New Study Illustrates Benefits Of Long Read Sequencing Technology For
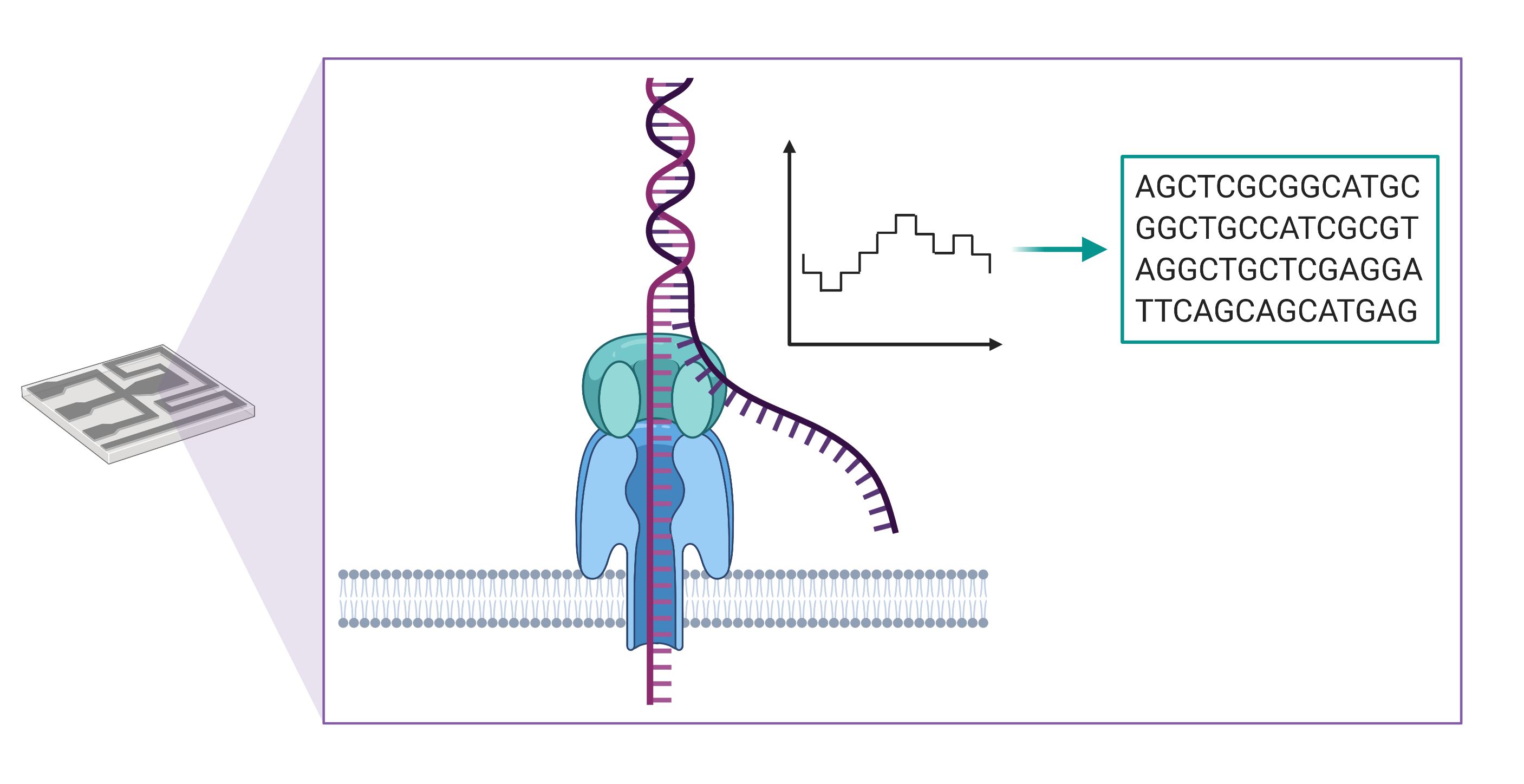
New Study Illustrates Benefits Of Long Read Sequencing Technology For Now, a new study published in genetics in medicine led by dr. steven jones, co director and head of bioinformatics at the gsc and dr. kasmintan schrader, scientist, staff physician and co director of the hereditary cancer program (hcp) at bc cancer, illustrates the significant benefit of implementing long read sequencing into precision oncology. 527 altmetric. metrics. to large scale projects and individual labs, long read sequencing has delivered new vistas and long wish lists for this technology’s future. to the delight of scientists.
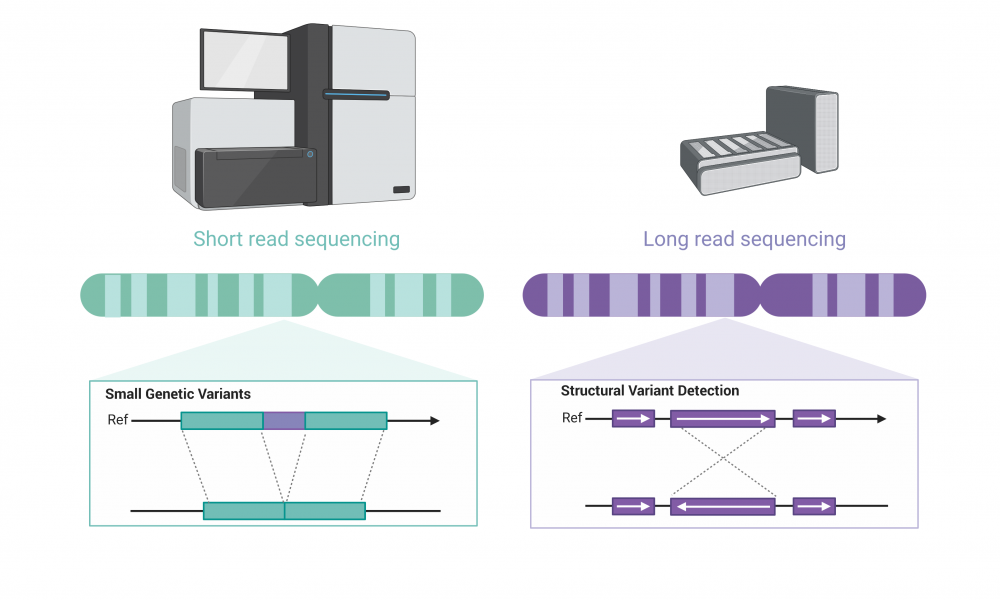
New Study Illustrates Benefits Of Long Read Sequencing Technology For Unveiling microbial diversity: harnessing long read sequencing technology. long read sequencing has recently transformed metagenomics, enhancing strain level pathogen characterization, enabling. Metrics. long read sequencing powers a more complete reading of genomic information. this june, we published a special issue highlighting the success of the telomere to telomere (t2t) consortium. The study of microbial communities has undergone significant advancements, starting from the initial use of 16s rrna sequencing to the adoption of shotgun metagenomics. however, a new era has emerged with the advent of long read sequencing (lrs), which offers substantial improvements over its predecessor, short read sequencing (srs). lrs produces reads that are several kilobases long, enabling. Next generation sequencing (ngs) is a powerful tool used in genomics research. ngs can sequence millions of dna fragments at once, providing detailed information about the structure of genomes, genetic variations, gene activity, and changes in gene behavior. recent advancements have focused on faster and more accurate sequencing, reduced costs.
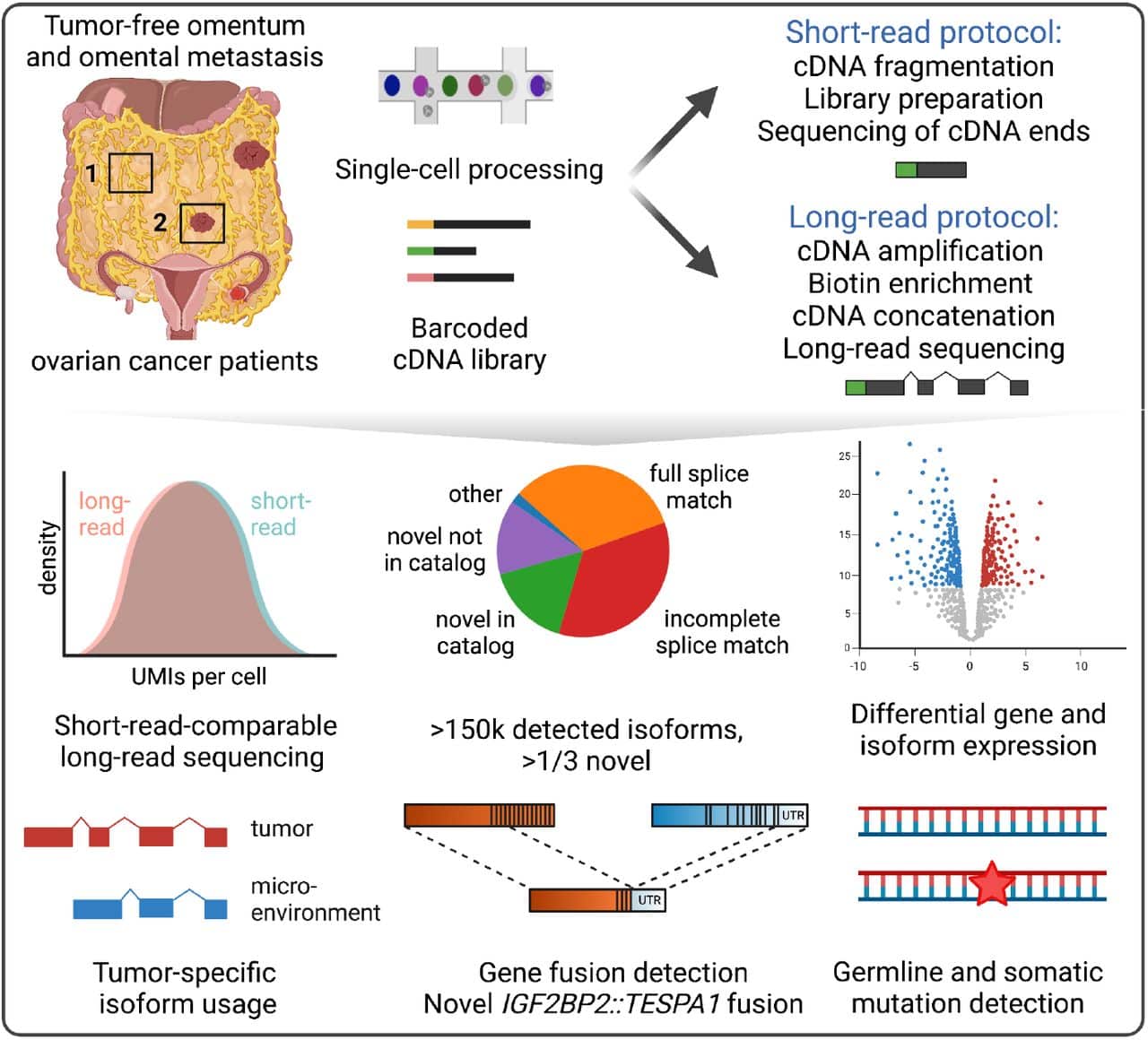
Long Read Sequencing The Key To A More Complete Cancer Transcriptome The study of microbial communities has undergone significant advancements, starting from the initial use of 16s rrna sequencing to the adoption of shotgun metagenomics. however, a new era has emerged with the advent of long read sequencing (lrs), which offers substantial improvements over its predecessor, short read sequencing (srs). lrs produces reads that are several kilobases long, enabling. Next generation sequencing (ngs) is a powerful tool used in genomics research. ngs can sequence millions of dna fragments at once, providing detailed information about the structure of genomes, genetic variations, gene activity, and changes in gene behavior. recent advancements have focused on faster and more accurate sequencing, reduced costs. Highlights. long read third generation sequencing technologies are causing a new revolution in genomics as they provide a way to study genomes, transcriptomes, and metagenomes at an unprecedented resolution. smrt and nanopore sequencing allow for the first time the direct study of different types of dna base modifications. Aaron wenger, a principal investigator on pacbio's bioinformatics team, said that the study and the tools developed could help move the field toward a "convergence of community standards," on par with standards that have been developed for short read sequencing. the study demonstrates a "maturation" in the long read sequencing field, he said.

For Cancer Research Long Read Sequencing Delivers New Insights Highlights. long read third generation sequencing technologies are causing a new revolution in genomics as they provide a way to study genomes, transcriptomes, and metagenomes at an unprecedented resolution. smrt and nanopore sequencing allow for the first time the direct study of different types of dna base modifications. Aaron wenger, a principal investigator on pacbio's bioinformatics team, said that the study and the tools developed could help move the field toward a "convergence of community standards," on par with standards that have been developed for short read sequencing. the study demonstrates a "maturation" in the long read sequencing field, he said.

Comments are closed.