General Embryo Organogenesis Doc Docdroid
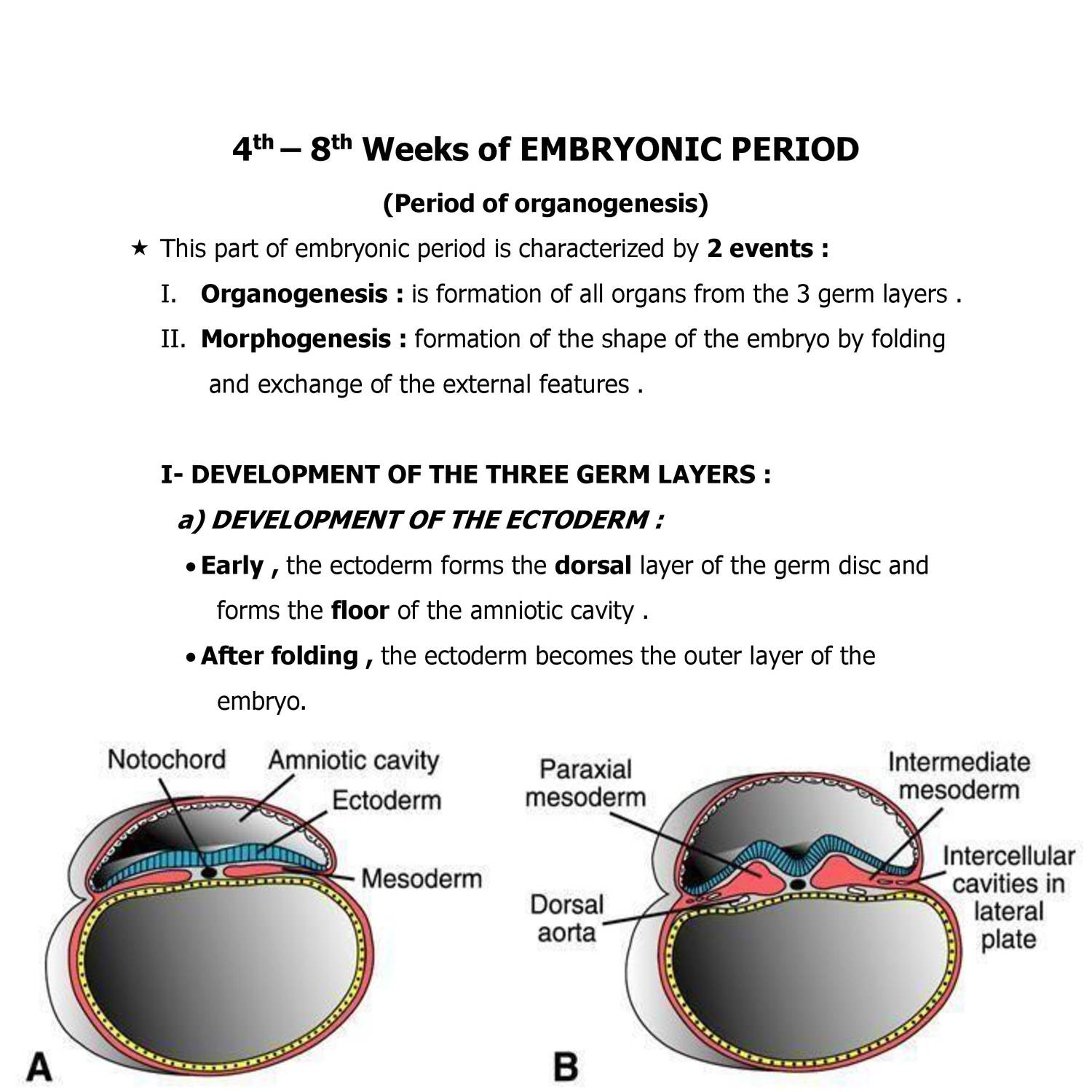
General Embryo Organogenesis Doc Docdroid 4th – 8th weeks of embryonic period (period of organogenesis) this part of embryonic period is characterized by 2 events : i. organogenesis : is formation of all organs from the 3 germ layers . ii. morphogenesis : formation of the shape of the embryo by folding and exchange of the external fea. Gametogenesis definition: it is the processes of production mature gametes ( sperms in males and ova in females ) . site : it takes place in the gonads ( testes and ovary ) . mechanism : conversion of the primordial germ cells ( spermatogonia and oogonia ) into mature male or female gametes in.

Organogenesis Phase Stages Of Embryonic Development Process Outline Yolk sac it is the cavity develops on the ventral aspect of the embryonic disc. development:. 1. primary yolk sac: • it appears at the 9th and 10th days. • flat cells from the hypoblast form heuser's membrane which lines the inner surface of the blastocele . • the original blastocele is now call. In human embryology, weeks 6 through 8 are characterized by the growth and differentiation of tissues into organs. this process is known as organogenesis and occurs from weeks 3 through 8, the embryonic period. during week 3, gastrulation occurs, establishing 3 distinct cell layers: the mesoderm, endoderm, and ectoderm. these are the primary germ cell layers from which organs arise during. Organogenesis. organogenesis is the process by which the three germ tissue layers of the embryo, which are the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm, develop into the internal organs of the organism. organs form from the germ layers through the differentiation: the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. during organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal organs of the organism. [1] the endoderm of vertebrates produces tissue within the lungs, thyroid, and.
Embryo Stages Of Development Organogenesis And Folding Notes Anatomy Organogenesis. organogenesis is the process by which the three germ tissue layers of the embryo, which are the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm, develop into the internal organs of the organism. organs form from the germ layers through the differentiation: the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. Organogenesis is the phase of embryonic development that starts at the end of gastrulation and continues until birth. during organogenesis, the three germ layers formed from gastrulation (the ectoderm, endoderm, and mesoderm) form the internal organs of the organism. [1] the endoderm of vertebrates produces tissue within the lungs, thyroid, and. By the end of the embryonic period, the embryo is approximately 3 cm (1.2 in) from crown to rump and weighs approximately 8 g (0.25 oz). figure 24.3.12 24.3. 12: embryo at 7 weeks. an embryo at the end of 7 weeks of development is only 10 mm in length, but its developing eyes, limb buds, and tail are already visible. Identify the anatomical axes formed in vertebrates. gastrulation leads to the formation of the three germ layers that give rise, during further development, to the different organs in the animal body. this process is called organogenesis. organogenesis is characterized by rapid and precise movements of the cells within the embryo.
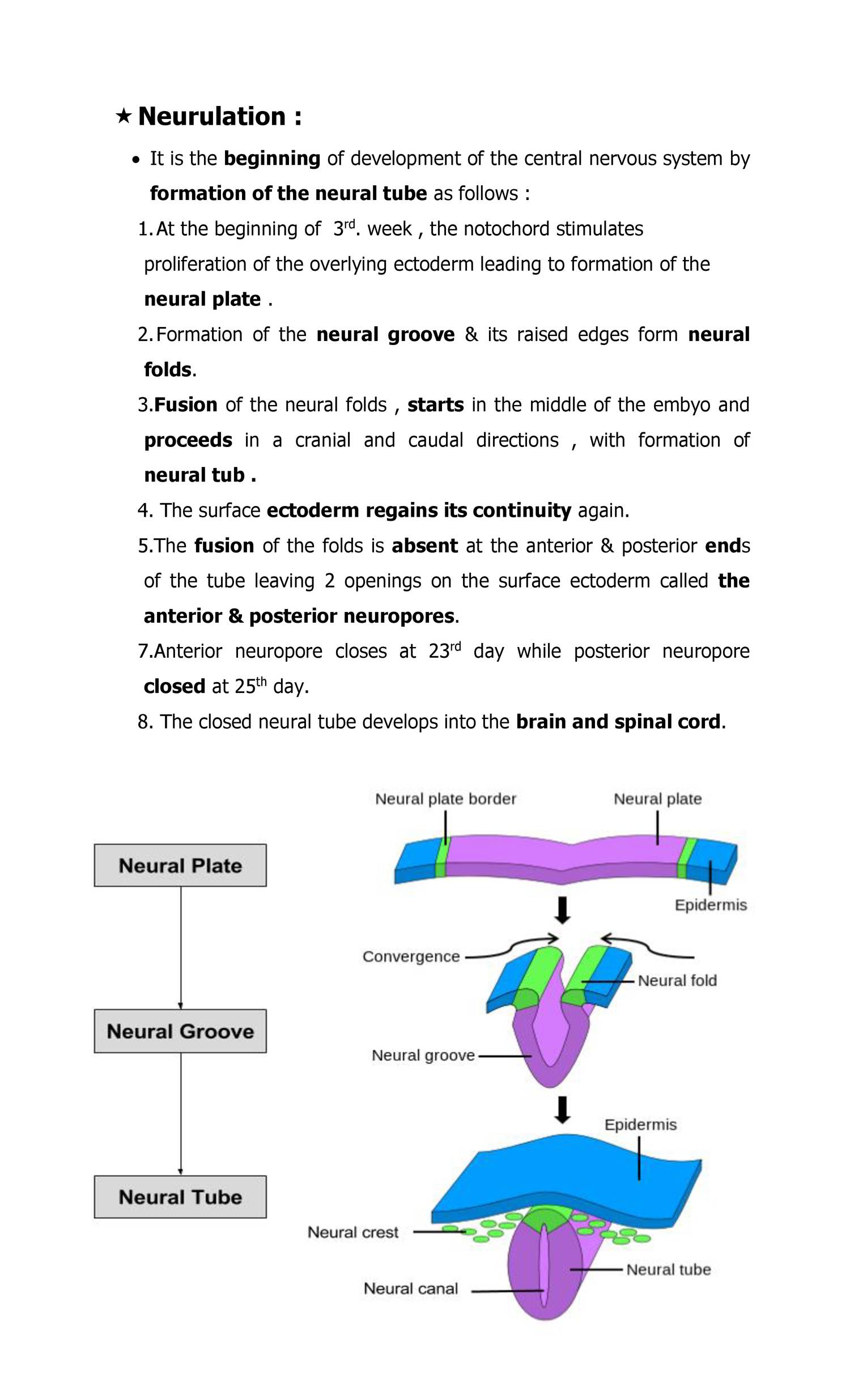
General Embryo Neurulation Doc Docdroid By the end of the embryonic period, the embryo is approximately 3 cm (1.2 in) from crown to rump and weighs approximately 8 g (0.25 oz). figure 24.3.12 24.3. 12: embryo at 7 weeks. an embryo at the end of 7 weeks of development is only 10 mm in length, but its developing eyes, limb buds, and tail are already visible. Identify the anatomical axes formed in vertebrates. gastrulation leads to the formation of the three germ layers that give rise, during further development, to the different organs in the animal body. this process is called organogenesis. organogenesis is characterized by rapid and precise movements of the cells within the embryo.

Comments are closed.