Mechanics Of Breathing Part I
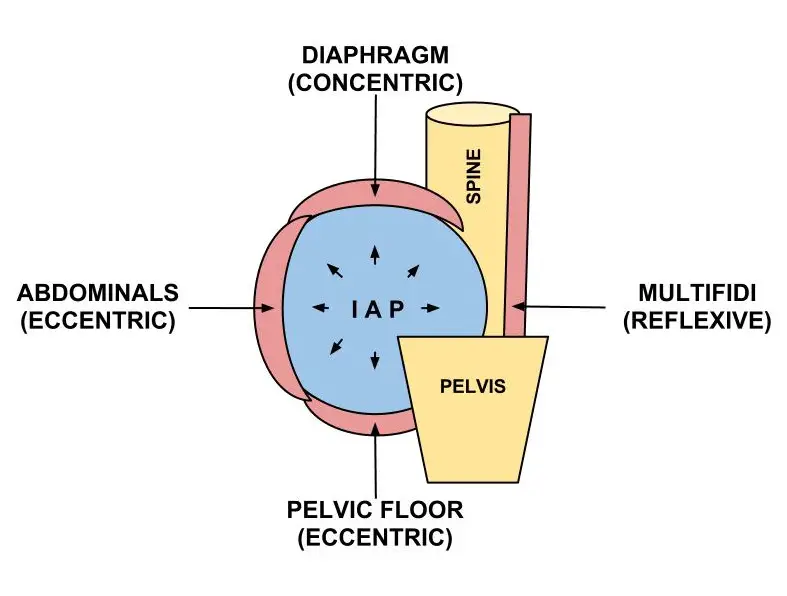
Breathing вђ Part I вђ Anatomy Mechanics Intrapleural pressure is the pressure in the space between the visceral and parietal pleura, or (physiologically) between the lungs and the chest wall. usually negative, typically 5cmh2o at rest. balance between the: outwards recoil of the chest wall. inwards recoil of the lungs (pel) varies with vertical distance in the lung. Lectures in respiratory physiology, john b west md, phd.
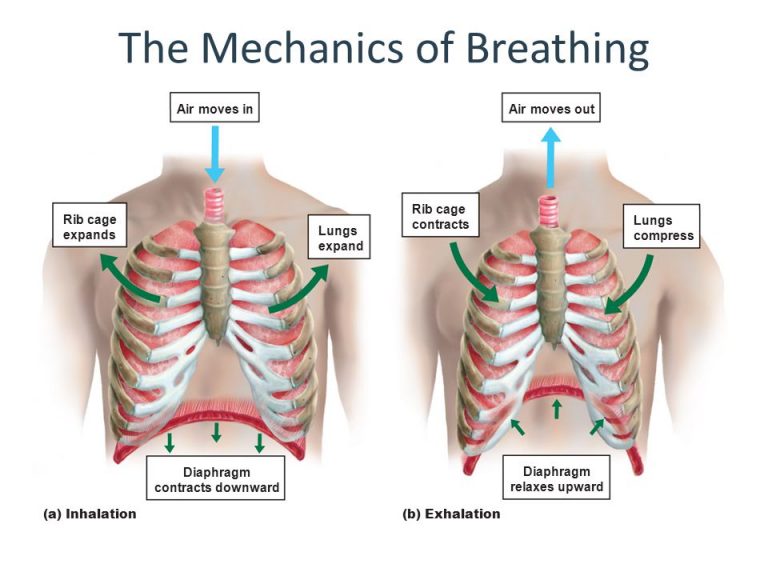
Mechanics Of Pulmonary Ventilation Pressure Changes During Mechanics of breathing. the processes of inspiration (breathing in) and expiration (breathing out) are vital for providing oxygen to tissues and removing carbon dioxide from the body. inspiration occurs via active contraction of muscles – such as the diaphragm – whereas expiration tends to be passive, unless it is forced. Official ninja nerd website: ninjanerd.orgninja nerds!in this lecture professor zach murphy will begin on our three part series outlining the mechani. Breathing is the process by which oxygen and co 2 are transported to and from the lungs (also known as ventilation). relevant physics and anatomy. in order to understand the mechanics of breathing it is important to be aware of the physics and anatomy that underpin this process. physics. boyle’s law helps us to understand the mechanics of. It overlies the lateral part of the thorax and forms the lateral wall of the axilla. it arises from the the 1st to 8th pairs of ribs and inserts onto the medial border of the scapula. by fixing the scapula in position, this muscle has an important role in laboured breathing when grasping a support or staying in the so called tripod position.

Comments are closed.