Groundwater Surface Connections

Surface Water Groundwater Connections вђ A Groundwater Flow Model For Groundwater and surface water physically overlap at the groundwater surface water interface through the exchange of water and chemicals. this exchange is a critical part of the hydrologic cycle. surface water supplies recharge to the underlying aquifer, where the groundwater can remain in storage for days, months, years, centuries, or even. These interactions take many forms. in many situations, surface water bodies gain water and solutes from ground water systems and in others the surface water body is a source of ground water recharge and causes changes in ground water quality. as a result, withdrawal of water from streams can deplete ground water or conversely, pumpage of.

Groundwater Surface Water Interactions Long Island U S Geological As part of most groundwater assessments we conduct hydrologic analyses to better understand and quantify the connections between groundwater and surface water. we conduct intensive site scale investigations to better understand the exchange of surface water and groundwater; and we integrate that information into computer models that simulate. The u.s. geological survey is integrating its water science programs to better address the nation’s greatest water resource challenges. at the heart of this effort are plans to intensively study at least 10 integrated water science (iws) basins — medium sized watersheds (10,000 20,000 square miles) and underlying aquifers — over the next. Surface water and groundwater systems are connected in most landscapes. streams interact with groundwater in three basic ways: streams gain water from inflow of groundwater through the streambed, streams lose water by outflow through the streambed, or they do both depending upon the location along the stream. it is the groundwater contribution. Groundwater connection with streams. the upland to lowland movement of groundwater continues if the water table under the hills is higher than the water level in, or under, the streams. sections of streams that receive groundwater are called gaining streams (figure 16a). as seen from the point of view of a rafter floating down a stream, gaining.

Surface Water Groundwater Interaction Surface water and groundwater systems are connected in most landscapes. streams interact with groundwater in three basic ways: streams gain water from inflow of groundwater through the streambed, streams lose water by outflow through the streambed, or they do both depending upon the location along the stream. it is the groundwater contribution. Groundwater connection with streams. the upland to lowland movement of groundwater continues if the water table under the hills is higher than the water level in, or under, the streams. sections of streams that receive groundwater are called gaining streams (figure 16a). as seen from the point of view of a rafter floating down a stream, gaining. Groundwater–surface water interaction can occur as streams or lakes showing gaining (discharge from groundwater), losing (recharge to groundwater), flow under, or flow through. (a) top panel shows cross sections with hypothetical contours and flow lines. (b) middle panel shows plan view for lakes. The interaction between surface water and groundwater constitutes a critical process to understand the quantitative and qualitative regime of dependent hydrosystems. a multi scale approach combining cross disciplinary techniques can considerably reduce uncertainties and provide an optimal understanding of groundwater and surface water exchanges.
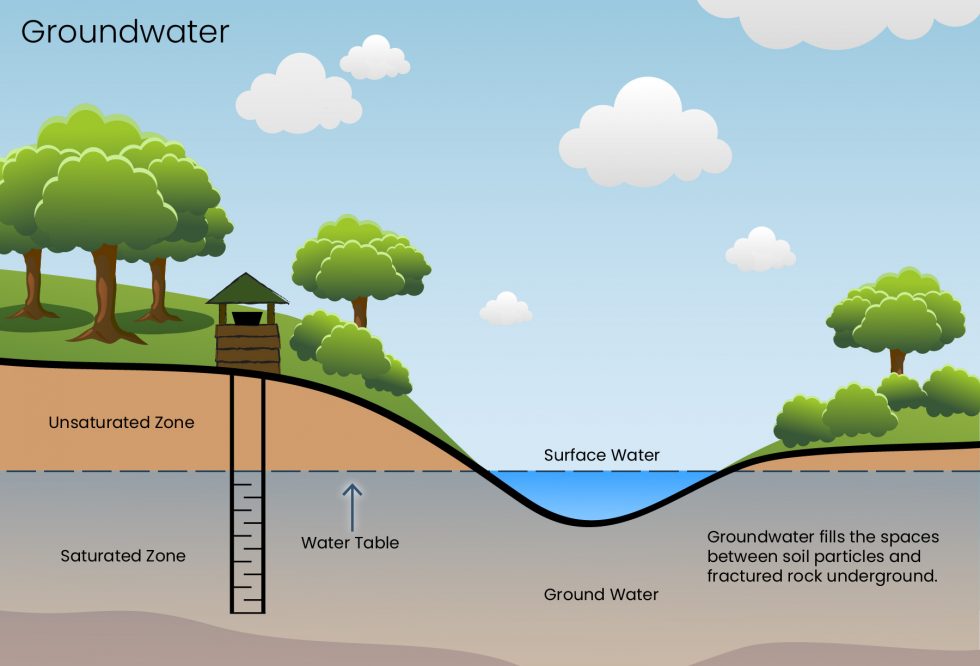
Surface Water Vs Groundwater Battle Creek Area Clean Water Partnership Groundwater–surface water interaction can occur as streams or lakes showing gaining (discharge from groundwater), losing (recharge to groundwater), flow under, or flow through. (a) top panel shows cross sections with hypothetical contours and flow lines. (b) middle panel shows plan view for lakes. The interaction between surface water and groundwater constitutes a critical process to understand the quantitative and qualitative regime of dependent hydrosystems. a multi scale approach combining cross disciplinary techniques can considerably reduce uncertainties and provide an optimal understanding of groundwater and surface water exchanges.

Surface Water Groundwater Interaction

Comments are closed.