Lecture 4 Protein Structure Lecture 4 Protein Structure Proteins Are

Lecture 4 Protein Structure Lecture 4 Protein Structure Proteins Are Lecture 4: protein structure. proteins are linear polymers of amino acids joined by peptide bonds for this reason, proteins are sometimes referred to as polypeptides proteins are made by translation of mrnas transcribed from genomic dna the basic biological point of dna and rna is to allow the synthesis of specific proteins, which carry out the. Lecture 4: protein structure slide 1: protein structure proteins are one of the four major classes of biomolecules. they consist of high molecular weight polymers of amino acids. because proteins generally constitute the largest fraction of the molecules in living cells, and they serve the most diverse functions, we will consider proteins first in our survey of basic biochemistry.
/protein-structure-373563_final11-5c81967f46e0fb00012c667d.png)
Basics Of Protein Structure Some functional proteins are composed of more than one polypeptide protein functions: structure organizing the genome, organelles, cytoplasm, protein complexes, and membranes in 3d shapes. Chapter 4 protein structure. 4 proteins are polymers of amino acids the chemical properties of amino acid side chains play a crucial role in determining the three dimensional structure of proteins. the chemical properties of amino acid side chains play a crucial role in determining the three dimensional structure of proteins. A domain can often retain much of its structure even if other parts of the same protein molecule are destroyed. semi autonomous. many protein subunits consist of only domain that form from aa chain. 1, 1. antibody molecules can have as many as domains formed from one chain of amino acids. Terms in this set (25) 4 what is the link between protein structure and function (1) protein structure defines its function primary sequence of amino acids encoded by dna define the structure and thus the function. 4 what is the two main classification of protein (2) · globular. · fibrillar. 8 describe the amino acid peptide bond.
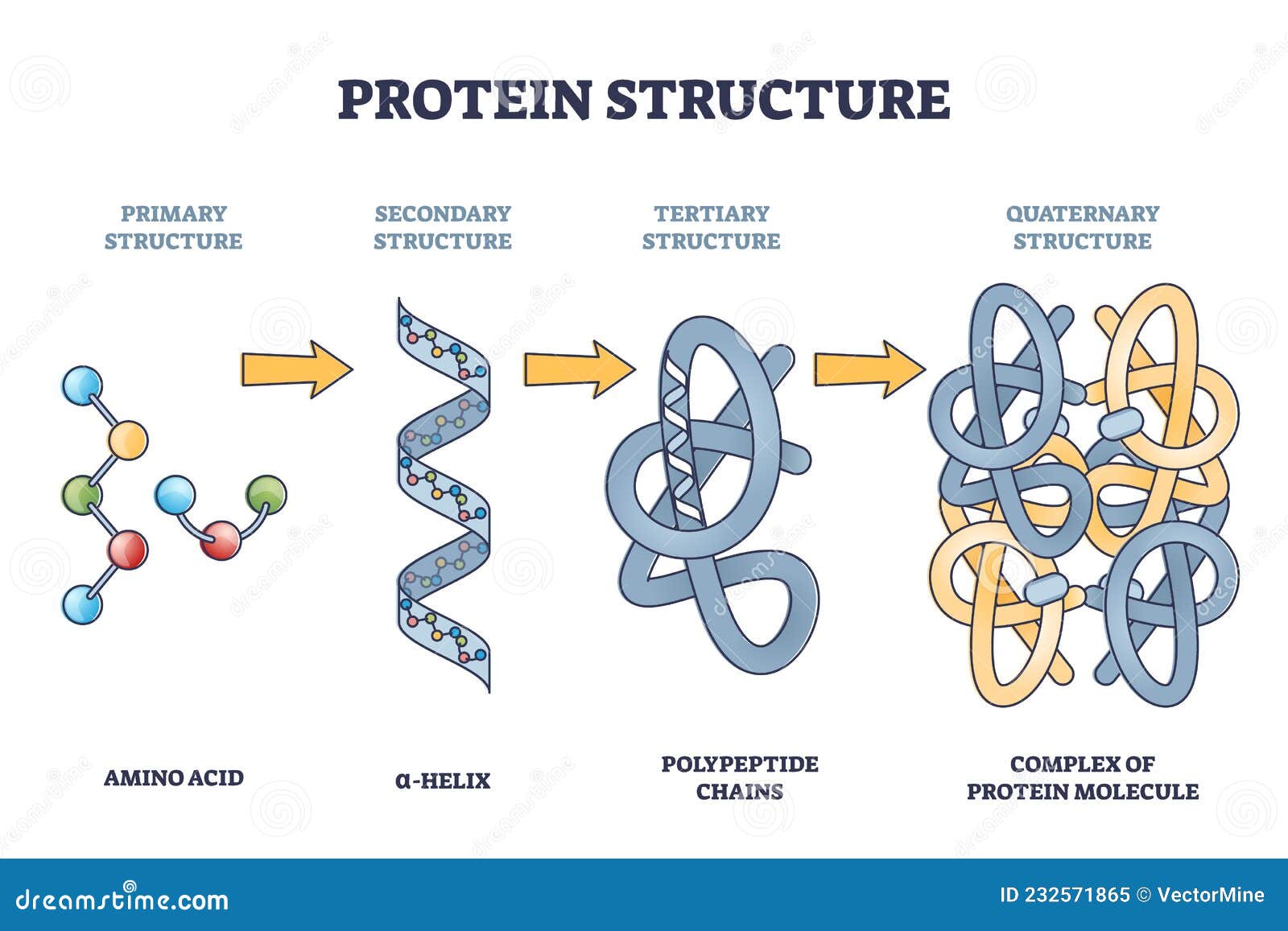
Levels Of Protein Structure Diagram A domain can often retain much of its structure even if other parts of the same protein molecule are destroyed. semi autonomous. many protein subunits consist of only domain that form from aa chain. 1, 1. antibody molecules can have as many as domains formed from one chain of amino acids. Terms in this set (25) 4 what is the link between protein structure and function (1) protein structure defines its function primary sequence of amino acids encoded by dna define the structure and thus the function. 4 what is the two main classification of protein (2) · globular. · fibrillar. 8 describe the amino acid peptide bond. Chapter 6: proteins: three dimensional structure. secondary structure. tertiary structure. quaternary structure and symmetry. protein stability. protein folding. chapter 7: protein function: myoglobin and hemoglobin, muscle contraction, and antibodies. oxygen binding to myoglobin and hemoglobin. Principles of biochemistry. 4: protein structure and function. 4.1: from amino acids to peptides. 4.2: levels of protein structure. proteins are the workhorses of the cell. virtually everything that goes on inside of cells happens as a result of the actions of proteins. among other things, protein enzymes catalyze the vast majority of cellular.
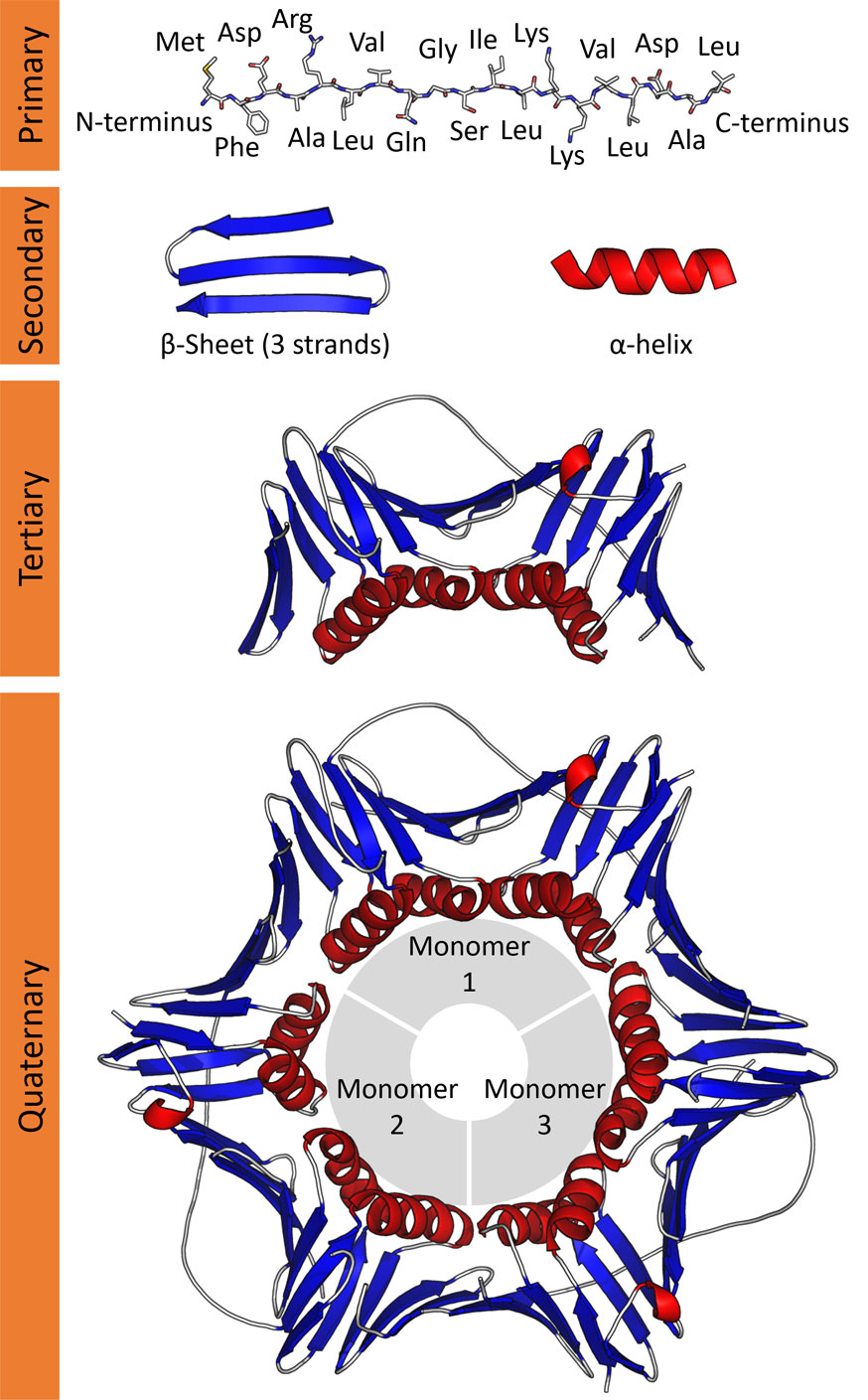
Protein Structure Short Lecture Notes Easybiologyclass Chapter 6: proteins: three dimensional structure. secondary structure. tertiary structure. quaternary structure and symmetry. protein stability. protein folding. chapter 7: protein function: myoglobin and hemoglobin, muscle contraction, and antibodies. oxygen binding to myoglobin and hemoglobin. Principles of biochemistry. 4: protein structure and function. 4.1: from amino acids to peptides. 4.2: levels of protein structure. proteins are the workhorses of the cell. virtually everything that goes on inside of cells happens as a result of the actions of proteins. among other things, protein enzymes catalyze the vast majority of cellular.

Comments are closed.