Haemoglobin Different Types And Reactions Hematology Physiology

Haemoglobin Different Types And Reactions Hematology Physiology Structure and function of hemoglobin. the primary function of hb is to transport oxygen (o 2) from the lung to tissues, binding and releasing o 2 in a cooperative manner, as demonstrated by the oxygen equilibrium curve (oec), which represents o 2 saturation of hb (so 2) at varying partial pressures of o 2 (po 2) (fig. 14.1). In this video you will learn i.e about haemoglobin its different types ( hb a, hb f , hb a1c) and reactions ( with o2 , co2 , co, drugs and oxidising agents.
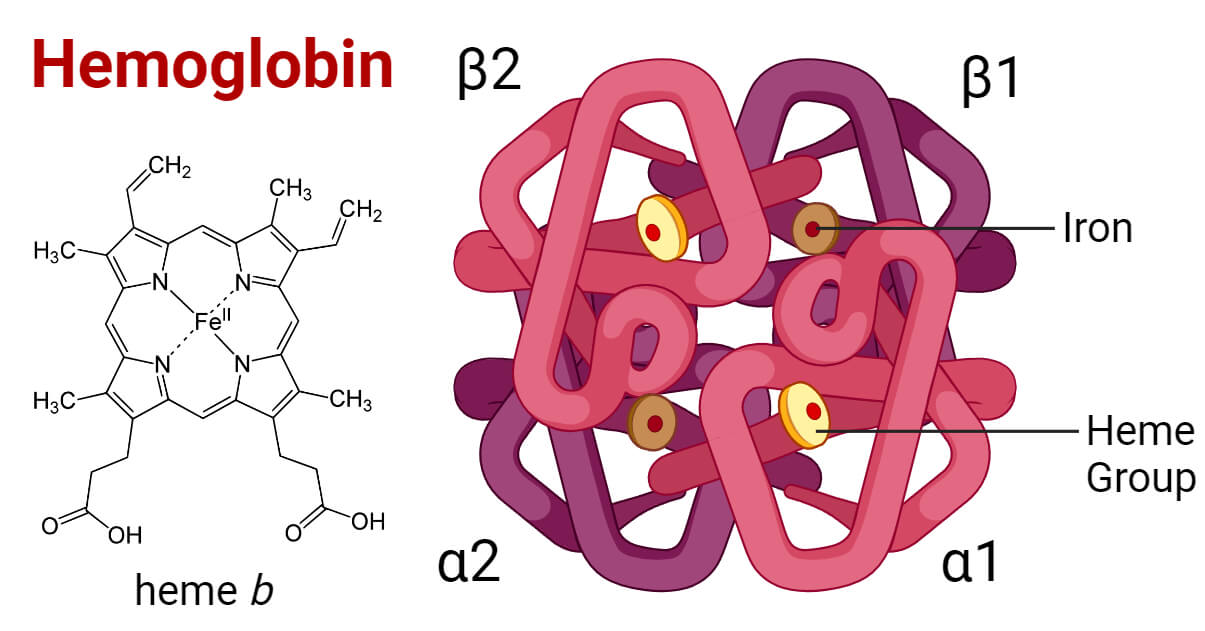
Hemoglobin Structure Types Functions Diseases Synthesis. a haemoglobin molecule is composed of four polypeptide globin chains (fig. 1). each contains a haem moiety which has an organic part (a protoporphyrin ring made up of four pyrrole rings) and a central iron ion in the ferrous state (fe 2 ). normal adult haemoglobin molecules (hba) have a molecular mass of 64 458 da with a complex. A higher glucose concentration results in more hb a 1c. because the reaction is slow, the hb a 1c proportion represents glucose level in blood averaged over the half life of red blood cells, is typically ~120 days. an hb a 1c proportion of 6.0% or less show good long term glucose control, while values above 7.0% are elevated. this test is. Hemoglobin is an oxygen binding protein found in erythrocytes that transports oxygen from the lungs to tissues. each hemoglobin molecule is a tetramer made of four polypeptide globin chains. each globin subunit contains a heme moiety formed of an organic protoporphyrin ring and a central iron ion in the ferrous state (fe2 ). the iron molecule in each heme moiety can bind and unbind oxygen. Haemoglobin is a heterotetramer protein composed of four subunits, two α and two β. its quaternary structure changes with oxygen binding to increase its affinity for oxygen. at the core is a haem molecule, which contains iron and which performs essential gas transport and redox functions. additionally, haemoglobin functions as a carrier for co2 and a buffer for the extracellular fluid.

Comments are closed.