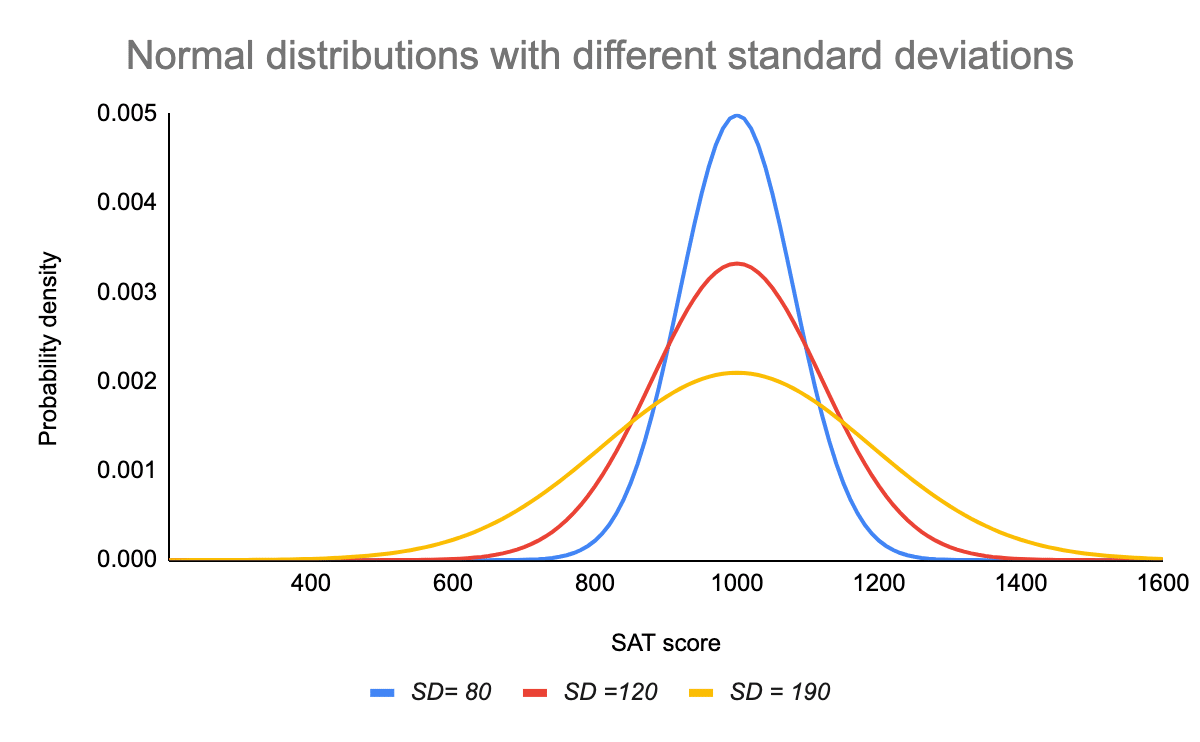
Normal Distribution Examples Formulas Uses Step 1: calculate a z score. to compare sleep duration during and before the lockdown, you convert your lockdown sample mean into a z score using the pre lockdown population mean and standard deviation. a z score of 2.24 means that your sample mean is 2.24 standard deviations greater than the population mean. The normal distribution, also called the gaussian distribution, is a probability distribution commonly used to model phenomena such as physical characteristics (e.g. height, weight, etc.) and test scores. due to its shape, it is often referred to as the bell curve: the graph of a normal distribution with mean of 0 0 and standard deviation of 1 1.

Comments are closed.