General Embryology 17 Organogenesis 1st Part By Dr Wahdan

General Embryology 17 Organogenesis 1st Part By Dr Wahdan Youtube Learn with dr. wahdan 2you can download the lecture from this link below docdro.id re50w2h. Learn with dr. wahdan 2 you can download the lecture from this link docdro.id x41m5ex.
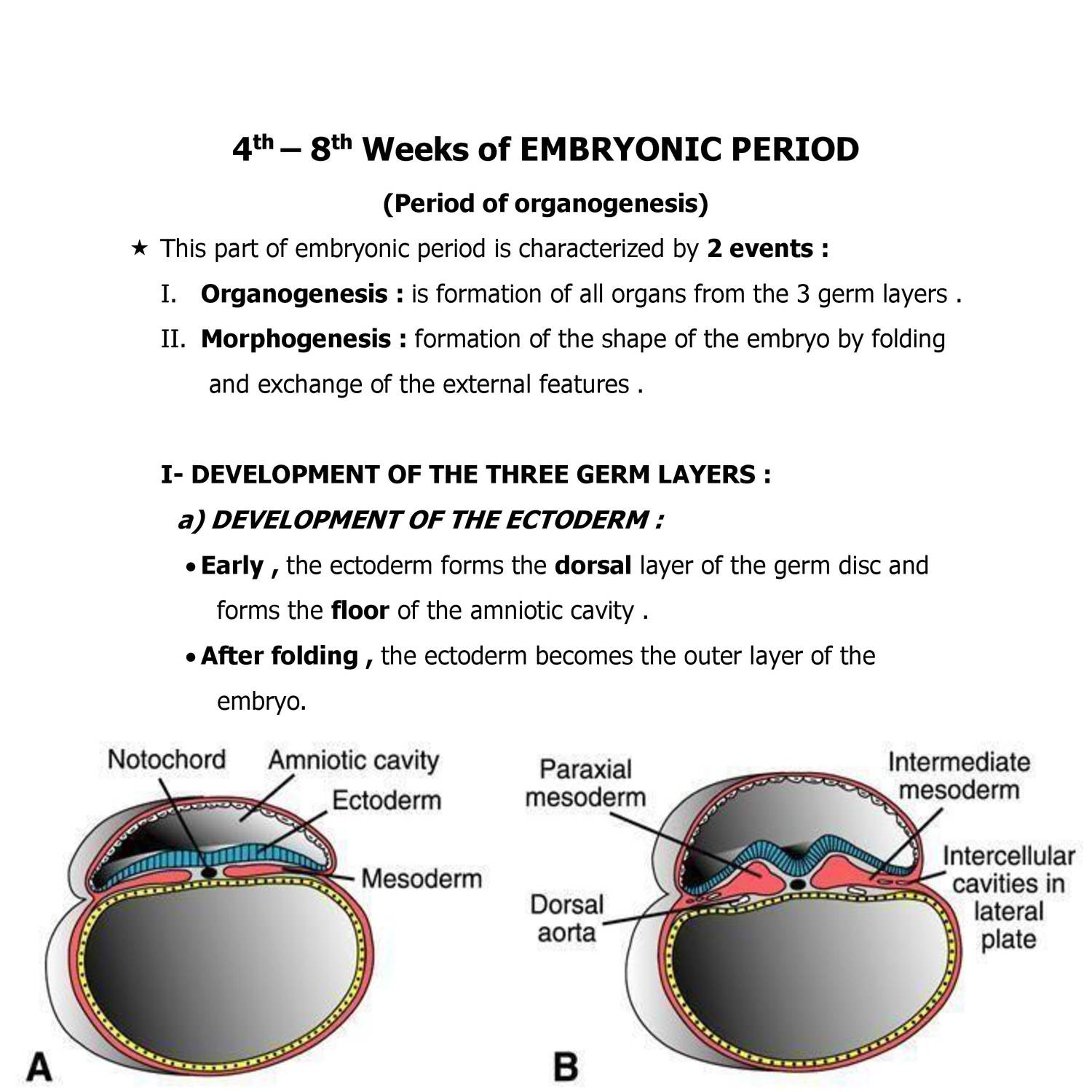
General Embryo Organogenesis Doc Docdroid Prof. dr. mohamed wahdan 5 5 general embryology part. pdf materials [ part 1] special embryology part. In human embryology, weeks 6 through 8 are characterized by the growth and differentiation of tissues into organs. this process is known as organogenesis and occurs from weeks 3 through 8, the embryonic period. during week 3, gastrulation occurs, establishing 3 distinct cell layers: the mesoderm, endoderm, and ectoderm. these are the primary germ cell layers from which organs arise during. General embryology experimental embryology: deals with the laboratory methods employed for normal development to properly understand histogenesis and or organogenesis or to manipulate the developmental process to assess the safety of environmental alterations, drugs, chemicals etc. the experiment could be in vivo or in vitro. Embryology: 1st week of development. the first week of embryonic development is filled with an eclectic arrangement of physical and biochemical changes. each step is a part of a cascade of events that must be intricately coordinated in order to produce a healthy baby at the end of the thirty eight to forty week period.

General Embryology Organogenesis And Organ Structure Flashcards Quizlet General embryology experimental embryology: deals with the laboratory methods employed for normal development to properly understand histogenesis and or organogenesis or to manipulate the developmental process to assess the safety of environmental alterations, drugs, chemicals etc. the experiment could be in vivo or in vitro. Embryology: 1st week of development. the first week of embryonic development is filled with an eclectic arrangement of physical and biochemical changes. each step is a part of a cascade of events that must be intricately coordinated in order to produce a healthy baby at the end of the thirty eight to forty week period. Organogenesis. organogenesis is the process by which the three germ tissue layers of the embryo, which are the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm, develop into the internal organs of the organism. organs form from the germ layers through the differentiation: the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. The placenta develops throughout the embryonic period and during the first several weeks of the fetal period; placentation is complete by weeks 14–16. as a fully developed organ, the placenta provides nutrition and excretion, respiration, and endocrine function (table 28.1 and figure 28.12). it receives blood from the fetus through the.
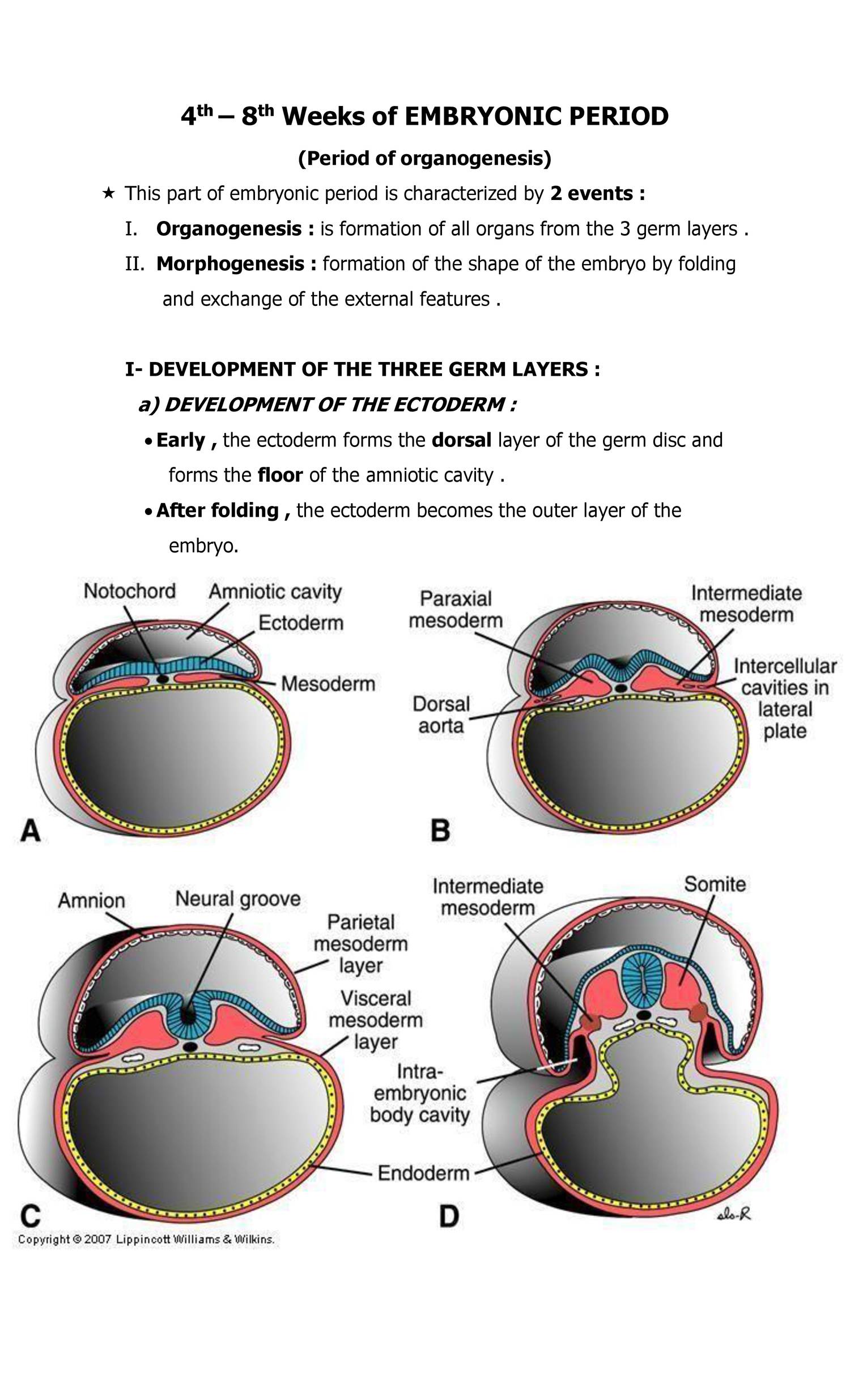
General Embryo Organogenesis Doc Docdroid Organogenesis. organogenesis is the process by which the three germ tissue layers of the embryo, which are the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm, develop into the internal organs of the organism. organs form from the germ layers through the differentiation: the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. The placenta develops throughout the embryonic period and during the first several weeks of the fetal period; placentation is complete by weeks 14–16. as a fully developed organ, the placenta provides nutrition and excretion, respiration, and endocrine function (table 28.1 and figure 28.12). it receives blood from the fetus through the.

Comments are closed.