How To Read The Numbers On A Hospital Monitor Livestrong

How To Read The Numbers On A Hospital Monitor Livestrong How to read blood pressure on a hospital monitor. 1. the top number is systolic pressure. locate the top number of the two numbers. this is the systolic blood pressure, which represents pressure within the heart during a beat. a healthy systolic pressure should be between 90 and 120, per the mayo clinic. 2. How to use a pulse oximeter. follow the manufacturer's instructions. put the oximeter on your index, middle or ring finger and make sure it fits well (not too loose, not too tight). to get the most accurate reading, allow 5 to 20 seconds for your pulse rate to stabilize and for the oximeter to detect your pulse.
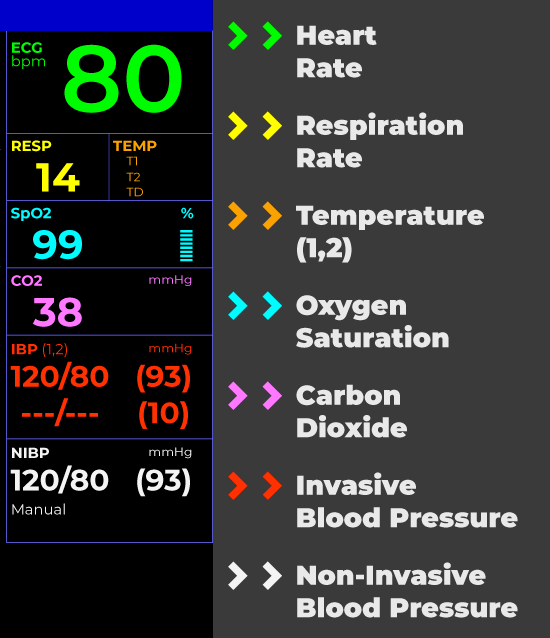
How To Read A Patient Monitor Numbers And Lines Explained With all of the multi colored numbers and wavy lines, things can get a bit confusing. so, our “how to read a patient monitor” article will help, covering most of the basic standard parameters of a patient monitor. the common layout is split, listing the numerical vital signs on the right and the waveforms on the left of the monitor screen. Read the numbers on the right hand side of the monitor to learn the patient's pulse rate, body temperature, and blood pressure. use the respiratory and oxygen saturation rates to keep tabs on the patient's breathing and circulatory system. watch the waveforms for any signs of irregular heartbeat or breathing. 1. Pulse oximetry measures the oxygen saturation of the blood, according to johns hopkins medicine. in other words, it checks how well oxygen is being sent around your body. your oxygen saturation level, per the american thoracic society, is a percentage of how much oxygen your blood is currently carrying compared to the maximum it can actually carry. Heart rate (hr): typically, the heart rate is presented at the top of the monitor in green. the number will be identified by a “hr” or “pr” (pulse rate) beside or just above it and is presented in beats per minute (bpm). a normal adult has a resting heart rate between 60 100 bpm. blood pressure (bp): the patient’s blood pressure is.
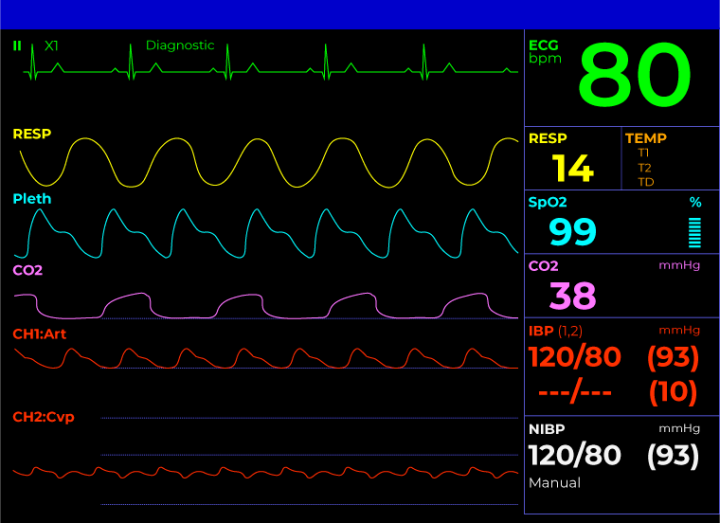
How To Read A Patient Monitor Numbers And Lines Explained Pulse oximetry measures the oxygen saturation of the blood, according to johns hopkins medicine. in other words, it checks how well oxygen is being sent around your body. your oxygen saturation level, per the american thoracic society, is a percentage of how much oxygen your blood is currently carrying compared to the maximum it can actually carry. Heart rate (hr): typically, the heart rate is presented at the top of the monitor in green. the number will be identified by a “hr” or “pr” (pulse rate) beside or just above it and is presented in beats per minute (bpm). a normal adult has a resting heart rate between 60 100 bpm. blood pressure (bp): the patient’s blood pressure is. Pulse rate or heart rate (hr). this is a measure of how many beats the heart is performing per minute. this is a measure of the body’s core temperature. this is a reading of how much oxygen in currently in the blood at the sensor site. respiration rate. this is a measure of how many breaths are taken per minute. This usually involves a beeping noise and a flashing color. many will highlight the problem reading in some way. if one or more vital signs spikes or drops sharply, the alarm may get louder.

Comments are closed.