Lesson 16 Finding Probability Using A Normal Distribution Part 5

Lesson 16 Finding Probability Using A Normal Distribution Part 5 This is just a few minutes of a complete course. get full lessons & more subjects at: mathtutordvd . Example 16 1. let \ (x\) denote the iq (as determined by the stanford binet intelligence quotient test) of a randomly selected american. it has long been known that \ (x\) follows a normal distribution with mean 100 and standard deviation of 16. that is, \ (x\sim n (100, 16^2)\).

Normal Distribution Find Probability Of Data Values Using Tables Youtu Section 16: finding probability usin . . . section 16: finding probability using a normal distribution, part 5 in this lesson, we will put numerous skills together and use the z chart table to solve statistical problems that involve the normal distribution. Lesson 16: normal distributions. 16.1 the distribution and its characteristics; 16.2 finding normal probabilities; 16.3 using normal probabilities to find x; 16.4 normal properties; 16.5 the standard normal and the chi square; 16.6 some applications; section 4: bivariate distributions. lesson 17: distributions of two discrete random. The theorem leads us to the following strategy for finding probabilities p (z <x <b) when a and b are constants, and x is a normal random variable with mean μ and standard deviation σ: 1) specify the desired probability in terms of x. 2) transform x, a, and b, by: z = x − μ σ. 3) use the standard normal n (0, 1) table, typically referred. This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide on using the normal distribution to find probability, a key concept in statistics and data analysis. ideal for s.
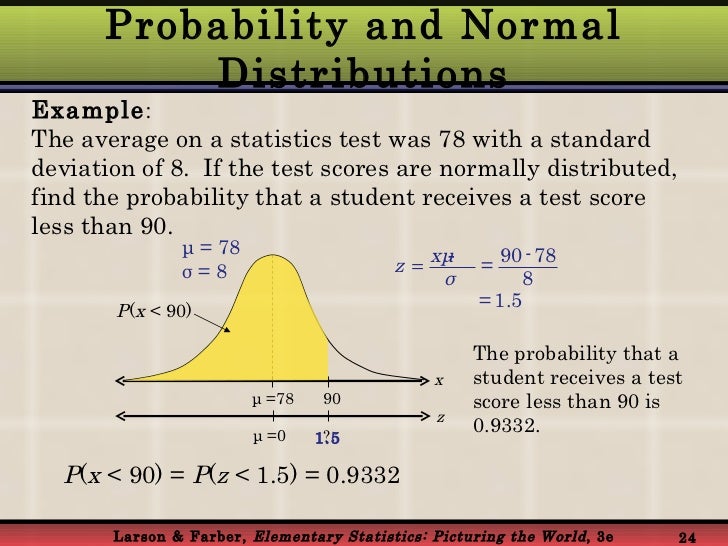
Normal Probability Distribution The theorem leads us to the following strategy for finding probabilities p (z <x <b) when a and b are constants, and x is a normal random variable with mean μ and standard deviation σ: 1) specify the desired probability in terms of x. 2) transform x, a, and b, by: z = x − μ σ. 3) use the standard normal n (0, 1) table, typically referred. This tutorial provides a comprehensive guide on using the normal distribution to find probability, a key concept in statistics and data analysis. ideal for s. Lesson 16: finding normal probabilities. hi everyone! read through the material below, watch the videos, work on the excel lecture and follow up with your instructor if you have questions. learning outcomes. create probability distributions, as well as identify bell shaped distributions (normal). assign probabilities to events using the normal. To calculate the probability, use the probability tables provided in appendix h tables without the use of technology. the tables include instructions for how to use them. the probability is represented by the area under the normal curve. to find the probability, calculate the z score and look up the z score in the z table under the z column.

Comments are closed.