Natural Draft Cooling Tower Diagram
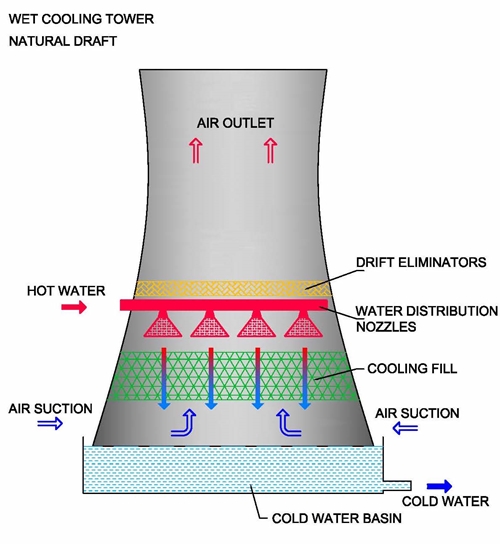
Natural Draft Cooling Towers Fans A S Natural draft cooling tower definition: a natural draft cooling tower is defined as a heat exchanger that cools water by direct contact with air, using convective flow for air circulation. working principle: it works by using sensible heat transfer and latent heat transfer to cool water and heat the air, driven by the density difference between. The first reason is that the shape reduces the amount of construction material required when building such a large tower. the second reason is that the paraboloid shape of the tower accelerates the air flow through the tower, which increases the tower’s cooling capacity. natural draft cooling towers are sometimes referred to as hyperbolic.

Cooling Towers Explained How Does A Cooling Tower Work Cooling tower? natural draft cooling towers are physically very simple machines. with reference to figure 3, conventional natural draft cooling towers typically include: • one or more vertical riser pipes that transport hot water to an appropriate elevation where it is distributed over a fixed plan area. A natural draft cooling tower is an essential component of many industrial processes, particularly in power plants and petrochemical refineries. its primary function is to provide cooling to the fluids or gases coming out of various equipment or processes. the design and operation of a natural draft cooling tower are based on the principles of. 8. how counter flow cooling towers work 9. how forced draft & induced draft cooling towers work 10. how natural draft cooling towers work 11. factory assembled cooling towers (fap) 12. field erected cooling towers (fep) 13. how are cooling towers relate to atmospheric vortex engines? 14. cooling tower parts & functions 15. 9.3.3 natural draft cooling tower. the performance of a natural draft dry cooling tower (nddct) is influenced by the characteristics of heat exchanger, the tower geometry, and ambient conditions. an nddct must meet the heat balance and draft equation at the specified ambient conditions. for an indirect dry cooling tower, the heat transfer by.

Natural Draft Cooling Tower Natural Draft Cooling Tower 8. how counter flow cooling towers work 9. how forced draft & induced draft cooling towers work 10. how natural draft cooling towers work 11. factory assembled cooling towers (fap) 12. field erected cooling towers (fep) 13. how are cooling towers relate to atmospheric vortex engines? 14. cooling tower parts & functions 15. 9.3.3 natural draft cooling tower. the performance of a natural draft dry cooling tower (nddct) is influenced by the characteristics of heat exchanger, the tower geometry, and ambient conditions. an nddct must meet the heat balance and draft equation at the specified ambient conditions. for an indirect dry cooling tower, the heat transfer by. Cooling towers can be hyperbolic or cylindrical. the gas and liquid flow can be in the countercurrent or crossflow directions. cooling towers can also either be natural draft, meaning that gas naturally flows into the tower, or mechanical draft, meaning that devices, typically fans, bring gas and liquid into the device at set rates. Natural draft cooling towers are part of centralized district cooling systems that provide chilled water to multiple buildings for air conditioning and cooling purposes. large industrial processes: various large scale industrial processes, such as paper manufacturing, cement production, and food processing, generate significant heat.

Natural Draft Cooling Tower Natural Draft Cooling Tower Cooling towers can be hyperbolic or cylindrical. the gas and liquid flow can be in the countercurrent or crossflow directions. cooling towers can also either be natural draft, meaning that gas naturally flows into the tower, or mechanical draft, meaning that devices, typically fans, bring gas and liquid into the device at set rates. Natural draft cooling towers are part of centralized district cooling systems that provide chilled water to multiple buildings for air conditioning and cooling purposes. large industrial processes: various large scale industrial processes, such as paper manufacturing, cement production, and food processing, generate significant heat.

Comments are closed.