Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Model Animation For A Level

Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Model Animation For A Level Hi guys! i thought the best way to explain this process was by animation. yes it took ages and yes, it's not getting 'best animated short' at the oscars, but. Sliding filament theory explains how muscles contract at a cellular level. learn more and test yourself with our quizzes here: teachpe anatomy.

Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Model Animation For A Level I've released the bhavsar cut! new and improved, extended cut of my sliding filament hypothesis animation. this one has text annotations to explain key point. The sliding filament model of contraction. when signaled by a motor neuron, a skeletal muscle fiber contracts as the thin filaments are pulled and then slide past the thick filaments within the fiber’s sarcomeres. this process is known as the sliding filament model of muscle contraction (figure 10.10). The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers. the process of contraction starts when an action potential reaches the muscle fiber and triggers the. The sliding filament theory. in 1954, scientists published two groundbreaking papers describing the molecular basis of muscle contraction. these papers described the position of myosin and actin.

Muscle Contraction Sliding Filament Model Animation For A Level The sliding filament model of muscle contraction describes how muscles generate force and produce movement. muscle contraction occurs as a result of the sliding of thin filaments (actin) over thick filaments (myosin) within muscle fibers. the process of contraction starts when an action potential reaches the muscle fiber and triggers the. The sliding filament theory. in 1954, scientists published two groundbreaking papers describing the molecular basis of muscle contraction. these papers described the position of myosin and actin. At a very basic level, each muscle fibre is made up of smaller fibres called myofibrils. these contain even smaller structures called actin and myosin filaments. these filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contraction hence called the sliding filament theory! the diagram above shows part of a myofibril called a sarcomere. The sliding filament theory is a fundamental concept in muscle physiology that explains how muscles contract to generate force. this theory is based on the interactions between two types of protein filaments—actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments)—within the muscle fibers. by understanding this theory, we gain insight into how.
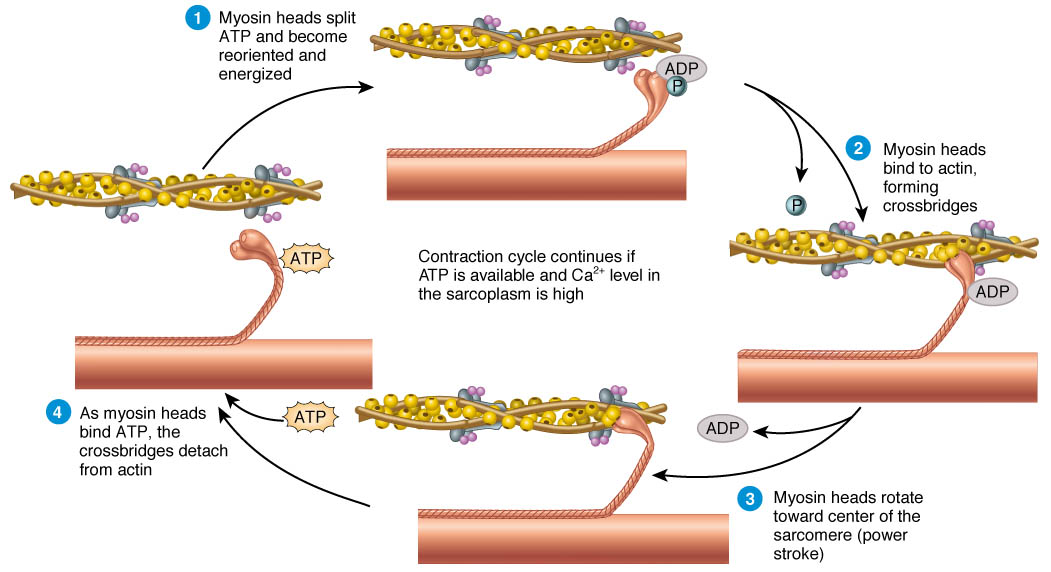
Sliding Filament Theory Of Muscle Contraction Online Biology Notes At a very basic level, each muscle fibre is made up of smaller fibres called myofibrils. these contain even smaller structures called actin and myosin filaments. these filaments slide in and out between each other to form a muscle contraction hence called the sliding filament theory! the diagram above shows part of a myofibril called a sarcomere. The sliding filament theory is a fundamental concept in muscle physiology that explains how muscles contract to generate force. this theory is based on the interactions between two types of protein filaments—actin (thin filaments) and myosin (thick filaments)—within the muscle fibers. by understanding this theory, we gain insight into how.

Comments are closed.