How Your Lungs Work

Lung Gas Exchange Diagram The respiratory system's main job is to move fresh air into your body while removing waste gases. once in the lungs, oxygen is moved into the bloodstream and carried through your body. at each cell in your body, oxygen is exchanged for a waste gas called carbon dioxide. your bloodstream then carries this waste gas back to the lungs where it is. After absorbing oxygen, the blood leaves your lungs and is carried to your heart. from there, it’s pumped through your body to provide oxygen to the cells of your tissues and organs. when cells use oxygen, they produce carbon dioxide and transfer it to your blood. your bloodstream carries the carbon dioxide back to your lungs.

Lungs Definition Structure Location Functions Diseases The lungs. your lungs are the pair of spongy, pinkish gray organs in your chest. when you inhale (breathe in), air enters your lungs, and oxygen from that air moves to your blood. at the same time, carbon dioxide, a waste gas, moves from your blood to the lungs and is exhaled (breathed out). this process, called gas exchange, is essential to life. Air fills your lung’s air sacs . your lungs have about 150 million alveoli. normally, your alveoli are elastic, meaning that their size and shape can change easily. alveoli are able to easily expand and contract because their insides are coated with a substance called surfactant. surfactant reduces the work it takes to breathe by helping the. Anatomy of the lungs. a spongy organ that moves oxygen through the bloodstream. the lungs are a major organ that is part of the respiratory system, taking in fresh air and getting rid of old, stale air. this mechanism of breathing also helps to allow you to talk. by taking in fresh air, the lungs are able to help oxygenate blood to be carried. The diaphragm is the chief muscle of breathing. this dome shaped wall of muscle does the most of the breathing work by expanding and contracting the chest to draw air in and out of your lungs. if your lungs are healthy, that's about 80 percent. when lungs need to be more efficient (e.g., you have a lung disease that impairs breathing or even if.
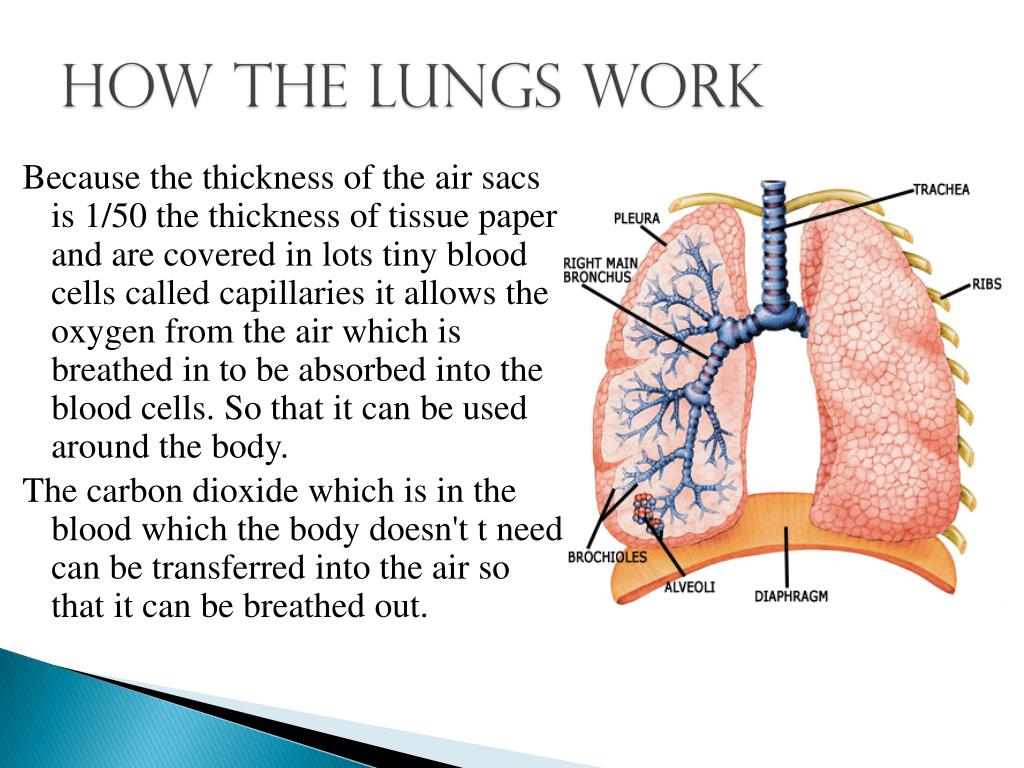
Ppt The Lungs Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 2956482 Anatomy of the lungs. a spongy organ that moves oxygen through the bloodstream. the lungs are a major organ that is part of the respiratory system, taking in fresh air and getting rid of old, stale air. this mechanism of breathing also helps to allow you to talk. by taking in fresh air, the lungs are able to help oxygenate blood to be carried. The diaphragm is the chief muscle of breathing. this dome shaped wall of muscle does the most of the breathing work by expanding and contracting the chest to draw air in and out of your lungs. if your lungs are healthy, that's about 80 percent. when lungs need to be more efficient (e.g., you have a lung disease that impairs breathing or even if. Lungs are the organs that help you breathe. they take a gas that your body needs to get rid of (carbon dioxide) and exchange it for a gas that your body can use (oxygen). they also work with your heart to make sure your body has the oxygen rich blood it needs to function properly. in this article, we will take a close look at how your lungs. To help adjust your breathing to changing needs, your body has sensors that send signals to the breathing centers in the brain. sensors in the airways detect lung irritants. the sensors can trigger sneezing or coughing. in people who have asthma, the sensors may cause the muscles around the airways in the lungs to contract.

How Do Lungs Work Respiratory Organs Locations Lungs are the organs that help you breathe. they take a gas that your body needs to get rid of (carbon dioxide) and exchange it for a gas that your body can use (oxygen). they also work with your heart to make sure your body has the oxygen rich blood it needs to function properly. in this article, we will take a close look at how your lungs. To help adjust your breathing to changing needs, your body has sensors that send signals to the breathing centers in the brain. sensors in the airways detect lung irritants. the sensors can trigger sneezing or coughing. in people who have asthma, the sensors may cause the muscles around the airways in the lungs to contract.

Infographic Lungs How Gas Exchange Works Carolina Biological Supply

Comments are closed.