How Three Phase Electricity Works The Basics Explained

Three Phase Electricity Explained The Engineering Mindset This is the basics of three phase electricity. this means more power is delivered and a more consistent speed is achieved. three phase electricity ac generator. there are still some small gaps between the phases and you could keep adding in more and more phases to fill in these gaps but this becomes more and more expensive to keep running all. See new video here: youtu.be c9gm nl7kyein this video we learn how three phase electricity works from the basics. the basics of three phase electrici.
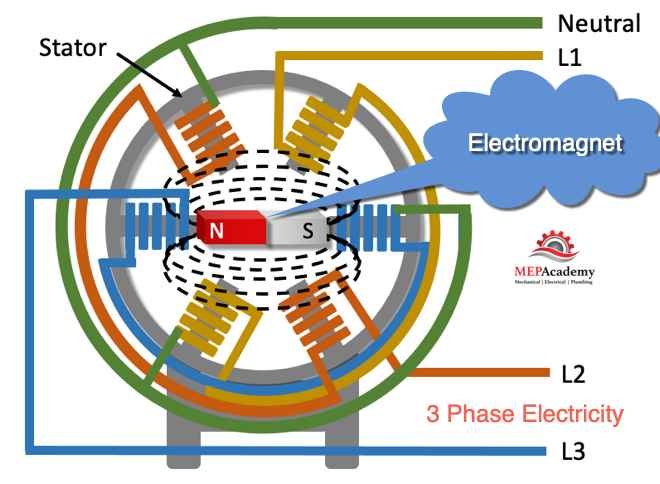
3 Phase Electricity How It Works Mep Academy Three phase transformer with four wire output for 208y 120 volt service: one wire for neutral, others for a, b and c phases. three phase electric power (abbreviated 3ϕ[1]) is a common type of alternating current (ac) used in electricity generation, transmission, and distribution. [2] it is a type of polyphase system employing three wires (or. Three phase electric power is a common method of alternating current electric power generation, transmission, and distribution. it is a type of polyphase system and is the most common method used by electrical grids worldwide to transfer power. it is also used to power large motors and other heavy loads. a three wire three phase circuit is. Raritan this video will take a close look at three phase power and explain how it works. three phase power can be defined as the common metho. Three phase has properties that make it very desirable in electric power systems. firstly the phase currents tend to cancel one another (summing to zero in the case of a linear balanced load). this makes it possible to eliminate the neutral conductor on some lines. secondly power transfer into a linear balanced load is constant, which helps to.

How Three Phase Electricity Works The Basics Explained Wiring Work Raritan this video will take a close look at three phase power and explain how it works. three phase power can be defined as the common metho. Three phase has properties that make it very desirable in electric power systems. firstly the phase currents tend to cancel one another (summing to zero in the case of a linear balanced load). this makes it possible to eliminate the neutral conductor on some lines. secondly power transfer into a linear balanced load is constant, which helps to. 120v and 240v. (a) the 3 phase system transmits 73% more power but uses only 50% more wire. (b) the power delivered by a single phase source is pulsating whereas the power delivered by a three phase system is relatively constant. (c) three phase motors are much smaller in size than comparable single phase motors. Nowadays, the three phase system serves as the basis of most electrical systems, which consist of energy generation, transmission and consumption. this is one of the most important innovations contributed by nikola tesla (1856 1943) because it enabled more efficient and simplified energy generation and transmission.

3 Phase Electricity How It Works Youtube 120v and 240v. (a) the 3 phase system transmits 73% more power but uses only 50% more wire. (b) the power delivered by a single phase source is pulsating whereas the power delivered by a three phase system is relatively constant. (c) three phase motors are much smaller in size than comparable single phase motors. Nowadays, the three phase system serves as the basis of most electrical systems, which consist of energy generation, transmission and consumption. this is one of the most important innovations contributed by nikola tesla (1856 1943) because it enabled more efficient and simplified energy generation and transmission.

Comments are closed.