Normal Distribution In Statistics Normal Distribution Explained With
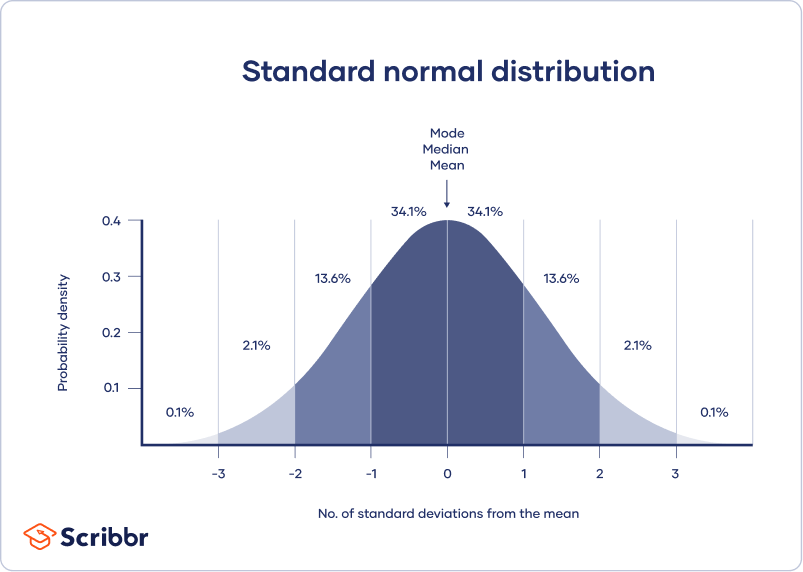
Normal Distribution Examples Formulas Uses Height, birth weight, reading ability, job satisfaction, or sat scores are just a few examples of such variables. because normally distributed variables are so common, many statistical tests are designed for normally distributed populations. understanding the properties of normal distributions means you can use inferential statistics to compare. By jim frost 181 comments. the normal distribution, also known as the gaussian distribution, is the most important probability distribution in statistics for independent, random variables. most people recognize its familiar bell shaped curve in statistical reports. the normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that is.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash_Final_The_Normal_Distribution_Table_Explained_Jan_2020-05-1665c5d241764f5e95c0e63a4855333e.jpg)
The Normal Distribution Table Definition This page titled 7.1: introduction to normal distributions is shared under a public domain license and was authored, remixed, and or curated by david lane via source content that was edited to the style and standards of the libretexts platform. the normal distribution is the most important and most widely used distribution in statistics. Probability theory. in probability theory and statistics, a normal distribution or gaussian distribution is a type of continuous probability distribution for a real valued random variable. the general form of its probability density function is the parameter is the mean or expectation of the distribution (and also its median and mode), while. The normal distribution is extremely important, but it cannot be applied to everything in the real world. properties of the normal distribution include: the curve of a normal distribution is symmetric and bell shaped. the center of a normal distribution is at the mean μ μ. in a normal distribution, the mean, the median, and the mode are equal. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org math statistics probability modelin.
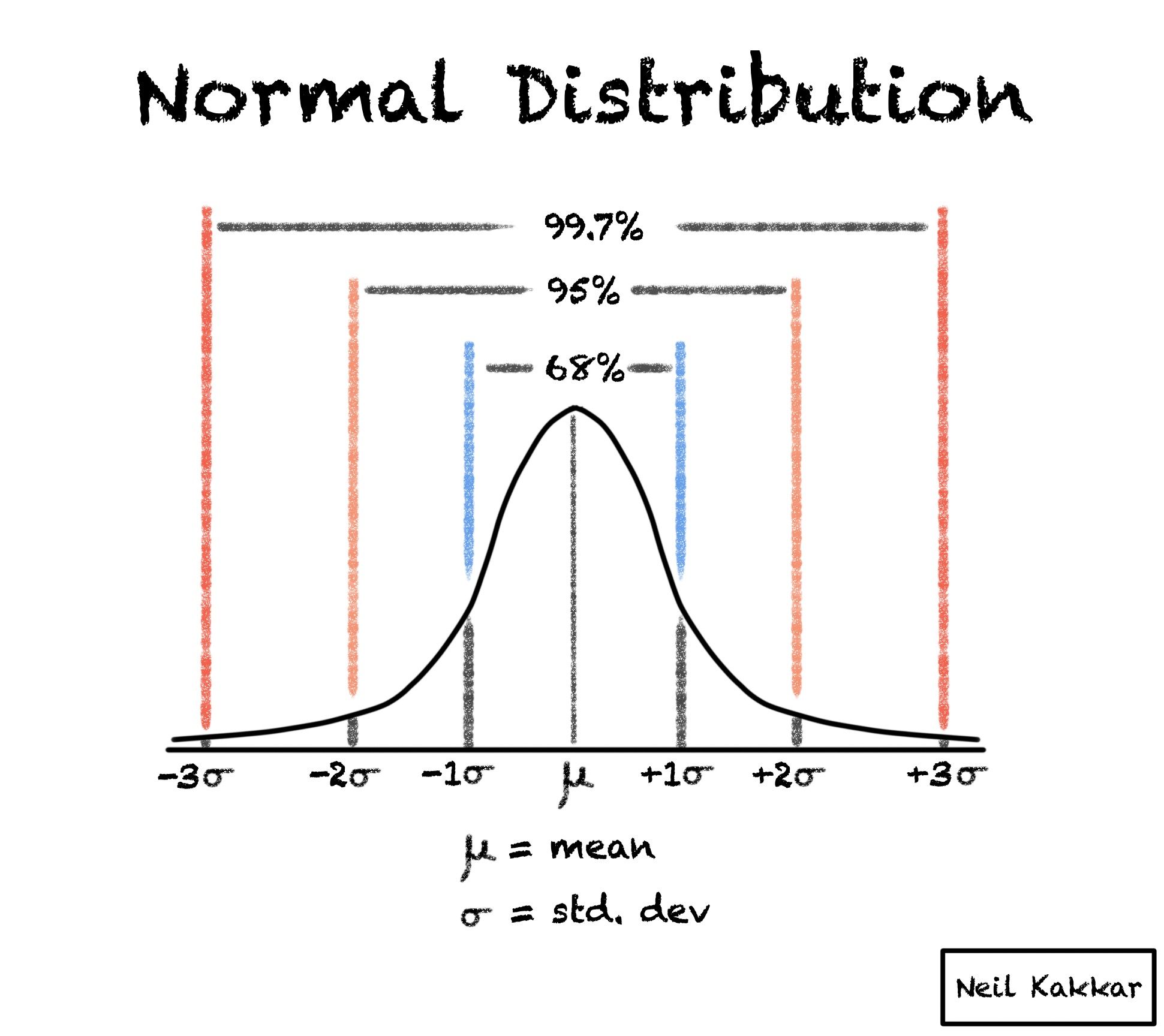
Normal Distribution Explained The normal distribution is extremely important, but it cannot be applied to everything in the real world. properties of the normal distribution include: the curve of a normal distribution is symmetric and bell shaped. the center of a normal distribution is at the mean μ μ. in a normal distribution, the mean, the median, and the mode are equal. Courses on khan academy are always 100% free. start practicing—and saving your progress—now: khanacademy.org math statistics probability modelin. The normal distribution, also called the gaussian distribution, is a probability distribution commonly used to model phenomena such as physical characteristics (e.g. height, weight, etc.) and test scores. due to its shape, it is often referred to as the bell curve: owing largely to the central limit theorem, the normal distributions is an appropriate approximation even when the underlying. The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics. it is often called gaussian distribution, in honor of carl friedrich gauss (1777 1855), an eminent german mathematician who gave important contributions towards a better understanding of the normal distribution.

Understanding Statistical Distributions Skillsyouneed The normal distribution, also called the gaussian distribution, is a probability distribution commonly used to model phenomena such as physical characteristics (e.g. height, weight, etc.) and test scores. due to its shape, it is often referred to as the bell curve: owing largely to the central limit theorem, the normal distributions is an appropriate approximation even when the underlying. The normal distribution is a continuous probability distribution that plays a central role in probability theory and statistics. it is often called gaussian distribution, in honor of carl friedrich gauss (1777 1855), an eminent german mathematician who gave important contributions towards a better understanding of the normal distribution.

Comments are closed.