Normal Distribution Part 1 Math Statistics Showme
Normal Distribution Part 1 Math Statistics Showme Normal distribution part 1 by kim imber july 21, 2013. math; statistics; like 0. you should do so only if this showme contains inappropriate content. The normal distribution, also called the gaussian distribution, is a probability distribution commonly used to model phenomena such as physical characteristics (e.g. height, weight, etc.) and test scores. due to its shape, it is often referred to as the bell curve: the graph of a normal distribution with mean of 0 0 and standard deviation of 1 1.

Normal Distribution Part 1 Statistics And Probability Youtube Height, birth weight, reading ability, job satisfaction, or sat scores are just a few examples of such variables. because normally distributed variables are so common, many statistical tests are designed for normally distributed populations. understanding the properties of normal distributions means you can use inferential statistics to compare. The standard deviation is 0.15m, so: 0.45m 0.15m = 3 standard deviations. so to convert a value to a standard score ("z score"): first subtract the mean, then divide by the standard deviation. and doing that is called "standardizing": we can take any normal distribution and convert it to the standard normal distribution. In statistics, because this pattern is so pervasive, it seems to fit to call it normal, or more formally, the normal distribution. the normal distribution is an extremely important concept, because it occurs so often in the data we collect from the natural world, as well as in many of the more theoretical ideas that are the foundation of statistics. Step 1: sketch a normal distribution with a mean of μ=30 lbs and a standard deviation of σ = 5 lbs. step 2: a weight of 35 lbs is one standard deviation above the mean. add the percentages above that point in the normal distribution. 13.5% 2.35% 0.15% = 16%. step 3: since there are 200 otters in the colony, 16% of 200 = 0.16 * 200 = 32.
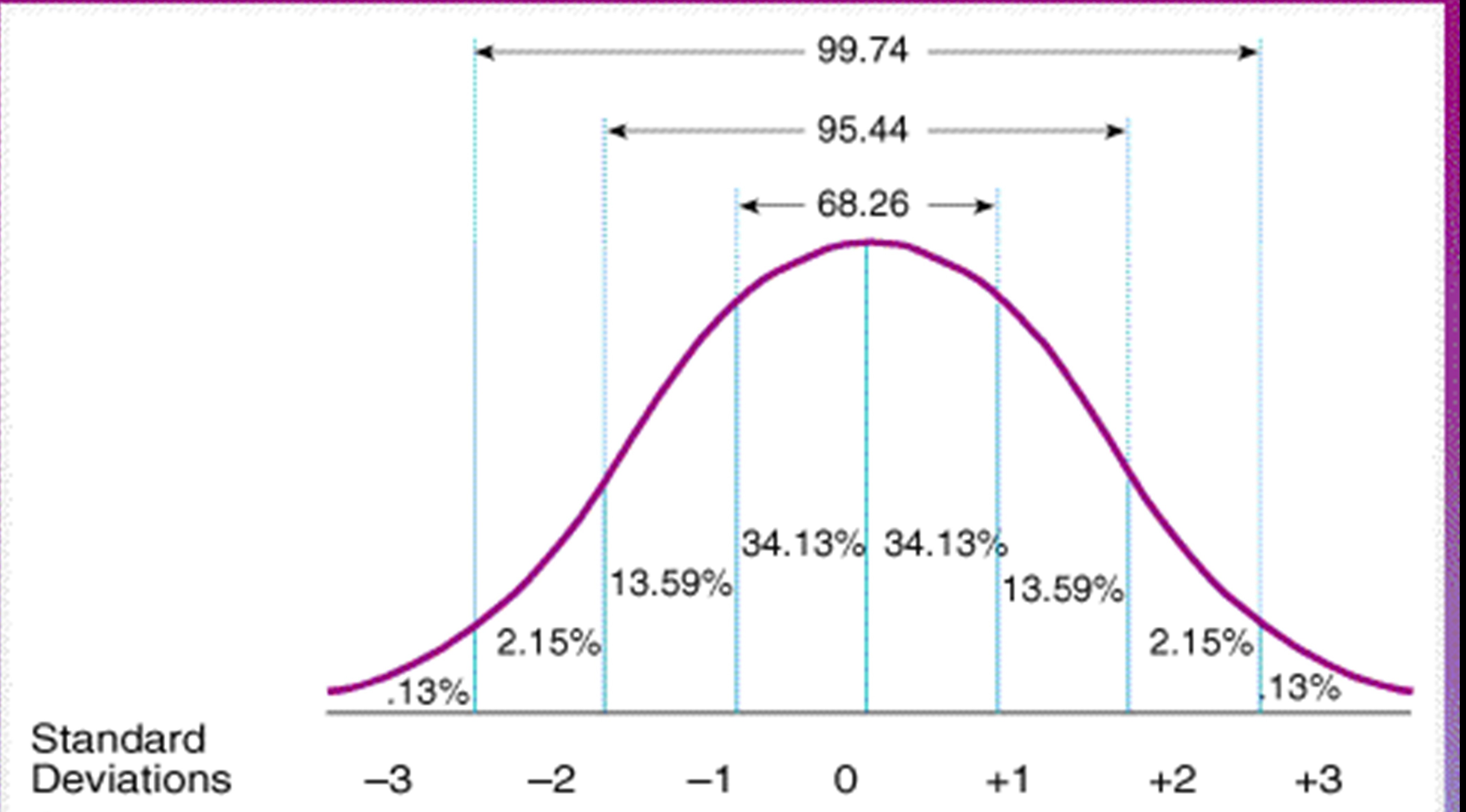
Standard Normal Distribution Math Definitions Letter S In statistics, because this pattern is so pervasive, it seems to fit to call it normal, or more formally, the normal distribution. the normal distribution is an extremely important concept, because it occurs so often in the data we collect from the natural world, as well as in many of the more theoretical ideas that are the foundation of statistics. Step 1: sketch a normal distribution with a mean of μ=30 lbs and a standard deviation of σ = 5 lbs. step 2: a weight of 35 lbs is one standard deviation above the mean. add the percentages above that point in the normal distribution. 13.5% 2.35% 0.15% = 16%. step 3: since there are 200 otters in the colony, 16% of 200 = 0.16 * 200 = 32. If a dataset is perfectly normally distributed, then 68% of the data values will fall within one standard deviation of the mean. for example, suppose we have a set of data that follows the normal distribution with mean 400 and standard deviation 100. this means 68% of the data would fall between the values of 300 (one standard deviation below. By marco taboga, phd. the normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics. it is often called gaussian distribution, in honor of carl friedrich gauss (1777 1855), an eminent german mathematician who gave important contributions towards a better understanding of the.
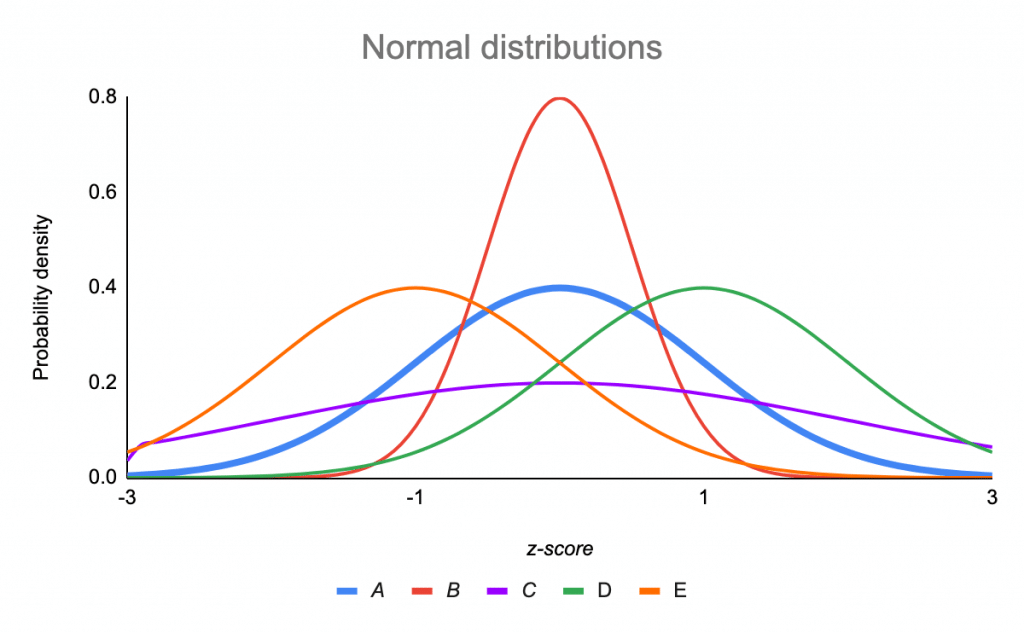
The Standard Normal Distribution Examples Explanations Uses If a dataset is perfectly normally distributed, then 68% of the data values will fall within one standard deviation of the mean. for example, suppose we have a set of data that follows the normal distribution with mean 400 and standard deviation 100. this means 68% of the data would fall between the values of 300 (one standard deviation below. By marco taboga, phd. the normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics. it is often called gaussian distribution, in honor of carl friedrich gauss (1777 1855), an eminent german mathematician who gave important contributions towards a better understanding of the.

Comments are closed.