Normal Distribution And Use Of Standard Deviation Explained

Normal Distribution And Use Of Standard Deviation Explained Youtube The standard normal distribution, also called the z distribution, is a special normal distribution where the mean is 0 and the standard deviation is 1. any normal distribution can be converted into the standard normal distribution by turning the individual values into z scores. Step 1: calculate a z score. to compare sleep duration during and before the lockdown, you convert your lockdown sample mean into a z score using the pre lockdown population mean and standard deviation. a z score of 2.24 means that your sample mean is 2.24 standard deviations greater than the population mean.
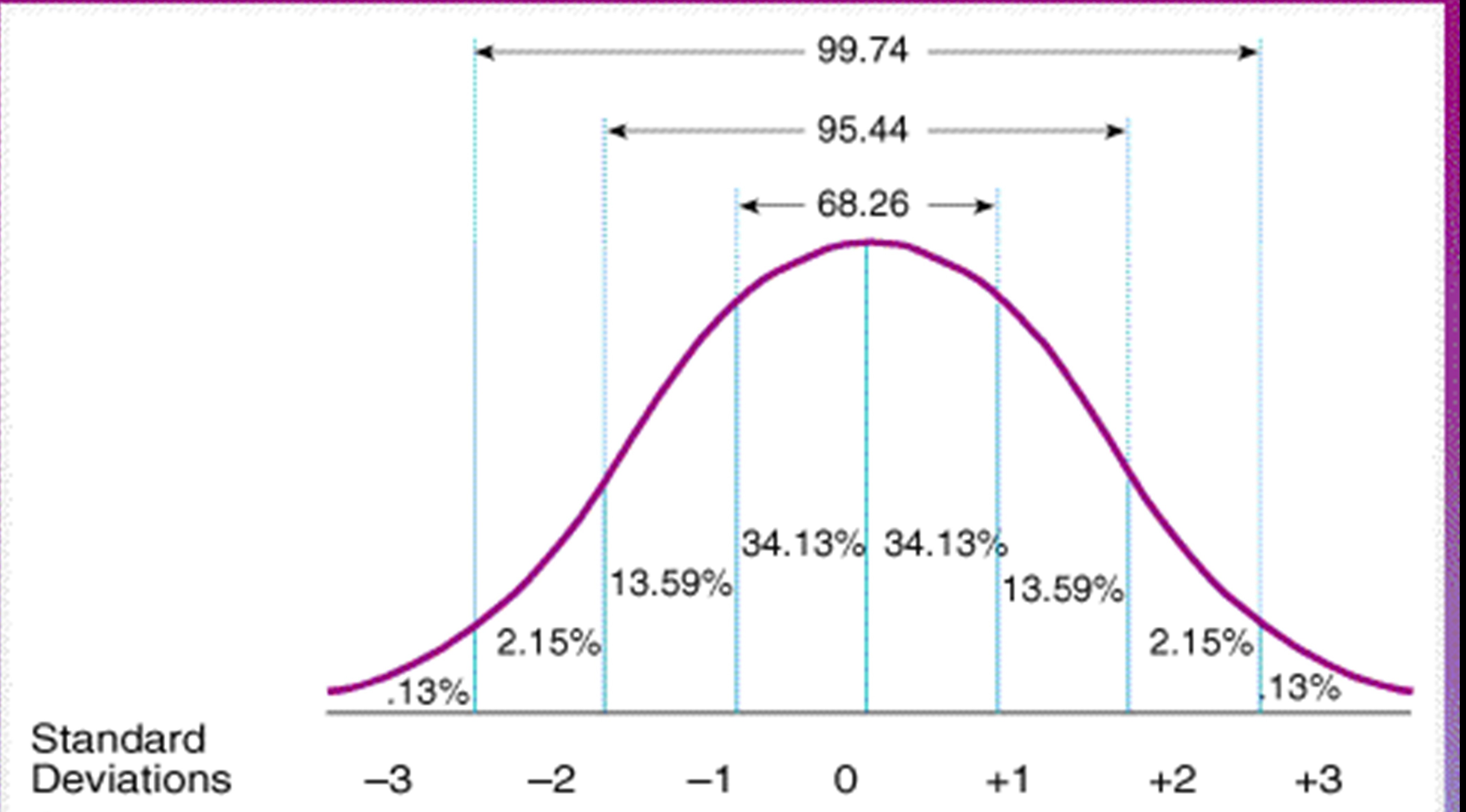
Standard Normal Distribution Math Definitions Letter S However, the standard normal distribution is a special case of the normal distribution where the mean is zero and the standard deviation is 1. this distribution is also known as the z distribution. a value on the standard normal distribution is known as a standard score or a z score. The values 50 – 6 = 44 and 50 6 = 56 are within one standard deviation from the mean 50. the z scores are –1 and 1 for 44 and 56, respectively. about 95% of the x values lie within two standard deviations of the mean. therefore, about 95% of the x values lie between –2σ = (–2) (6) = –12 and 2σ = (2) (6) = 12. Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean. the mean, median, and mode of a normal distribution are equal. the area under the normal curve is equal to 1.0 1.0. normal distributions are denser in the center and less dense in the tails. normal distributions are defined by two parameters, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ). A normal distribution is determined by two parameters the mean and the variance. a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 is called a standard normal distribution. figure 1. a standard normal distribution (snd). this is the distribution that is used to construct tables of the normal distribution.
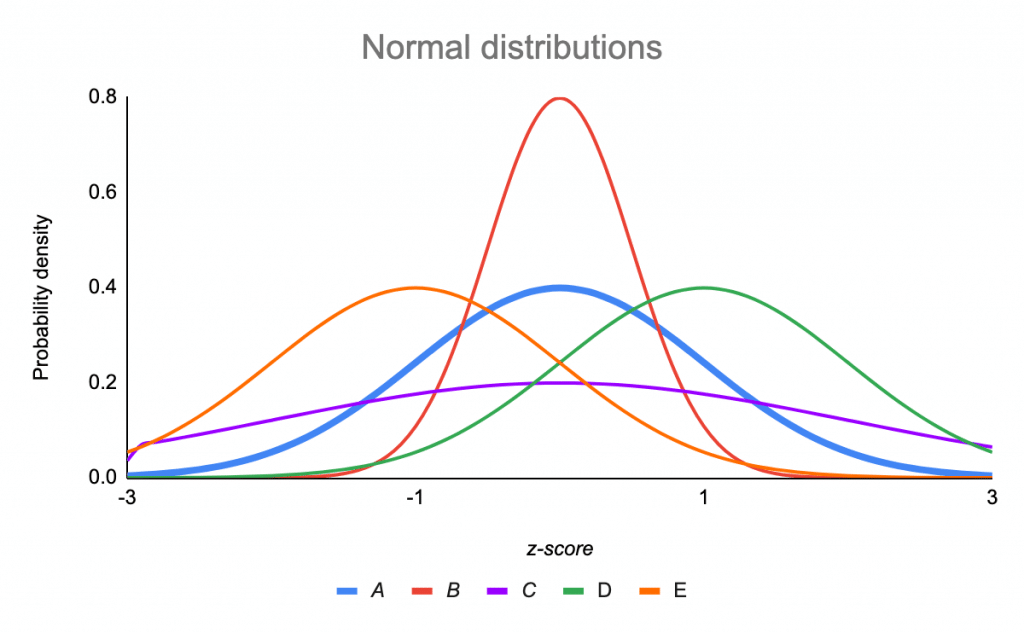
The Standard Normal Distribution Examples Explanations Uses Normal distributions are symmetric around their mean. the mean, median, and mode of a normal distribution are equal. the area under the normal curve is equal to 1.0 1.0. normal distributions are denser in the center and less dense in the tails. normal distributions are defined by two parameters, the mean (μ) and the standard deviation (σ). A normal distribution is determined by two parameters the mean and the variance. a normal distribution with a mean of 0 and a standard deviation of 1 is called a standard normal distribution. figure 1. a standard normal distribution (snd). this is the distribution that is used to construct tables of the normal distribution. The standard deviation is 0.15m, so: 0.45m 0.15m = 3 standard deviations. so to convert a value to a standard score ("z score"): first subtract the mean, then divide by the standard deviation. and doing that is called "standardizing": we can take any normal distribution and convert it to the standard normal distribution. Exercise 3.1.3. head lengths of brushtail possums follow a nearly normal distribution with mean 92.6 mm and standard deviation 3.6 mm. compute the z scores for possums with head lengths of 95.4 mm and 85.8 mm. answer. we can use z scores to roughly identify which observations are more unusual than others.
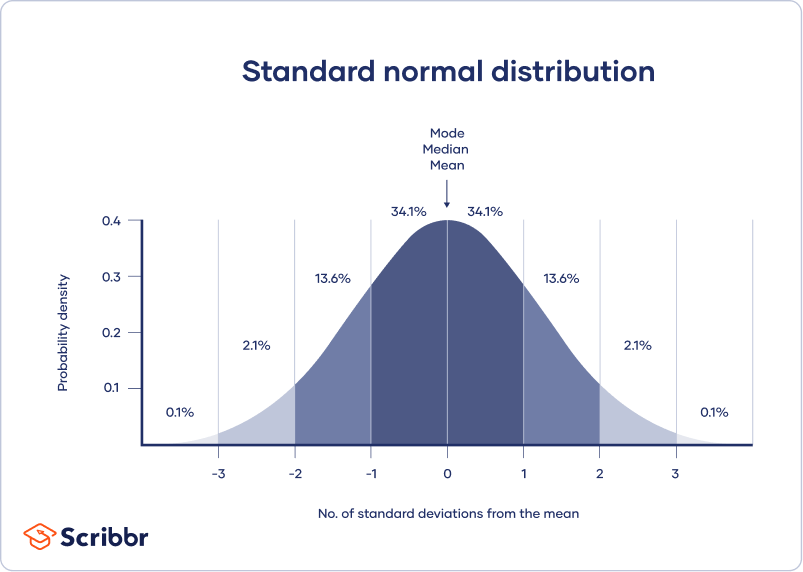
Normal Distribution Examples Formulas Uses The standard deviation is 0.15m, so: 0.45m 0.15m = 3 standard deviations. so to convert a value to a standard score ("z score"): first subtract the mean, then divide by the standard deviation. and doing that is called "standardizing": we can take any normal distribution and convert it to the standard normal distribution. Exercise 3.1.3. head lengths of brushtail possums follow a nearly normal distribution with mean 92.6 mm and standard deviation 3.6 mm. compute the z scores for possums with head lengths of 95.4 mm and 85.8 mm. answer. we can use z scores to roughly identify which observations are more unusual than others.

Comments are closed.