Major Salivary Glands Anatomyexplained Humanbody Sciencefacts Biology Science
Anatomy Of The Salivary Glands Video shows the major salivary glandsfor more anatomy lecture videos channel ucaybe vxldmlaq d4umlgfa videosjoin facebook group@ http. 1 3. synonyms: glandula parotis. the salivary glands are exocrine glands which produce a digestive fluid called saliva. they are accessory organs of the digestive system and are positioned in the head, in and around the oral cavity and secrete their salivary contents into the mouth. the salivary glands are divided into the major and minor.

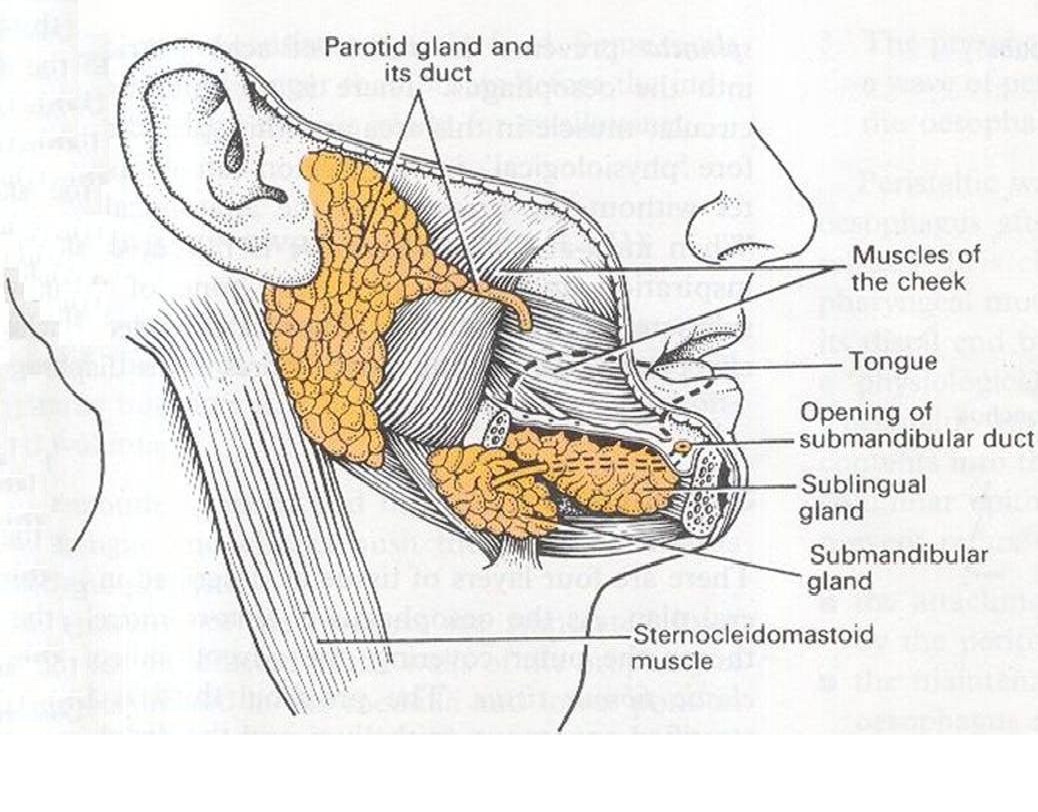
Anatomy Of The Salivary Glands Your salivary glands lubricate your mouth, help you swallow, aid in digestion and help protect your teeth against harmful bacteria. you have three major types of salivary glands, including your sublingual, submandibular and parotid. common symptoms of salivary gland disorders include fever, headaches and a lump in your cheek or under your chin. The salivary glands are exocrine glands that make, modify and secrete saliva into the oral cavity. they are divided into two main types: the major salivary glands, which include the parotid, submandibular and sublingual glands, and the minor salivary glands, which line the mucosa of the upper aerodigestive tract and the overwhelming entirety of the mouth [1]. The salivary glands produce saliva and secrete it into the mouth. saliva plays a role in helping a person chew and swallow food by making it moist. it also lubricates the surfaces within the mouth. Viral infections: viruses can make the salivary glands swell and become infected. ranula (cyst): this is a fluid filled sac that can form in the salivary glands because of an injury, infection, trauma, or surgery. sialolithiasis: salivary duct stones can cause pain and swelling. sialadenitis: this inflammation of the salivary gland causes swelling.
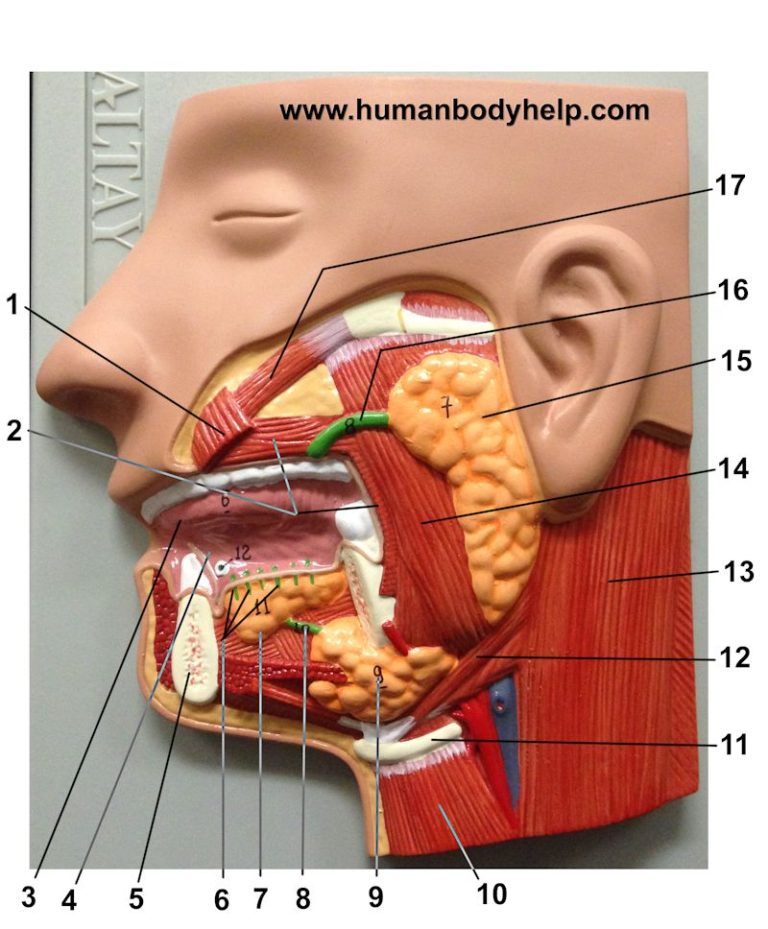
Salivary Glands вђ Human Body Help The salivary glands produce saliva and secrete it into the mouth. saliva plays a role in helping a person chew and swallow food by making it moist. it also lubricates the surfaces within the mouth. Viral infections: viruses can make the salivary glands swell and become infected. ranula (cyst): this is a fluid filled sac that can form in the salivary glands because of an injury, infection, trauma, or surgery. sialolithiasis: salivary duct stones can cause pain and swelling. sialadenitis: this inflammation of the salivary gland causes swelling. It's like watching the mummy all over again. image captured from human anatomy atlas. 2. saliva is 99% water. actually, saliva is around 99.5% water, which is why it's so important for you to stay hydrated. in addition to water, enzymes and "buffers" (things that maintain a balanced ph level) help keep the status quo in the oral cavity. Defining the morphology of adult human salivary glands. human major salivary glands consist of three pairs of glands known as parotid, submandibular, and sublingual glands; together they are responsible for 90% of the total saliva. minor salivary glands in turn, comprise ∼600–1000 glands distributed throughout the oral cavity.

Comments are closed.