Hydrogen Cycle Diagram

Hydrogen Cycle Diagram T. e. the hydrogen cycle consists of hydrogen exchanges between biotic (living) and abiotic (non living) sources and sinks of hydrogen containing compounds. hydrogen (h) is the most abundant element in the universe. [1] on earth, common h containing inorganic molecules include water (h 2 o), hydrogen gas (h 2), hydrogen sulfide (h 2 s), and. Learn how hydrogen moves through the water cycle and the earth's systems, and what are its functions and uses. the web page explains the phases of the hydrogen cycle, such as evaporation, condensation, transpiration and precipitation, with examples and diagrams.
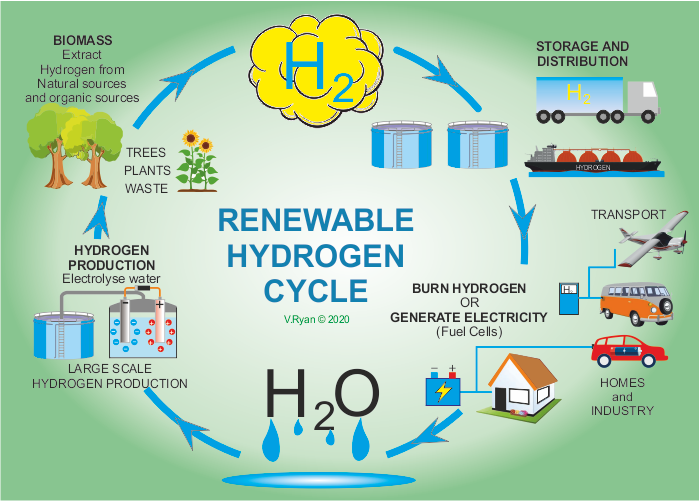
Untitled Document Technologystudent Learn how hydrogen is extracted from water and used in fuel cells to produce electricity and water. explore the advantages and disadvantages of hydrogen as an energy source and the challenges of the hydrogen economy. Learn about the processes of evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, and runoff that make up the water cycle. see diagrams, examples, and activities to explore the earth atmosphere system. Learn about the water cycle, a continuous exchange of moisture between the oceans, the atmosphere, and the land, powered by energy from the sun. see a diagram of the water cycle and explore resources for different grade levels. Water cycle, cycle that involves the continuous circulation of water in the earth atmosphere system. of the many processes involved in the water cycle, the most important are evaporation, transpiration, condensation, precipitation, and runoff. although the total amount of water within the cycle remains essentially constant, its distribution.

Comments are closed.