Intestinal Toxicity Assessment With Patient Derived Organoids

Intestinal Toxicity Assessment With Patient Derived Organoids Youtube Intestinal organoid differentiation begins with lgr5 positive stem cells located in the epithelium, which are either harvested from patient samples, or induced from human embryonic or induced pluripotent stem cells. by supplying the correct growth factors, these cells will differentiate, proliferate, and form tight intercellular junctions much. Organoids are regarded as physiologically relevant cell models and useful for compound screening for drug development; however, their applications are currently limited because of the high cost of.

Intestinal Toxicity Assessment With Patient Derived Organoids Publish date: october 14, 2022. patient derived intestinal organoids have proven to be a useful model system for assessing toxicity of potential therapeutic compounds. in collaboration with scientist , stemcell’s dr. martin stahl covers their applications and the resources available. The various applications of intestinal organoids are as follows: (1) developing in vitro models of intestinal organoids derived from adult tissues, pluripotent stem cells, or embryonic stem cells. (2) constructing organoid from healthy individuals or patients for biobanks and drug screening. (3) utilizing organoids for transplantation in the. Patient derived intestinal organoids and tumouroids supplemented with immune cells can be used to predict and study the on target off tumour toxicities of t cell engaging bispecific antibodies and. Abstract. organoids are three dimensional structures fabricated in vitro from pluripotent stem cells or adult tissue stem cells via a process of self organization that results in the formation of organ specific cell types. human organoids are expected to mimic complex microenvironments and many of the in vivo physiological functions of relevant.

Intestinal Toxicity Assessment With Patient Derived Organoids Patient derived intestinal organoids and tumouroids supplemented with immune cells can be used to predict and study the on target off tumour toxicities of t cell engaging bispecific antibodies and. Abstract. organoids are three dimensional structures fabricated in vitro from pluripotent stem cells or adult tissue stem cells via a process of self organization that results in the formation of organ specific cell types. human organoids are expected to mimic complex microenvironments and many of the in vivo physiological functions of relevant. The "organoid" is derived from the patient’s normal intestinal mucosa (including iscs), and cultured in vitro in 3d to form 0.1–0.2 mm diameter "organoids", which are then endoscopically. The aim of this review is to illustrate the potential use of organoids for therapy personalization by focusing on the most significant advances in ibd research achieved through the use of adult stem cells derived intestinal organoids. keywords: inflammatory bowel disease, organoids, intestinal epithelium, 3d cell cultures, personalized medicine.
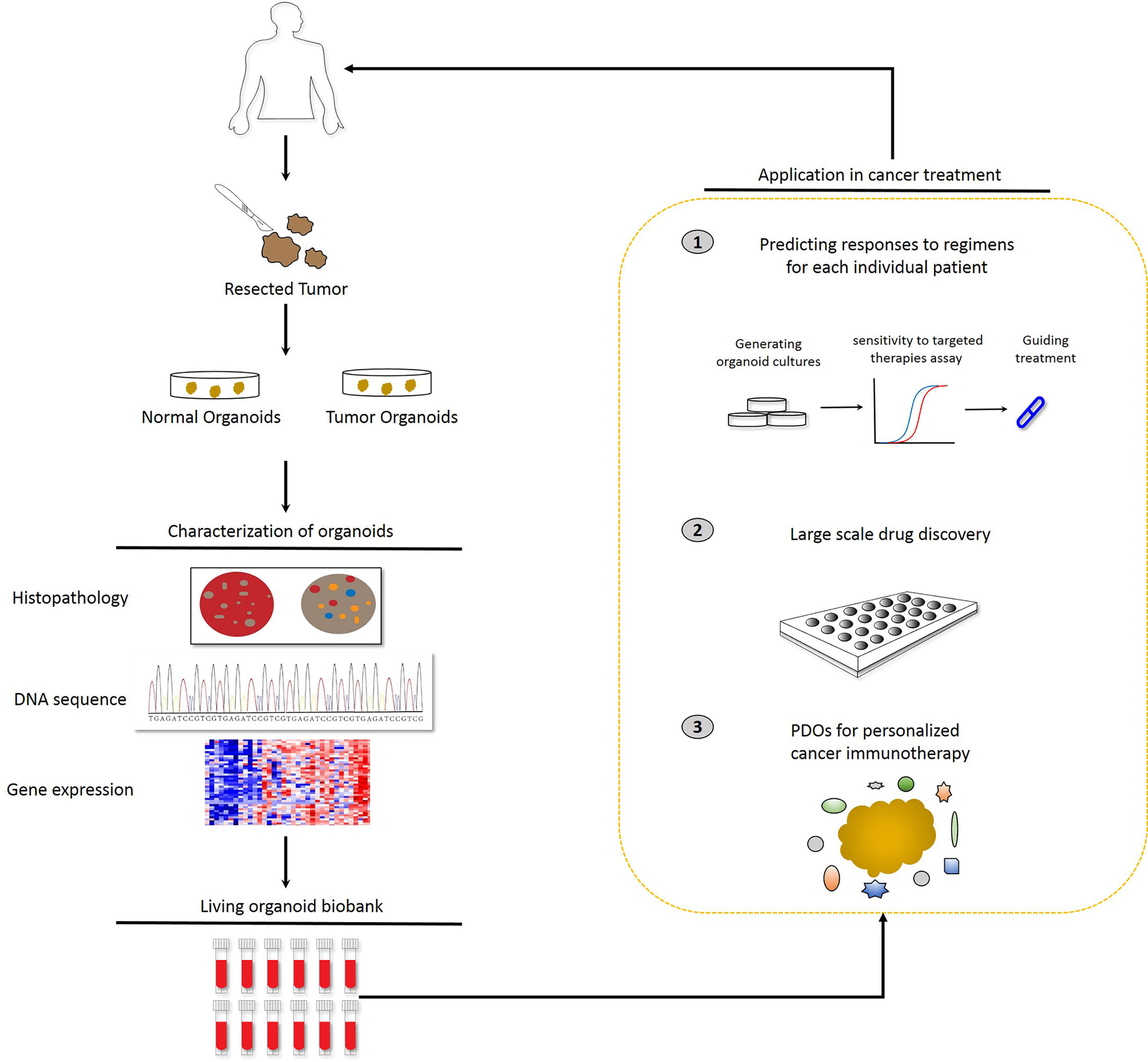
Frontiers Patient Derived Organoids In Precision Medicine Drug The "organoid" is derived from the patient’s normal intestinal mucosa (including iscs), and cultured in vitro in 3d to form 0.1–0.2 mm diameter "organoids", which are then endoscopically. The aim of this review is to illustrate the potential use of organoids for therapy personalization by focusing on the most significant advances in ibd research achieved through the use of adult stem cells derived intestinal organoids. keywords: inflammatory bowel disease, organoids, intestinal epithelium, 3d cell cultures, personalized medicine.

Comments are closed.